1.1 字符串类的设计
1.1.1 继承关系图
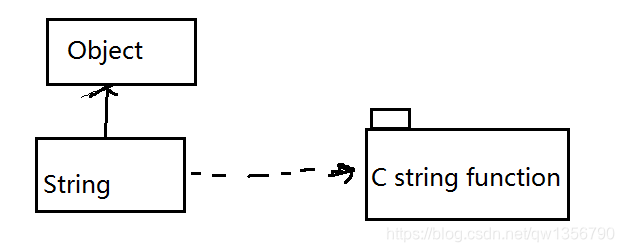
1.1.2 字符串类的实现
1.1.3 注意事项
- 无缝实现String对象和 char * 字符串的互操作
- 操作符重载函数需要考虑是否支持const 版本
- 通过C语言中的字符串函数实现String的成员函数
1.2字符串中常用的成员函数
1.2.1成员函数
| 成员函数 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| operator[] | 操作符重载函数,访问指定下标的字符 |
| startWith(s) | 判断字符串是否以s开头 |
| endOf(s) | 判断字符串是否以S结尾 |
| insert(i,s) | 在字符串的位置i处插入s |
| trim() | 去掉字符串两端的空白 |
1.2.2操作符重载函数
char& operator[](int i);
char operator[](int i) const;
- 注意事项
- 当i的取值不合法时,抛出异常
- 合法范围:
( 0 <= i) && (i < m_length)
1.2.3 函数声明
class String : public Object
{
protected:
char* m_str;
int m_length;
void init(const char* s);
bool equal(const char* l, const char* r, int len) const;
public:
String();
String(char c);
String(const char* s);
String(const String&s);
int length() const;
const char* str() const;
bool operator == (const String& s)const;
bool operator == (const char* s)const;
bool operator != (const String& s)const;
bool operator != (const char* s)const;
bool operator > (const String& s)const;
bool operator > (const char* s)const;
bool operator < (const String& s)const;
bool operator < (const char* s)const;
bool operator >= (const String& s)const;
bool operator >= (const char* s)const;
bool operator <= (const String& s)const;
bool operator <= (const char* s)const;
String operator + (const String& s) const;
String operator + (const char* s) const;
String& operator += (const String& s);
String& operator += (const char* s);
String& operator = (const String& s);
String& operator = (const char* s);
String& operator = (char c);
char& operator[](int i);
char operator[](int i) const;
bool startWith(const char* s) const;
bool startWith(const String&s) const;
bool endOf(const char* s) const;
bool endOf(const String&s) const;
String& insert(int i, const char* s);
String& insert(int i, const String&s);
String& trim(); // 为啥是返回引用,因为可以这样使用 s2.trim().str()
~String();
};
1.2.4 思考
- 如何在目标字符重查找是否存在指定的子串 ?
String s = "zhangsan";
int pos = s.indexof("san"); // pos = 5
1.3KMP 算法
1.3.1
- 如何在目标字符重查找是否存在指定的子串 ?
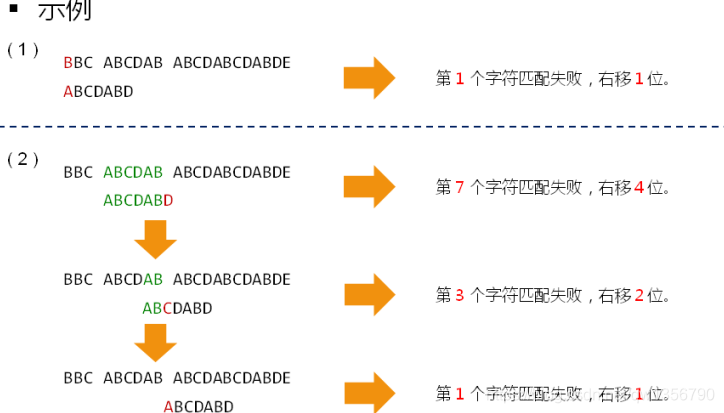
1.3.2 伟大的发现
- 匹配失败时的右移位数与
子串本身相关, 和目标串无关 移动位数= 已匹配的字符数 -对应的部分匹配值- 任意子串都存在一个
唯一的部分匹配值
1.3.3 部分匹配表示例
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | A | B | D |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
- 用法

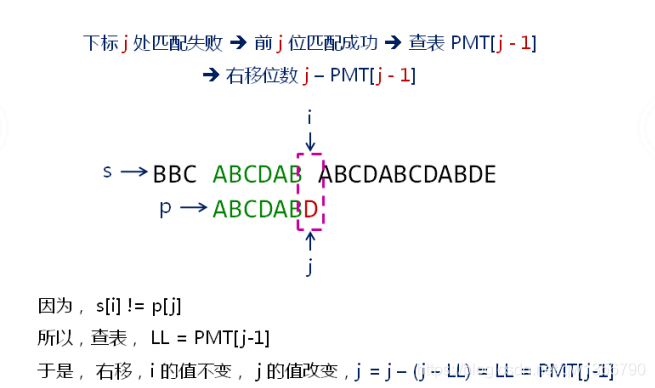
- 第7 位 匹配失败----> 前6 位匹配成功----> 查表PMT[6]
----> 右移位数6 - PMT[6] = 6 - 2 = 4; - 当我们知道部分匹配表就可以很清楚的知道,当匹配失败的时候,我们可以知道跳过几个字符
1.3.4 部分匹配如何获取
前缀: 除了最后一个字符以外,一个字符串的全部头部组合后缀: 除了第一个字符以外,一个字符串的全部尾部组合部分匹配值: 前缀和后缀最长共有元素的长度- 举例:

- 示例:
| 0 | 字符 | 前缀 | 后缀 | 交集 | 匹配值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | 空 | 空 | 空 | 0 |
| 2 | AB | A | B | 空 | 0 |
| 3 | ABC | A,AB | C,BC | 空 | 0 |
| 4 | ABCD | A,AB,ABC | D,CD,BCD | 空 | 0 |
| 5 | ABCDA | A,AB,ABC,ABCD | BCDA,CDA,DA,A | A | 1 |
| 6 | ABCDAB | A,AB,ABC,ABCD,ABCDA | BCDAB,CDAB,DAB,AB,B | AB | 2 |
| 7 | ABCDABD | A,AB,ABC,ABCD,ABCDA,ABCDAB | 省略 | 空 | 0 |
1.3.5 部分匹配如何产生
- 实现关键
- PMT[1] =0 (下标为0 的元素匹配值为0)
- 从第二个字符开始递推(从下标为1的字符开始递推)
- 假设PMT[N] = PMT[n - 1] + 1 (·
最长共有元素的长度) - 当假设不成立,PMT[n]在PMT[n - 1]的基础上减小
1.4
1.4.1部分匹配表实现

- 代码实现
int* make_pmt(const char* p)
{
int len = strlen(p);
int* ret = static_cast<int*> (malloc(sizeof(int) * len));
if(ret != NULL)
{
int ll = 0; // longest length
ret[0] = 0;
for(int i =1; i < len; i++)
{
while((ll > 0) && (p[ll] != p[i]))
{
ll = ret[ll - 1];
}
if(p[ll] == p[i])
{
ll++;
}
ret[i] = ll;
}
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
// ababax
int* pmt = make_pmt("ABCDABD");
for(int i = 0; i < strlen("ABCDABD"); i++)
{
cout << i << " : " << pmt[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
1.4.2 KMP的实现
- 代码实现
int kmp(const char* s, const char* p)
{
int ret = -1;
int sl =strlen(s);
int pl =strlen(p);
int * pmt = make_pmt(p);
if((pmt != NULL) && (0 < pl) && ( pl < sl))
{
for(int i =0,j =0; i < sl; i++)
{
while((j > 0) && (s[i] != p[j]))
{
j = pmt[j - 1];
}
if(s[i] = p[j])
{
j++;
}
if( j == pl)
{
ret = i + 1 - pl;
break;
}
}
}
free(pmt);
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cout << kmp("zhangsan","zhangsan") << endl;
return 0;
}
1.5 KMP算法的应用
1.5.1 字符串类中的新功能
| 成员函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| indexOf(s) | 查找子串s在字符串中位置 |
| remove(s) | 将字符串中的子串s删除 |
| operator - (s) | 定义字符串减法 |
| replace(s,t) | 将字符串中的子串替换为t |
| sub(i, len) | 从字符串中创建子串 |
参考一 : 狄泰软件课程
如有侵权:请联系邮箱 1986005934@qq.com





 本文详细介绍了KMP算法的原理与应用,探讨了字符串类的设计与实现,包括成员函数、操作符重载及异常处理等内容。同时,深入解析了如何在目标字符串中查找子串,以及KMP算法在字符串类中的新功能实现。
本文详细介绍了KMP算法的原理与应用,探讨了字符串类的设计与实现,包括成员函数、操作符重载及异常处理等内容。同时,深入解析了如何在目标字符串中查找子串,以及KMP算法在字符串类中的新功能实现。
















 3392
3392

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








