目录
SELECT 学号, 姓名, 性别, 出生日期, 班号 FROM 学生表 等价于: SELECT * FROM 学生表
*表示所有列
SELECT结果去重
SELECT distinct 关键字 FROM
查询结果限制返回行数
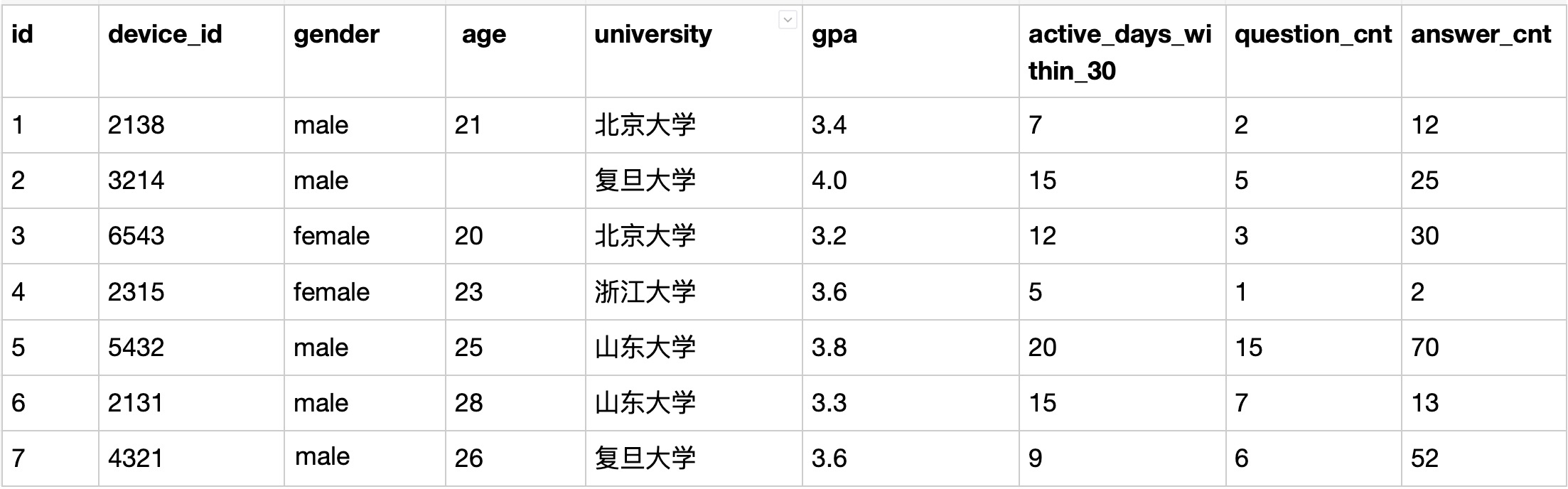
题目:现在运营只需要查看前2个用户明细设备ID数据,请你从用户信息表 user_profile 中取出相应结果。
Solution: limit or where
SELECT device_id FROM user_profile where id<3
%% select * from tableName limit i,n
%% 参数
tableName : 为数据表;
i : 为查询结果的索引值(默认从0开始);
n : 为查询结果返回的数量查询后的列重新命名
SELECT (AS) RENAME
FROM tableNAME
查找某个年龄段的用户信息
SELECT device_id,gender,age
FROM user_profile
where age>=20 and age<=23
或者 where age between 20 and 24
%% 不能使用 20<=age<=23WHERE FUNCTION ( != 代表不等于 ) 除XXX的XXX信息
用WHERE过滤空值 WHERE XXX is not null
模糊查询
like表示模糊搜索,%表示不确定搜索对象前后各有几个字
查找最值
查找GPA最高值#
两种方法:
where筛选 + 排序
排序与多列排序
排序子句语法:order by 列名 asc/desc
(升序和降序要给每个字段单独设定)
SELECT device_id,gpa,age from user_profile order by gpa,age;#默认以升序排列
SELECT device_id,gpa,age from user_profile order by gpa,age asc;
SELECT device_id,gpa,age from user_profile order by gpa asc,age asc;where筛选 复旦大学条件,因最高的gpa,max(gpa)求出最大值也可
select
max(gpa )
from user_profile
WHERE
university='复旦大学'计数,round函数与求mean
计数,count函数;求平均值用avg函数
ROUND() 函数 ROUND 函数用于把数值字段舍入为指定的小数位数。
SQL ROUND() 语法
SELECT ROUND(column_name,decimals)
FROM table_name column_name 要舍入的字段decimals 要返回的小数位数
分组计算
SELECT gender,university,
COUNT(id) AS user_num,
AVG(active_days_within_30)AS avg_active_day,
AVG(question_cnt) AS avg_question_cnt
FROM user_profile
GROUP BY gender,universityselect 类别, sum(数量) as 数量之和
from A
group by 类别
聚合函数用(select;Having;order by)
SELECT university,
AVG(question_cnt) AS avg_question_cnt,
AVG(answer_cnt) AS avg_answer_cnt
FROM user_profile
GROUP BY university
HAVING avg_question_cnt<5
OR avg_answer_cnt<20Solution
SQL语句的执行过程是:
FROM - ON - JOIN - WHERE - GROUP BY - WITH - HAVING - SELECT - DISTINCT - ORDER BY - LIMIT
第一步:from 选择表
第二步:where 筛选条件,筛选对象--行
第三步:group by 将筛选出来的数据进行分组
第四步:having 筛选条件,筛选对象--组
第五步:select 选取最后的结果
第六步:order by 将结果按照特定顺序排列
聚合函数出现在where子句中是个伪命题!举个简单的例子,现在需要select出所有员工中那些工资大于平均工资的员工信息,如果sql语句写成select * from 表名 where sal > avg(sal);肯定是要报错的。因为聚合函数的实现,是基于所有完整数据的基础上,例如,求和,统计数据总数,最大值,最小值,必须保证所有列的数据全部用到。但是,聚合函数如果出现在where子句中,它就要受到整个语句的限制,因为这条语句最终是需要对数据进行筛选的,也就是说整条sql语句产生的结果将会是所有数据中的部分数据,而不是全部的完整数据。这与聚合函数实现的前提——完整的所有数据是相悖的,因此,聚合函数不能出现在where子句中。
连接查询(四种常考)
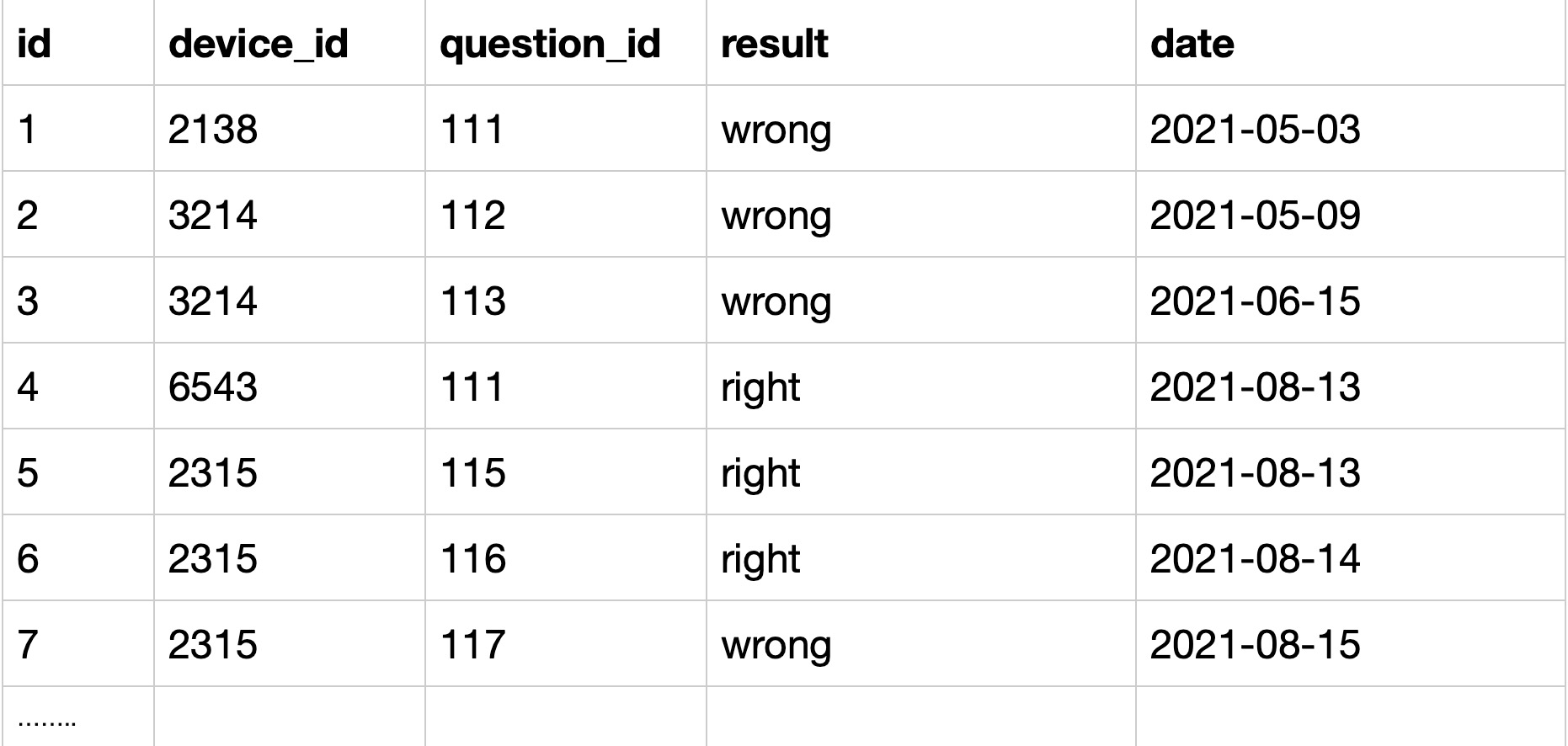
限定条件:来自浙江大学的用户,学校信息在用户画像表,答题情况在用户练习明细表,因此需要通过device_id关联两个表的数据;
方法1:join两个表,用inner join,条件是on up.device_id=qpd.device_id and up.university='浙江大学'
CODE:
select qpd.device_id, qpd.question_id, qpd.result
from question_practice_detail as qpd
inner join user_profile as up
on up.device_id=qpd.device_id and up.university='浙江大学'方法2:先从画像表找到浙江大学的所有学生id列表where university='浙江大学',再去练习明细表筛选出id在这个列表的记录,用where in
CODE:
select device_id, question_id, result
from question_practice_detail
where device_id in (
select device_id from user_profile
where university='浙江大学'
)EXAMPLE:
统计每个学校的用户平均答题数#
题意明确:
每个学校的用户平均答题数量
问题分解:
限定条件:无;
每个学校:按学校分组,group by university
平均答题数量:在每个学校的分组内,用总答题数量除以总人数即可得到平均答题数量count(question_id) / count(distinct device_id)。
表连接:学校和答题信息在不同的表,需要做连接
细节问题:
表头重命名:as
完整代码:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
EXAMPLE:
计算每个学校用户不同难度下的用户平均答题题目数
问题分解:
限定条件:无;
每个学校:按学校分组group by university
不同难度:按难度分组group by difficult_level
平均答题数:总答题数除以总人数count(qpd.question_id) / count(distinct qpd.device_id)
来自上面信息三个表,需要联表,up与qpd用device_id连接,qd与qpd用question_id连接。
细节问题:
表头重命名:as
平均值精度未明确要求,忽略
select
university,
difficult_level,
count(qpd.question_id) / count(distinct qpd.device_id) as avg_answer_cnt
from question_practice_detail as qpd
left join user_profile as up
on up.device_id=qpd.device_id
left join question_detail as qd
on qd.question_id=qpd.question_id
group by university, difficult_level进阶使用
or与union的
Q:想要分别查看学校为山东大学或者性别为男性的用户的device_id、gender、age和gpa数据,请取出相应结果,结果不去重。
solution:这里的坑是使用or,因为or自带去重,而union等价于or,但union all 可以不去重,所以考察or与union的细节使用。
select device_id , gender , age , gpa from user_profile where university = '山东大学'
UNION ALL
select device_id , gender , age , gpa from user_profile where gender = 'male'CASE函数
Q:
现在运营想要将用户划分为25岁以下和25岁及以上两个年龄段,分别查看这两个年龄段用户数量
本题注意:age为null 也记为 25岁以下
Solution:
CASE 函数:是一种多分支的函数,可以根据条件列表的值返回多个可能的结果表达式中的一个。
可用在任何允许使用表达式的地方,但不能单独作为一个语句执行。
SELECT
case
when age >= 25 then '25岁及以上'
else '25岁以下'
end as age_cut,
count(device_id) as number
FROM user_profile
GROUP by age_cut;EXAMPLE:
查询班级表中的学生的班号、班名、系号和班主任号,并对系号作如下处理:
当系号为1时,显示 “计算机系”;
当系号为2时,显示 “软件工程系”;
当系号为3时,显示 “物联网系”。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
date_format函数&year/month函数
Q:想要计算出2021年8月每天用户练习题目的数量
S:
select
day(date) as day,
count(question_id) as question_cnt
from question_practice_detail
where month(date)=8 and year(date)=2021
group by date拓宽思路:2021年8月,写法有很多种,比如用year/month函数的year(date)=2021 and month(date)=8,比如用date_format函数的date_format(date, "%Y-%m")="202108"
留存率问题
SQL T29
Q:用户在某天刷题后第二天再来刷题的平均概率
S:
问题分解:
- 限定条件:第二天再来。
- 解法1:表里的数据可以看作是全部第一天来刷题了的,那么我们需要构造出第二天来了的字段,因此可以考虑用left join把第二天来了的拼起来,限定第二天来了的可以用
date_add(date1, interval 1 day)=date2筛选,并用device_id限定是同一个用户。 - 解法2:用lead函数将同一用户连续两天的记录拼接起来。先按用户分组
partition by device_id,再按日期升序排序order by date,再两两拼接(最后一个默认和null拼接),即lead(date) over (partition by device_id order by date)
- 解法1:表里的数据可以看作是全部第一天来刷题了的,那么我们需要构造出第二天来了的字段,因此可以考虑用left join把第二天来了的拼起来,限定第二天来了的可以用
- 平均概率:
- 解法1:可以count(date1)得到左表全部的date记录数作为分母,count(date2)得到右表关联上了的date记录数作为分子,相除即可得到平均概率
- 解法2:检查date2和date1的日期差是不是为1,是则为1(次日留存了),否则为0(次日未留存),取avg即可得平均概率。
- 附:lead用法,date_add用法,datediff用法,date函数
细节问题:
- 表头重命名:as
- 去重:需要按照devece_id,date去重,因为一个人一天可能来多次
- 子查询必须全部有重命名
完整代码:
select count(date2) / count(date1) as avg_ret
from (
select
distinct qpd.device_id,
qpd.date as date1,
uniq_id_date.date as date2
from question_practice_detail as qpd
left join(
select distinct device_id, date
from question_practice_detail
) as uniq_id_date
on qpd.device_id=uniq_id_date.device_id
and date_add(qpd.date, interval 1 day)=uniq_id_date.date
) as id_last_next_date解法2:
select avg(if(datediff(date2, date1)=1, 1, 0)) as avg_ret
from (
select
distinct device_id,
date as date1,
lead(date) over (partition by device_id order by date) as date2
from (
select distinct device_id, date
from question_practice_detail
) as uniq_id_date
) as id_last_next_date字符串截取之substring_index
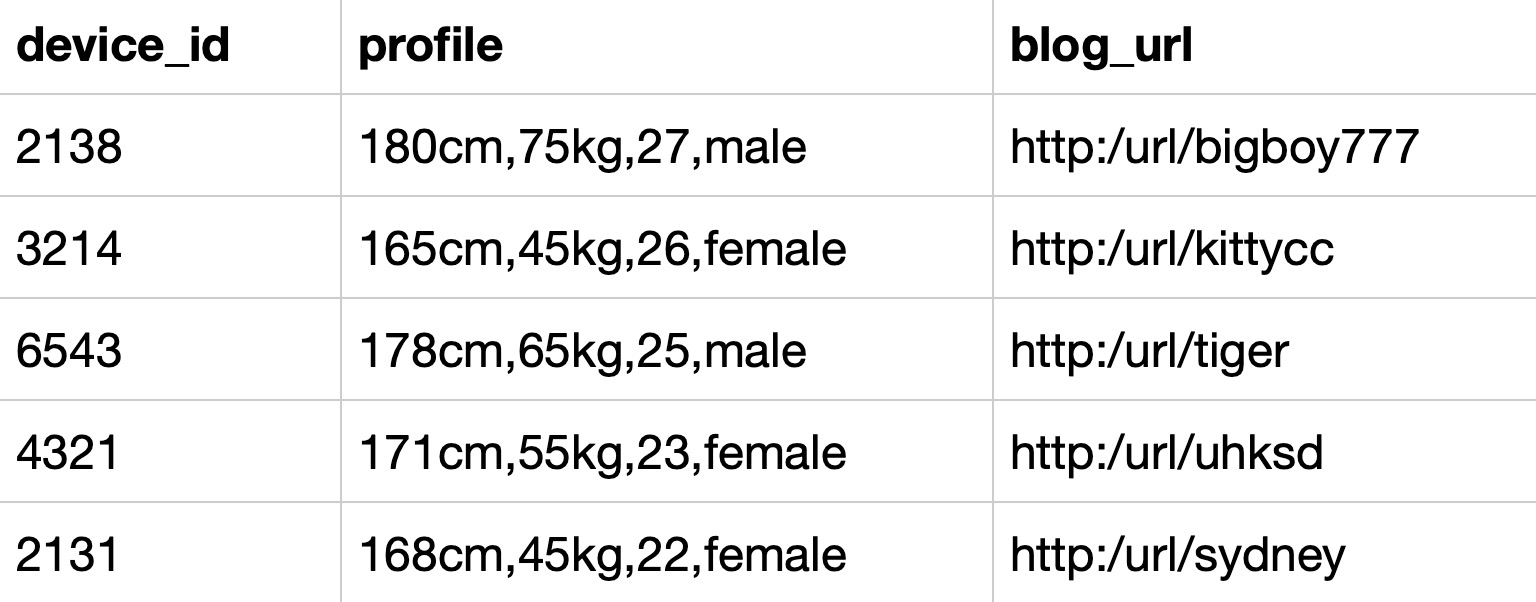
Q:统计每个性别的用户分别有多少参赛者
问题分解:
- 限定条件:无;
- 每个性别:按性别分组group by gender,但是没有gender字段,需要从profile字段截取,按字符,分割后取出即可。可使用substring_index函数可以按特定字符串截取源字符串。
substring_index(FIELD, sep, n)可以将字段FIELD按照sep分隔:
(1).当n大于0时取第n个分隔符(n从1开始)之后的全部内容;
(2).当n小于0时取倒数第n个分隔符(n从-1开始)之前的全部内容;
因此,本题可以直接用substring_index(profile, ',', -1)取出性别。
附:substring_index函数解析
(SUBSTRING_INDEX(str,delim,count),是一个通过特定标识符"delim"来截取子串的函数,我们日常使用频率是很高的;
delim:通过该标识符来进行截取的,delim可以为任意字符,不要为空;
count:代表第几次出现;count为正数,代表从左边取标识符出现第count次之前的子串;负数则相反,从右边取标识符出现第count次之后的子串。【'左边’代表‘前’, '右边’代表‘后’】)
- 多少参赛者:计数统计,count(device_id)
细节问题:
- 表头重命名:as
完整代码:
select
substring_index(profile, ',', -1) as gender,
count(device_id) as number
from user_submit
group by gender拓展:提取blogurl中的用户名
法1:字符串函数
select
device_id,substring_index(blog_url,'/',-1) as user_name
# substr(blog_url,11) as user_name
from user_submit;
法2:替换函数
select
device_id,
replace('http:/url/','') as user_name
from user_submit;
法3:trim函数
select
device_id ,
trim('http:/url/' from blog_url) as user_name
from user_submit
窗口函数找最值
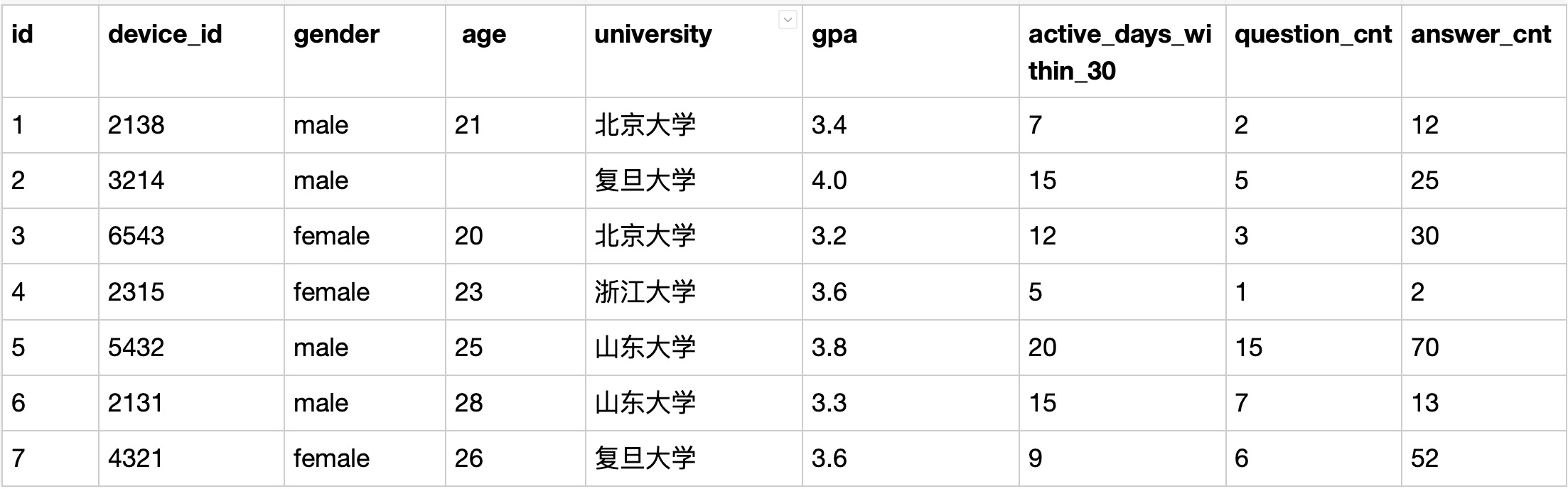
Q:找到每个学校gpa最低的同学来做调研,请你取出每个学校的最低gpa。
S:
问题分解:
- 限定条件:gpa最低,看似min(gpa),但是要留意,是每个学校里的最低,不是全局最低。min(gpa)的时候对应同学的ID丢了,直接干是拿不到最低gpa对应的同学ID的;
- 每个学校最低:
第一种方式是用group by把学校分组,然后计算得到每个学校最低gpa,再去找这个学校里和这个gpa相等的同学ID。注意这样如果最低gpa对应多个同学,都会输出,题目没有明确此种情况,心理明白就行。
第二种方式是利用窗口函数,先按学校分组计算排序gpa,得到最低gpa的记录在用子查询语法拿到需要的列即可。此题中rou_number可以得到排序后的位序,取位序为1即可得到最小值(升序时)。 - 窗口函数语法:row_number/rank/dense_rank over (partition by FIELD1 order by FIELD2),传送链接
细节问题:
- 如果题目明确了有多个最低gpa情况下,输出结果情况,需要留意
- 表头重命名:as
完整代码:
select device_id, university, gpa
from (
select *,
row_number() over (partition by university order by gpa) as rn
from user_profile
) as univ_min
where univ_min.rn=1
# 方法二:
select a.device_id, a.university, a.gpa
from user_profile a
right join
(
select university, min(gpa) as gpa
from user_profile
group by university
) as b
on a.university=b.university and a.gpa=b.gpa
order by a.university子查询做法:
利用相关子查询,把每个学校的最低gpa当作查询条件,去找出每个学校的gpa最低的同学。因为每个学校只有一个gpa最低的同学,所以最后出来的结果不需要再用group by,用order by排序就好。看代码!!
在子查询中,我们利用到了主查询的表,WHERE university = u.university 这个条件使得mysql去主表得每一行进行查询,比如第一行是2138的北京大学的同学,那么子查询会找出所有北京大学的同学,并且找出其中最低得gpa,如果他是最低的那个就留下,不是就下一个。以此类推找出所有大学的最低gpa的同学,最后排序得最终结果。
S:
SELECT
device_id,
university,
gpa
FROM user_profile u
WHERE gpa =
(SELECT MIN(gpa)
FROM user_profile
WHERE university = u.university)
ORDER BY university综合查询例题(review)
题意明确:
复旦大学的每个用户在8月份练习的总题目数和回答正确的题目数情况
问题分解:
- 限定条件:需要是复旦大学的(来自表user_profile.university),8月份练习情况(来自表question_practice_detail.date)
- 从date中取month:用month函数即可;
- 总题目:count(question_id)
- 正确的题目数:
sum(if(qpd.result='right', 1, 0)) - 按列聚合:需要输出每个用户的统计结果,因此加上
group by up.device_id
细节问题:
- 8月份没有答题的用户输出形式:题目要求『对于在8月份没有练习过的用户,答题数结果返回0』因此明确使用left join即可,即输出up表中复旦大学的所有用户,如果8月没有练习记录,输出0就好了
- 老样子-表头:as语法重命名后两列就好
完整代码:
select up.device_id, up.university,
count(question_id) as question_cnt,
sum(if(qpd.result='right', 1, 0)) as right_question_cnt
from user_profile as up
left join question_practice_detail as qpd
on qpd.device_id = up.device_id and month(qpd.date) = 8
where up.university = '复旦大学'
group by up.device_id
#IF 表达式
IF( expr1 , expr2 , expr3 )
expr1 的值为 TRUE,则返回值为 expr2
expr1 的值为FALSE,则返回值为 expr3SQL JOIN 综合例题
T35
浙江大学的用户在不同难度题目下答题的正确率情况,按照准确率升序输出
问题分解:
- 限定条件:浙江大学的用户;
- 不同难度:difficult_level(question_detail表中的列),需要分组统计,因此用到group by,语法详情;
- 正确率:表面理解就是正确数÷总数,正确的是result='right'(question_practice_detail表),数目用函数count,总数是count(question_id);
- 多张表联合查询:需要用到join,join有多种语法,因为条件限定需要是浙江大学的用户,所以需要是user_profile表的并且能统计出题目难度的记录,因此用user_profile表inner join另外两张表。
- join语法:语法详解,图解:
-
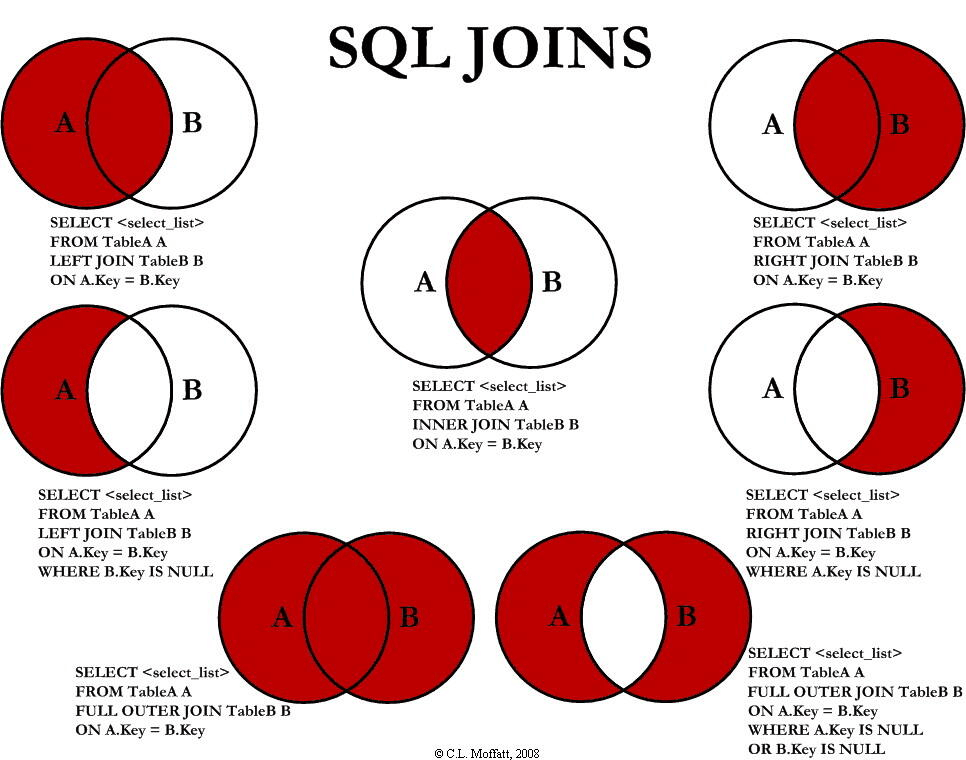
细节问题:
- 表头重命名:根据输出示例,正确率用as语法重命名
- 升序输出:order by xxx asc
- 正确率的计算方式:判断result是否为right,是的话赋值为1,对于正确的数目,可以用count,也可以用sum,正确率还可以直接用avg计算。
- join方式选择:如果前面inner join改成left join,为了防止结果中有难度为None的结果,需要在order by前加一句
having qd.difficult_level != 'None'
因此完整代码呼之欲出:
select difficult_level,
avg(if(qpd.result='right', 1, 0)) as correct_rate
# sum(if(qpd.result='right', 1, 0)) / count(qpd.question_id) as correct_rate
# count(if(qpd.result='right', 1, null)) / count(qpd.question_id) as correct_rate
from user_profile as up
inner join question_practice_detail as qpd
on up.device_id = qpd.device_id
inner join question_detail as qd
on qd.question_id = qpd.question_id
where up.university = '浙江大学'
group by qd.difficult_level
order by correct_rate asc;
## 方法2
select difficult_level,
(sum(case when qpd.result = "right" then 1 else 0 end)/count(u.answer_cnt)) as correct_rate
from user_profile u inner join question_practice_detail qpd on u.device_id = qpd.device_id
inner join question_detail qd on qd.question_id = qpd.question_id
where university = "浙江大学"
group by difficult_level
order by correct_rate;
like函数综合例题
题意明确:
2021年8月份所有练习过题目的总用户数和练习过题目的总次数
问题分解:
- 限定条件:2021年8月份,匹配date字段即可,匹配方法主要有三种:
(1)like语法:date like "2021-08%"
(2)year、month函数:year(date)='2021' and month(date)='08';
(3)date_format函数:date_format(date, '%Y-%m')='2021-08'; - 2:总用户数:count函数计数,因为用户有重复,所以需要distinct去重,即
count(distinct device_id) - 3:总次数:count(question_id)即可
细节问题:
- 表头重命名:as语法
完整代码:
select
count(distinct device_id) as did_cnt,
count(question_id) as question_cnt
from question_practice_detail
where date like "2021-08%"
#第二种方法
SELECT count(DISTINCT device_id) as did_cnt,count(question_id) as question_cnt
from question_practice_detail
where date >= '2021-08-01' and date <= '2021-08-31';




 这篇博客详细介绍了MySQL的高级查询技术,包括SELECT结果去重、查询限制、列重命名、年龄范围查询、模糊查询、最值查找、排序、统计函数、分组计算、SQL执行流程、连接查询以及进阶的OR、UNION、CASE函数、日期格式化、留存率计算、窗口函数和综合查询例题等,适合提升MySQL操作技能。
这篇博客详细介绍了MySQL的高级查询技术,包括SELECT结果去重、查询限制、列重命名、年龄范围查询、模糊查询、最值查找、排序、统计函数、分组计算、SQL执行流程、连接查询以及进阶的OR、UNION、CASE函数、日期格式化、留存率计算、窗口函数和综合查询例题等,适合提升MySQL操作技能。
















 1253
1253

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








