在计算机视觉领域,传统卷积神经网络(CNN)虽擅长提取局部特征,但在捕捉长距离依赖关系上存在局限,难以处理复杂场景中多目标或重叠物体的信息关联。而基于 Transformer 的模型虽能通过自注意力机制建模全局依赖,却因自注意力的二次复杂度带来巨大的计算和内存开销,且缺乏 CNN 的局部性归纳偏置,易忽略细粒度细节,尤其在低分辨率图像任务中,这些问题更为突出。为平衡局部特征提取、全局上下文捕捉与计算效率,Mask Attention 应运而生,旨在通过选择性关注重要区域,在降低计算成本的同时,提升模型对关键信息的捕捉能力,适用于资源受限场景下的视觉任务。
1. MaskAttention原理
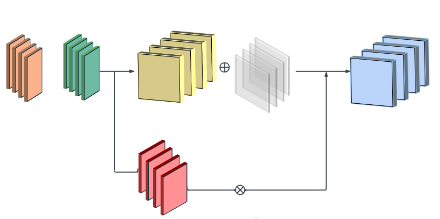
Mask Attention 的核心原理是在自注意力机制基础上引入可学习或动态计算的掩码矩阵(M),对注意力权重进行调制。首先,将输入特征图重塑后,通过线性变换得到查询(Q)、键(K)和值(V)向量;接着,在计算缩放点积注意力时,加入掩码矩阵 M,该矩阵会抑制无信息区域的贡献,使注意力集中在相关空间位置,计算公式为![]() 其中dk为 Q 和 K 的维度);之后,将多头掩码自注意力的输出进行融合,并通过残差连接与原始输入结合;以此实现对重要特征的强化和无关信息的抑制,高效捕捉长距离依赖。
其中dk为 Q 和 K 的维度);之后,将多头掩码自注意力的输出进行融合,并通过残差连接与原始输入结合;以此实现对重要特征的强化和无关信息的抑制,高效捕捉长距离依赖。
2. MaskAttention习作思路
在目标检测任务中:Mask Attention 能够通过掩码矩阵精准筛选出图像中的目标区域,抑制背景等无关信息的干扰,让模型更专注于目标的轮廓、纹理等关键特征,提升目标定位的准确性。同时,其对长距离依赖的高效捕捉能力,可帮助模型更好地理解目标之间的空间关系,比如多个目标的相对位置、遮挡情况等,减少因目标遮挡或密集排列导致的漏检、误检问题,并且相较于传统自注意力,更低的计算开销使得模型在处理高分辨率图像或复杂场景时,仍能保持较快的推理速度,满足实时检测的需求。
在目标检测任务中:在图像分割任务中,Mask Attention 可针对不同类别或实例生成专属的掩码,精准区分图像中不同物体或区域的边界,提升分割的精细度,尤其在处理低分辨率图像或复杂纹理区域时,能有效保留细粒度细节,避免区域混淆。此外,其结合残差连接和前馈网络的结构,能在整合全局上下文信息的同时,不丢失局部特征,让模型既能把握整体场景结构,又能精准分割局部小目标或复杂形状的区域,且较低的计算复杂度使其在资源受限设备上也能高效运行,拓宽了分割模型的应用场景。
3. YOLO与MaskAttention的结合
将 Mask Attention 融入 YOLO 中,可使 YOLO 在保持快速推理优势的同时,通过掩码抑制背景干扰,提升对小目标、密集目标的检测精度;还能帮助 YOLO 更好地理解目标间的空间关联,减少因遮挡导致的检测误差,进一步增强 YOLO 在复杂场景下的适应性。
4.MaskAttention代码部分
YOLO11|YOLO12|改进| 掩码注意力Mask Attention,选择性强化图像关键区域特征、抑制无关背景信息,提高遮挡、小目标的检测能力_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
YOLOv11模型改进讲解,教您如何修改YOLOv11_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
代码获取:YOLOv8_improve/YOLOV12.md at master · tgf123/YOLOv8_improve · GitHub
5. MaskAttention到YOLOv11中
第一: 将下面的核心代码复制到D:\model\yolov11\ultralytics\change_model路径下,如下图所示。
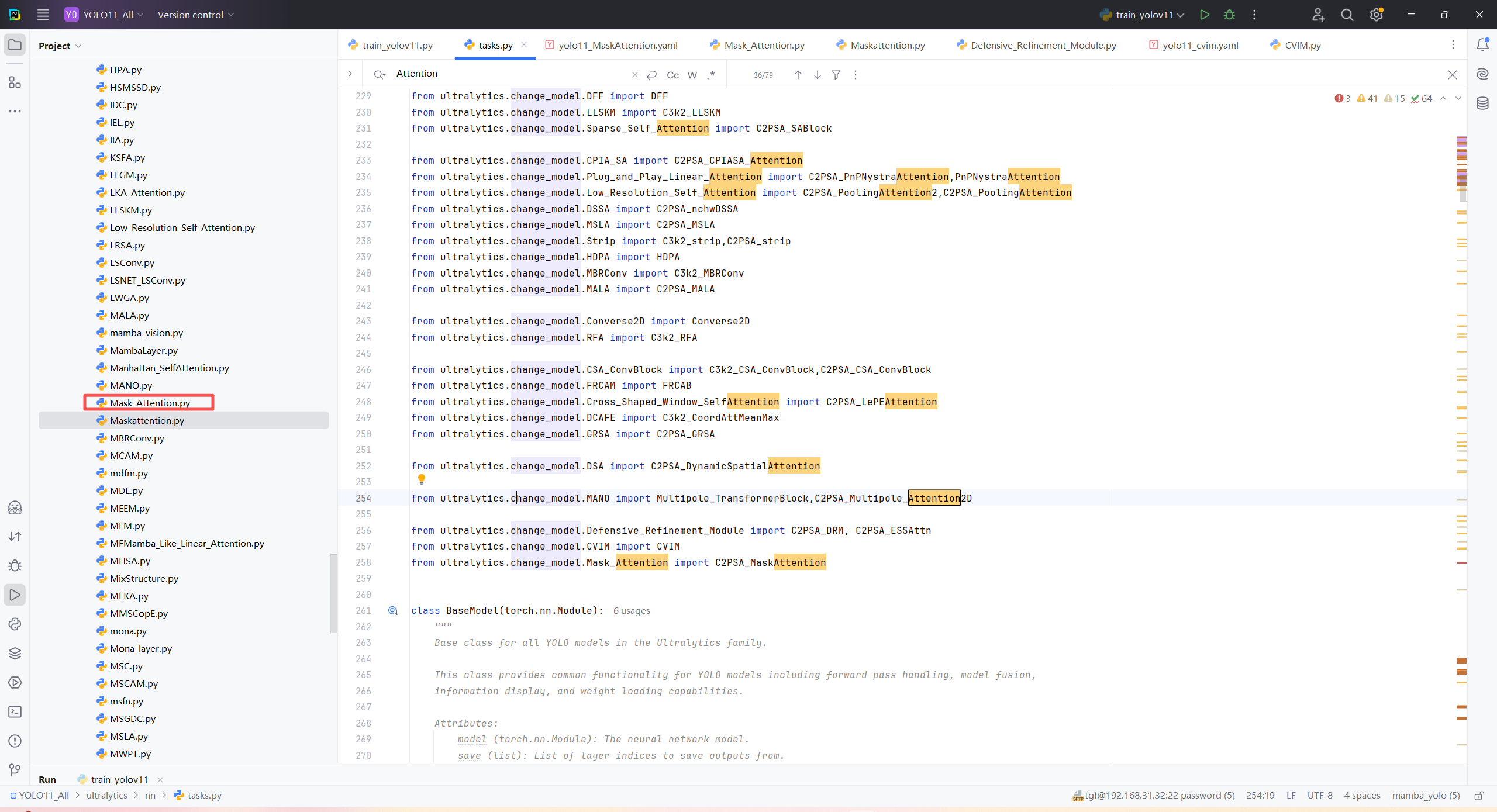
第二:在task.py中导入包
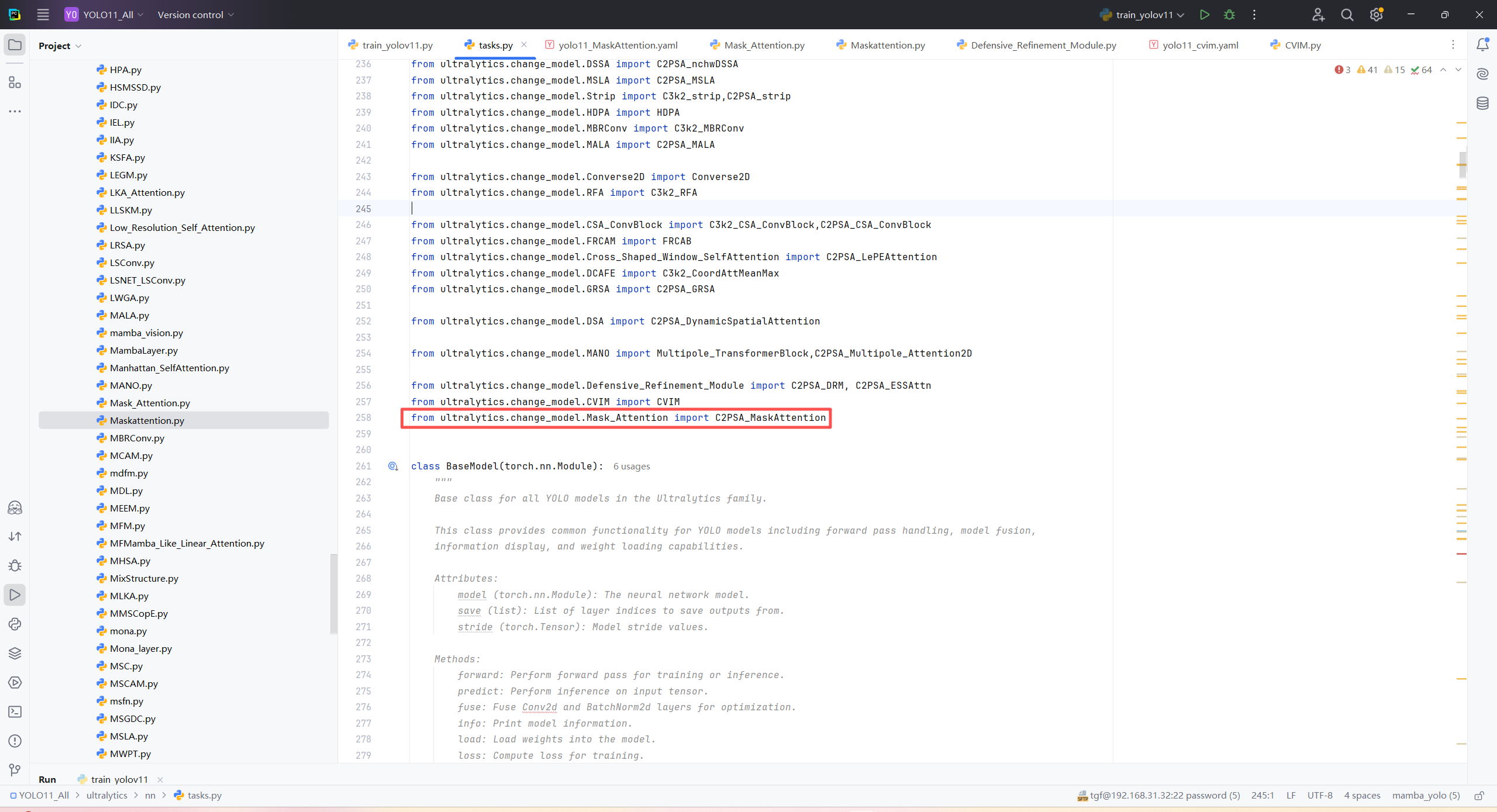
第三:在task.py中的模型配置部分下面代码
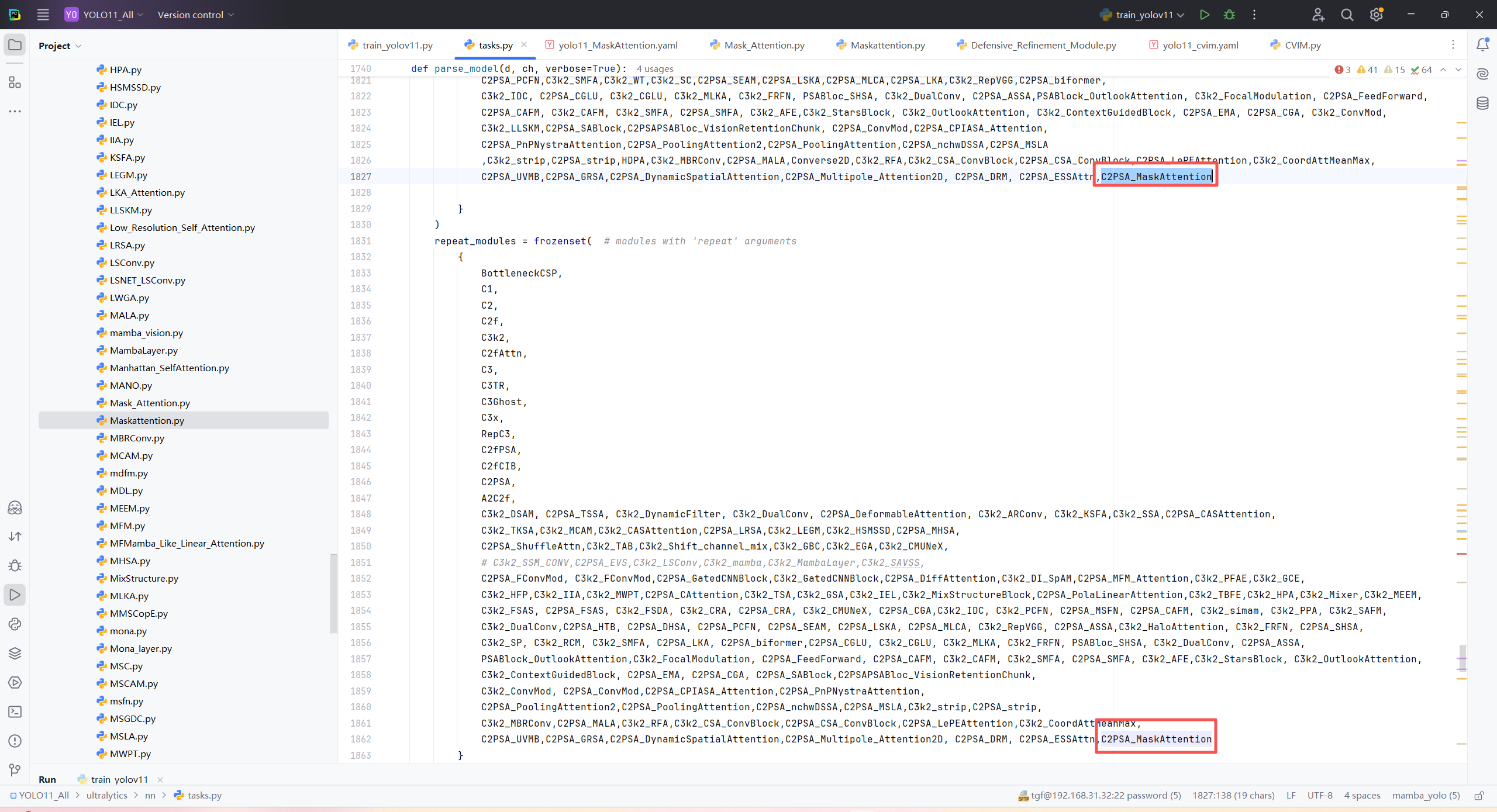
第四:将模型配置文件复制到YOLOV11.YAMY文件中
第五:运行代码
from ultralytics.models import NAS, RTDETR, SAM, YOLO, FastSAM, YOLOWorld
import torch
if __name__=="__main__":
# 使用自己的YOLOv8.yamy文件搭建模型并加载预训练权重训练模型
model = YOLO("/home/shengtuo/tangfan/YOLO11/ultralytics/cfg/models/11/yolo11_MaskAttention.yaml")\
# .load(r'E:\Part_time_job_orders\YOLO\YOLOv11\yolo11n.pt') # build from YAML and transfer weights
results = model.train(data="/home/shengtuo/tangfan/YOLO11/ultralytics/cfg/datasets/VOC_my.yaml",
epochs=300,
imgsz=640,
batch=4,
# cache = False,
# single_cls = False, # 是否是单类别检测
# workers = 0,
# resume=r'D:/model/yolov8/runs/detect/train/weights/last.pt',
amp = False
)





















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








