一、前言
给定一组正弦数据,我们希望能够利用最小二乘的思想对该组数据进行拟合,拟合公式为:
y
=
A
s
i
n
(
w
x
+
ϕ
)
+
b
y=Asin(wx+\phi)+b
y=Asin(wx+ϕ)+b
一般拟合分两种情况:
- 给定数据没有任何先验条件,需要直接根据给定的数据使用正弦函数进行拟合,这种情况的拟合是一种非线性的拟合,需要使用更高级的数学工具和优化算法,如遗传算法、粒子群优化、贝叶斯优化等;
- 给定数据已知它的角频率 w w w,根据这个先验条件对给定的数据使用正弦函数进行拟合,这种情况拟合就比较简单了,可以使用最小二乘的方法。
对于未给定角频率的情况,由于涉及更高级的算法,只用最小二乘没有办法很好的解决问题,所以接下来的讨论只针对第二种情况,已知一组数据它的角频率
w
w
w。
二、最小二乘拟合sin曲线(数据)原理分析
已知一组符合sin函数分布规律的数据:
(
x
1
,
x
2
,
…
,
x
n
)
,
(
y
1
,
y
2
,
…
,
y
n
)
(x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n),(y_1, y_2, \dots, y_n)
(x1,x2,…,xn),(y1,y2,…,yn)
我们知道,正弦曲线的一般形式是:
y
=
A
s
i
n
(
w
x
+
ϕ
)
+
b
y=Asin(wx+\phi)+b
y=Asin(wx+ϕ)+b,同时,他可以表示为
y
=
p
1
s
i
n
w
x
+
p
2
c
o
s
w
x
+
p
3
y=p_1sinwx+p_2coswx+p_3
y=p1sinwx+p2coswx+p3,他们这些参数之间的对应关系为:
{
A
=
p
1
2
+
p
2
2
ϕ
=
a
r
c
t
a
n
(
p
2
p
1
)
b
=
p
3
\begin{equation} \left\{ \begin{aligned} A&=\sqrt{p_1^2+p_2^2}\\ \phi&=arctan(\frac{p_2}{p_1})\\ b&=p_3 \end{aligned} \right. \end{equation}
⎩
⎨
⎧Aϕb=p12+p22=arctan(p1p2)=p3
我们的思路是先求出
p
1
,
p
2
,
p
3
p_1,p_2,p_3
p1,p2,p3,然后再根据公式(1)来计算
A
,
ϕ
,
b
A,\phi,b
A,ϕ,b
根据给定的数据建立以下方程组:
{
y
1
=
p
1
s
i
n
w
x
1
+
p
2
c
o
s
w
x
1
+
p
3
y
2
=
p
1
s
i
n
w
x
2
+
p
2
c
o
s
w
x
2
+
p
3
⋮
y
n
=
p
1
s
i
n
w
x
n
+
p
2
c
o
s
w
x
n
+
p
3
\begin{equation} \left\{ \begin{aligned} y_1&=p_1sinwx_1+p_2coswx_1+p_3\\ y_2&=p_1sinwx_2+p_2coswx_2+p_3\\ & \vdots \\ y_n&=p_1sinwx_n+p_2coswx_n+p_3\\ \end{aligned} \right. \end{equation}
⎩
⎨
⎧y1y2yn=p1sinwx1+p2coswx1+p3=p1sinwx2+p2coswx2+p3⋮=p1sinwxn+p2coswxn+p3
我们将方程组(2)写成矩阵的形式:
[
s
i
n
w
x
1
c
o
s
w
x
1
1
s
i
n
w
x
2
c
o
s
w
x
2
1
⋮
s
i
n
w
x
n
c
o
s
w
x
n
1
]
∗
[
p
1
p
2
p
3
]
=
[
y
1
y
2
⋮
y
n
]
\begin{equation} \begin{bmatrix} sinwx_1 & coswx_1&1 \\ sinwx_2 & coswx_2&1 \\ &\vdots\\ sinwx_n & coswx_n&1 \end{bmatrix}* \begin{bmatrix} p_1 \\ p_2 \\ p_3 \end{bmatrix}= \begin{bmatrix} y_1 \\ y_2 \\ \vdots\\ y_n \end{bmatrix} \end{equation}
sinwx1sinwx2sinwxncoswx1coswx2⋮coswxn111
∗
p1p2p3
=
y1y2⋮yn
这样就变成了我们熟悉的问题:
A
x
=
b
Ax=b
Ax=b,求解这类问题有许多现成的算法,这里我就不展开讨论,利用上述矩阵等式可以求解出参数
p
1
,
p
2
,
p
3
p_1,p_2,p_3
p1,p2,p3,进而求解出
A
,
ϕ
,
b
A,\phi,b
A,ϕ,b
三、代码展示
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <Eigen/Dense> // 使用Eigen库进行矩阵计算
#define PI 3.1415926
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
// 定义sin函数模型,A是振幅,omega是频率,phi是相位,b是偏移量
double sinFunc(double A, double omega, double phi, double b, double x) {
return A * sin(omega * x + phi) + b;
}
// 最小二乘拟合sin函数
void fitSinCurve(const vector<double>& xData, const vector<double>& yData, double omega, double& A, double& phi, double& b) {
int n = xData.size();
MatrixXd AMatrix(n, 3);
VectorXd bVector(n);
// 构造系数矩阵和右侧向量
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
AMatrix(i, 0) = sin(omega * xData[i]);
AMatrix(i, 1) = cos(omega * xData[i]);
AMatrix(i, 2) = 1.0;
bVector(i) = yData[i];
}
// 使用最小二乘法计算拟合参数
Vector3d params = AMatrix.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(bVector);
A = sqrt(params(0) * params(0) + params(1) * params(1));
phi = atan2(params(1), params(0));
b = params(2); // 偏移量b
}
int main() {
// 指定测试参数
double true_A = 1.5;
double true_omega = 2.0;
double true_phi = PI / 4.0;
double true_b = 0.5;
// 生成一组测试数据
vector<double> xData;
vector<double> yData;
for (double x = 0.0; x <= 10.0; x += 0.1) {
double y = sinFunc(true_A, true_omega, true_phi, true_b, x);
xData.push_back(x);
yData.push_back(y);
}
// 执行sin函数拟合,拟合结果存储在以下变量中
double fitted_A, fitted_phi, fitted_b;
// 调用拟合函数
fitSinCurve(xData, yData, true_omega, fitted_A, fitted_phi, fitted_b);
// 输出拟合结果和指定的参数结果
cout << "指定参数:" << endl;
cout << "振幅 A: " << true_A << endl;
cout << "角频率 omega: " << true_omega << endl;
cout << "相位 phi: " << true_phi << endl;
cout << "偏移量 b: " << true_b << endl;
cout << "---------------------------" << endl;
cout << "拟合结果:" << endl;
cout << "振幅 A: " << fitted_A << endl;
cout << "相位 phi: " << fitted_phi << endl;
cout << "偏移量 b: " << fitted_b << endl;
return 0;
}
结果如下所示:
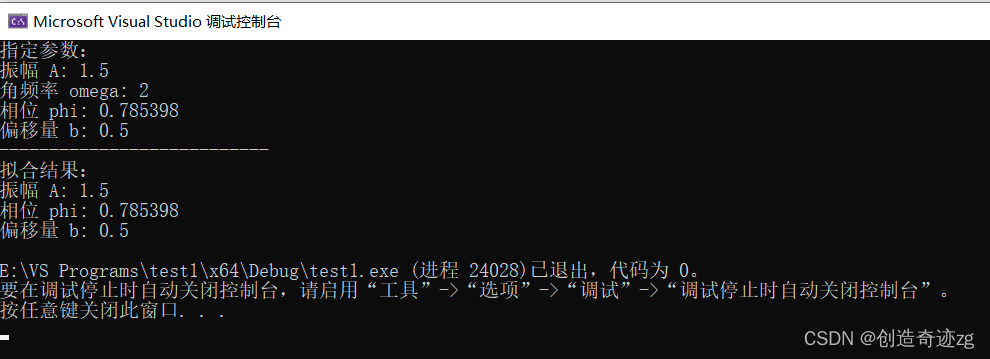
可以看出,拟合结果与真实结果相同,为了检验该算法稳定性,我们可以在原始数据上添加噪声,代码如下:
高斯噪声生成函数
// 生成高斯随机数,用于生成噪声
// mu为均值,sigma为标准差
double generateGaussianNoise(double mu, double sigma) {
static default_random_engine generator;
normal_distribution<double> distribution(mu, sigma);
return distribution(generator);
}
测试数据生成代码
double noise_mean = 0.0; // 噪声均值
double noise_stddev = 0.1; // 噪声标准差
for (double x = 0.0; x <= 10.0; x += 0.1) {
double y_true = sinFunc(true_A, true_omega, true_phi, true_b, x);
double y_noise = generateGaussianNoise(noise_mean, noise_stddev);
double y = y_true + y_noise;
xData.push_back(x);
yData.push_back(y);
}
结果如下所示:

结果分析:
通过上述结果可以看出,在添加一定的高斯噪声的情况下,该算法依旧可以很好地对数据进行拟合,效果还是非常好的。
四、总结
以上拟合问题是在实际研究过程中遇到的问题,为了提高数据计算的精度,在网上看过许多拟合方法,但是都比较复杂,最终采用一种简单的方法来实现,希望对大家有所帮助和启发。如果大家还有什么想法,欢迎在评论区交流,有什么内容上或者其它的建议,也欢迎大家批评指出,谢谢。























 2275
2275

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








