JavaScript学习 Day4~Day5
文章目录
1、方法
let a ={
name:"xiaoming",
bitrh:2002,
// 方法
age:function () { // 似乎和函数毫无差别
let now = new Date().getFullYear(); // 获取当前年份
return now - this.bitrh;
}
}
// 属性
a.name
// 方法 要带括号
a.age()
function getAge() {
let now = new Date().getFullYear();
return now - this.bitrh; // this 只会指向调用它的对象
}
let a ={
name:"xiaoming",
bitrh:2002,
// 方法
age:getAge // 这里不要()
}
// 可以把方法放到上面写,用a.age调用会成功,不能直接调用
apply() 所有函数都有的一个函数
在 js 中控制 this 的指向
// 函数后不要()
getAge.apply(a,[]); // (指向对象,参数) 参数是数组对象
2、内部对象
typeof 123
'number'
typeof "123"
'string'
typeof NaN
'number'
typeof true
'boolean'
typeof []
'object'
typeof {}
'object'
typeof getAge
'function'
typeof undefined
'undefined'
1.1 Date
耶?朕在发博客的是否发现了它,这对吗?
let a = new Date();
console.log(a.getFullYear()); // 年
console.log(a.getMonth()); // 月
console.log(a.getDate()); // 日
console.log(a.getDay()); // 星期
console.log(a.getHours()); // 小时
console.log(a.getMinutes()); // 分钟
console.log(a.getSeconds()); // 秒
console.log(a.getTime()); // 时间戳
console.log(new Date(a.getTime())); // 时间戳转时间
console.log(a.toLocaleString());
console.log(a.toGMTString());

2.2 JSON
JSON 是什么
早期,所有的数据传输都是用xml文件!
- Json 是轻量级的数据交换格式
- 简洁清晰的层次结构
- 提升网络传输效率
格式:
- 对象{}
- 数组[]
- 键值对 key : value
JSON 字符串 和 js 对象的转化
let a = {
ha : "wu",
xi : 10,
wu : "wu"
}
console.log(a);
let b = JSON.stringify(a);
console.log(b); // {"ha":"wu","xi":10,"wu":"wu"}
let c = JSON.parse('{"ha":"wu","xi":10,"wu":"wu"}'); // 里面""外面就不能用了"",得用'',反之亦然
console.log(c);
3、 面向对象编程
3.2 继承
原型对象
let a = {
name : "xiaohong",
run : function () {
console.log(this.name + " run...")
}
};
let xiaoming = {
name: "xiaoming"
};
xiaoming.__proto__ = a; // 继承!
console.log(xiaoming);
let fly = {
fly : function () {
console.log(this.name + " fly...")
}
}
xiaoming.__proto__ = fly; // 还可以换一个继承
console.log(xiaoming);
class 继承 ES6
1.定义一个类
class a {
constructor(name) { // 构造方法
this.name = name;
}
hello() { // 甚至不要返回值类型
alert("hello");
}
}
let aa = new a("xiaomiung");
aa.hello();
2.继承
class b extends a{...} // 和java一样
bb
b {name: 'xiaohong', age: 12}
age: 12
name:"xiaohong"
[[Prototype]]: a
本质:查看对象原型
原型链
查看对象原型的时候就在控制台点↓
// 拿前面的bb举例
[[Prototype]]: a
// 然后这个点开还有一个Prototype
[[Prototype]]: Object
// 再点开
[[Prototype]]: Object
点到一堆乱七八糟的玩意里,这时候看到最下面没有那个Prototype了
但是随便点开一个,再顺着Prototype点点点
就又要回到了 [[Prototype]]: Object,形成了一个闭环
4、操作BOM对象(重点)
BOM:浏览器对象模型
window
window代表 浏览器窗口
// 内部的宽高
window.innerHeight
686
window.innerWidth
387
// 外部的宽高
window.outerHeight
831
window.outerWidth
782
Navigator 类
navigator 对象(不建议使用)
封装了浏览器的信息
navigator.appName
'Netscape'
navigator.appVersion
'5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/126.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
navigator.userAgent
'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/126.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
navigator.platform
'Win32'
大多数不使用 navigator,因为会被人修改
不建议用这些属性来判断和编写
screen
屏幕尺寸
screen.height
864
screen.width
1536
location(重要)
当前页面URL信息
host: "www.baidu.com" // 主机
href: "https://www.baidu.com/"
protocol: "https:" // 协议
reload: ƒ reload() // 刷新网页
location.assign('https://www.bilibili.com/') // 跳转
document
代表当前页面,HTML DOM文档树
document.title
'哔哩哔哩 (゜-゜)つロ 干杯~-bilibili'
document.title = "哈哈"
'哈哈'
获取具体的文档树节点
<dl id = 'aa'>
<dt>a</dt>
<dd>b</dd>
<dd>c</dd>
</dl>
<script>
let a = document.getElementById("aa");
</script>
获取 cookie
document.cookie
''
cookie 是用来登录网站之类的
服务器端可以设置 cookie : httpOnly(只读)
history(不建议使用)
history.back() // 后退
history.forward() // 前进
5、操作BOM对象2(重点)
核心
浏览器网页就是一个Dom 树形结构
- 更新:更新Dom节点
- 遍历Dom节点:得到Dom节点(上面document)
- 删除…
- 添加…
操作Dom节点,就要获得Dom节点
1.获得Dom节点
<div id = "ha">
<h1>h1</h1>
<p id = "id">p1</p>
<p class="class">p2</p>
</div>
<script>
let h1 = document.getElementsByTagName("h1"); // 标签
let id = document.getElementById("id"); // id
let c = document.getElementsByClassName("class"); // class
let ha = document.getElementById("ha");
let cl = ha.children; // 获取所有子节点
ha.firstChild; // 第一个孩子
ha.lastChild; // 最后一个孩子
这是原生代码,之后尽量使用jQuery
2.更新节点
inner
id1.innerText = "haha"
'haha'
id1.innerHTML = "<strong>xixi</strong>"
'<strong>xixi<strong>
id1.style.color = "red" // 属性使用字符串
'red'
id1.style.fontSize = "50px"
'50px'
id1.style.padding = "20px"
'20px'
注意:这两都是 = ,不是方法
3.删除节点
删除节点的步骤:先找父节点,再删除
f.removeChild()
let f = z.parentElement // 找父亲
f.removeChild(z) // 不带引号
f.children
ha.children
HTMLCollection(3) [h1, p#id, p.class, id: p#id]
ha.children[0] // 可以通过下标来找
<h1>h1</h1>
// 那就可以用下标删除
ha.removeChild(ha.children[0])
<h1>h1</h1>
ha.children[0] // 但是这个时候删除了[0],[1]就变成了[0]了
<p id="id">p1</p>
所以要注意child是随时变化的
4.插入节点
inner在dom节点没东西的时候是插入,有的话就覆盖了
<body>
<p id = "JS">JS</p>
<div id = "div">
<p id = "p1">p1</p>
<p id = "p2">p2</p>
</div>
<script>
let Js = document.getElementById("JS");
let div = document.getElementById("div");
let p1 = document.getElementById("p1");
let p2 = document.getElementById("p1");
</script>
</body>
剪切或新建 .appendChild(JS)
JS
p1
p2
div.appendChild(JS) // 剪切了已存在的节点
p1
p2
JS
创建新的标签
let new_p = document.createElement('p'); // 创建了一个新的p节点
new_p.id = "new_p"; // 设置id
new_p.innerText = "new_p"; // 标签里的文本
div.append(new_p); // 插入
带有属性的标签 .setAttribute(‘’,‘’)
// 创建一个标签节点 刚才创建了一个p标签
let hei = document.createElement('script');
hei.setAttribute('type','text/javascript'); // 相当于type = 'text/javascript'
// 还可以设置("id","p12") --> id = "p12 相当于设置属性和属性值
div.appendChild(hei)
<div id="div">
<p id="p1">p1</p>
<p id="p2">p2</p>
<p id="new_p">new_p</p>
<script type="text/javascript"></script> // 这样就添加了一个带有属性的标签
</div>
设置样式
let body = document.getElementsByTagName("body"); // 这时候body里是个数组 0:body
body[0].setAttribute('bgcolor','red');
// 也可以获取head标签,在里面appendChild style标签,设置type = "text/css",再innerHTML 来更改样式
let head = document.getElementsByTagName("head");
let myStyle = document.createElement("style");
myStyle.innerHTML = "body{background-color:yellow}"; // 添加css语句
head[0].append(myStyle);
// 注意 getElementsByTagName 是数组
body
HTMLCollection [body]
0: body
length: 1
[[Prototype]]: HTMLCollection
insertBefore
// insertBefore()
div.insertBefore(p2,p1);
// 在div(父节点)里,把p2放到p1前面
6、操作表单
form 、input
- 文本框 text
- 下拉框
- 单选框 radio
- 多选框 checkbox
- 隐藏域 hidden
- 密码框 password
- …
6.1操作表单
text
<form>
<p>
<span>用户名:</span><input type="text" id ="username" value="admin">
<!-- 可以通过设置value设置初始值 -->
</p>
</form>
<script>
let username = document.getElementById("username");
username.value = "haha"; // 那就可以设置value来更改属性
</script>
radio
<p>
<span>性别:</span>
<input type="radio" name="sex" id = "man">男
<input type="radio" name="sex">女
</p>
<script>
let sex = document.getElementsByName("sex"); // 可以去到 name = "sex" 的值
// let man = document.getElementById("man"); 也可以设置id,用id来选
// 获取到的是一个数组
sex
NodeList(2) [input, input]
0: input
1: input
length: 2
// 不设置value,默认是'on',没啥用
sex[0].value
'on'
// 更改是使用 sex[数].checked = true 改中谁选谁
</script>
6.2 提交表单
<form action="#" method="post">
<p>
<span>用户名:</span> <input type="text" id ="username" name="username">
</p>
<p>
<span>密码:</span> <input type="password" id ="password" name="password">
</p>
<!--提交按钮,onclick 是绑定事件-->
<button type="submit" onclick="a()">提交</button>
<!--但是如果type = "button"(普通按钮) 就会没有请求-->
</form>
<script>
function a() { // 绑定了a()函数
let username = document.getElementById("username");
let password = document.getElementById("password");
console.log(username.value);
console.log(password.value);
password.value = "***"
}
</script>
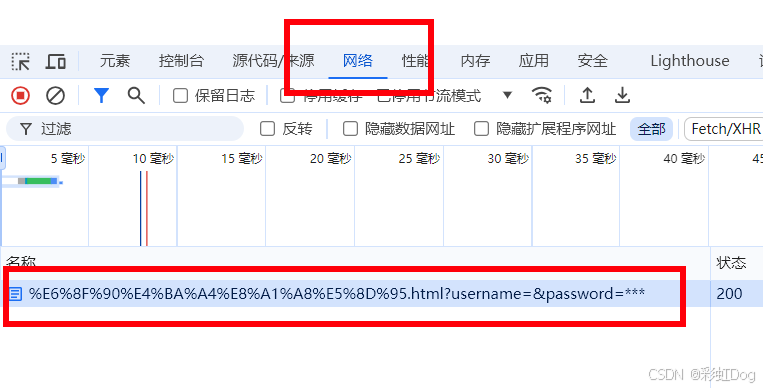
查看请求
点进去之后,选择载荷,里面有两个
- 查询字符串参数,这个不知道来自哪
- 表单数据,这个来自给input设置的name,不设置name就没有
提交2 onsubmit
<!--
onsubmit 提交后是否请求
里面写 return true/false
false 的话就没有请求 action 的跳转也没用了
-->
<form action="#" method="post" onsubmit="return a()">
<p>
<span>用户名:</span> <input type="text" id ="username" name="username">
</p>
<p>
<span>密码:</span> <input type="password" id ="password" name="password">
</p>
<input type="hidden" id="md5pwd"> <!--用隐藏的hidden来接收-->
<button type="submit">提交</button> <!--这里就可以不用设置onclick-->
</form>
<script>
function a() {
let username = document.getElementById("username");
let password = document.getElementById("password");
let md5psw = document.getElementById("md5pwd"); // pwd也会接受到这里来
// md5psw.value = md5(md5psw.value); 用隐藏框接收的使用
// MD5 用来加密 但是我还没下MD5工具包
// password.value = md5(password.value);
return true;
}
</script>
6.3 其他
(1)focus
用于获取焦点
<span>用户名:</span> <input type="text" id ="username" name="username">
...
<script>
let username = document.getElementById("username");
username.focus();
</script>
这样,网页一打开光标就在这个 username 的框里




















 1269
1269

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








