文章目录
回溯
穷举所有可能情况来找到所有解的算法。1个候选解最后被发现并不是可行解,回溯算法会舍弃它,并在前面的一些步骤做出一些修改,并重新尝试找到可行解。
1079. 活字印刷
添加链接描述
tiles中每一个位置的字符在组合中只能出现一次, 所以可以用一个标记辅助
当去组合新的组合时,可以与tiles中的每一个位置组合,unordered_set可以天然去重,DFS + 回溯:
1.当前组合不为空, 则插入set中
2.继续给当前组合拼接新的组合,尝试拼接tiles每一个位置的字符
3.如果当前位置已在组合中出现过,返回到2,否则标记当前位置,继续拼接更长的组合
4.回溯,尝试组合其它位置,返回2
当所有位置都已经使用过时,当前递归就结束了,继续向上层DFS回退
最终返回set的大小即为组合数目

void dfs(string& tiles, string curStr, vector<int>& usedIdx, unordered_set<string>&
totalString)
{
if (!curStr.empty())
{
totalString.insert(curStr);
}
//标记保证所有位都用完之后,就结束了
for (int i = 0; i < tiles.size(); ++i)
{
//当前位置的字符已用过,直接跳过
if (usedIdx[i])
continue;
usedIdx[i] = 1;
dfs(tiles, curStr + tiles[i], usedIdx, totalString);
//回溯,尝试其它字符
usedIdx[i] = 0;
}
}
int numTilePossibilities(string tiles) {
if (tiles.empty())
return 0;
unordered_set<string> totalString;
//标记全部初始化为未使用
vector<int> usedIdx(tiles.size(), 0);
dfs(tiles, "", usedIdx, totalString);
return totalString.size();
51. N 皇后
添加链接描述
从第一行开始放置皇后,每确定一个位置,判断是否会冲突: 是否在同一列,撇,捺, 不可能在同一行,
同一列:纵坐标相同
“撇”,对应的位置,横坐标加上纵坐标的值是相同的。
“捺”,对应的位置,横坐标减去纵坐标的值也是相同的。
当前行位置确定之后, 继续确定下一行的位置
回退,尝试当前行的其它位置
// i.second == col: 第i个皇后与当前这个点在同一列
// i.first + i.second == row + col: 第i个皇后与当前点在撇上,横坐标+纵坐标值相同
// i.first - i.second == row - col:第i个皇后与当前点在捺上, 横坐标-纵坐标值相同
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
//按坐标位置存放所有解决方案
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> solutions;
//存放一种解决方案中的所有皇后的位置
vector<pair<int, int>> solution;
nQueensBacktrack(solutions, solution, 0, n);
//把坐标位置转成string
return transResult(solutions, n);
}
void nQueensBacktrack(vector<vector<pair<int, int>>>& solutions,
vector<pair<int, int>>& solution, int curRow, int n) {
if (curRow == n) solutions.push_back(solution);每1行都确定了1个皇后,1种方案产生
//尝试当前行的每一个位置是否可以放置一个皇后
for (int col = 0; col < n; ++col) {
if (isValid(solution, curRow, col)) {
//直接调用构造函数,内部构造pair, 或者调用make_pair
solution.emplace_back(curRow, col);确定当前行皇后的位置
nQueensBacktrack(solutions, solution, curRow + 1, n);确定下一行皇后的位置
//回溯,删除当前位置,尝试当前行的其它位置
solution.pop_back();
}
}
}
// solution: 一个解决方案,从第一行开始到当前行的上一行每一行已经放置皇后的点
bool isValid(vector<pair<int, int>>& solution, int row, int col) {
// 判断当前行尝试的皇后位置是否和前面几行的皇后位置有冲突
for (pair<int, int> &i : solution)
if (i.second == col || i.first + i.second == row + col
|| i.first - i.second == row - col)
return false;
return true;
}
vector<vector<string>> transResult(vector<vector<pair<int, int>>>& solutions, int n)
{
vector<string> tmp();
//把每一种解决方案都转换为string形式,最终结果
vector<vector<string>> ret;
for (vector<pair<int, int>>& solution : solutions) {
//n*n char: 每行有n个元素,
vector<string> solutionString(n, string(n, '.'));
for (pair<int, int>& i : solution) {
solutionString[i.first][i.second] = 'Q';把皇后的位置修改为Q
}
ret.push_back(solutionString);保存
}
return ret;
}
HJ43 迷宫问题
每个点都要走过,不知道哪里是墙,走到墙的位置,走不通,再退回来:回溯。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int N, M; //分别代表行和列
vector<vector<int>> maze;//迷宫矩阵
vector<vector<int>> path_temp;//存储当前路径,临时路径,第一维表示位置,走过的路径放到path_temp
vector<vector<int>> path_best;//存储最佳路径
void MazeTrack(int i, int j) {
maze[i][j] = 1;//表示当前节点已走,不可再走
path_temp.push_back({ i, j });//将当前节点加入到路径中
if (i == N - 1 && j == M - 1) //判断是否到达终点
//向4个方向探索,哪个方向走的通,走哪个方向
if (path_best.empty() || path_temp.size() < path_best.size())
path_best = path_temp;//寻找最短路径
if (i - 1 >= 0 && maze[i - 1][j] == 0)//探索向上走是否可行
MazeTrack(i - 1, j);
if (i + 1 < N && maze[i + 1][j] == 0)//探索向下走是否可行
MazeTrack(i + 1, j);
if (j - 1 >= 0 && maze[i][j - 1] == 0)//探索向左走是否可行
MazeTrack(i, j - 1);
if (j + 1 < M && maze[i][j + 1] == 0)//探索向右走是否可行
MazeTrack(i, j + 1);
maze[i][j] = 0; //恢复现场,设为未走,4个方向都走不通,回溯
path_temp.pop_back();//之前进去的点要删除
}
int main()
{
while (cin >> N >> M)
{
maze = vector<vector<int>>(N, vector<int>(M, 0));//初始化为0
path_temp.clear();
path_best.clear();//1组数据测试完了,清除,不用累加
for (auto &i : maze)//输入迷宫
for (auto &j : i)
cin >> j;
MazeTrack(0, 0);//回溯寻找迷宫最短通路,从(0,0)开始走
for (auto i : path_best)
cout << '(' << i[0] << ',' << i[1] << ')' << endl;//输出通路
}
return 0;
}
幸运的袋子
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int getLuckyPacket(vector<int>&x, int n, int pos, int sum, int multi)
{
int count = 0;
for (int i=pos; i<n; ++i)
{
sum += x[i];
multi *= x[i]; //判断幸运是否·
if (sum > multi)
count += 1+getLuckyPacket(x,n,i + 1,sum,multi);
else if (x[i]== 1)
count += getLuckyPacket(x, n, i + 1, sum, multi);
else
break; //不幸运,回溯
sum -= x[i];
multi /= x[i];
//去重,113 131是同一种
while (i < n - 1 && x[i] == x[i + 1])
i++;
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while (cin >> n)
{
vector<int> x(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
cin >> x[i];
sort(x.begin(), x.end());
cout << getLuckyPacket(x,n,0,0,1) << endl;
}return 0;
}
113
1135:此时已经不是幸运袋子,后面的不需要再尝试
11357:不需要再尝试,
回溯到11开头的,135:不是幸运袋子;137:不是幸运袋子

深度优先
字符串的全排列
字典序:只要字符的ascii码值一样,继续比下一个字符;若不一样的字符,按升序排列,则把码值小的放前面
添加链接描述

void swap(string &str, int i, int j)
{
char temp = str[i];
str[i] = str[j];
str[j] = temp;
}
bool IsExist(vector<string>& result, string &str)
{是否存在
auto it = result.begin();
for (; it != result.end(); ++it)
{
if (*it == str)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void PermutationHelper(string &str, int start, vector<string>& result){str:待选结果;目标结果集:result
if (start == str.length() - 1)
{去掉重复的字符串
if (!IsExist(result, str))
{不存在时,把str加入result
result.push_back(str);
}
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < (int)str.size(); i++)
{
swap(str, start, i); //以i对应的字符作为开始
PermutationHelper(str, start + 1, result);//以i开头的所有的可能性全部处理并保存到了result中
swap(str, start, i);
}
}
vector<string> Permutation(string str)
{
vector<string> result;
if (str.length() > 0)
{
PermutationHelper(str, 0, result);0下标元素
sort(result.begin(), result.end());排序
}sort:ascii码值排序,重载了小于号
return result;
}
下标:start 和 i 的关系是:表示以谁开始 。start:永远表示第1个元素,i和start交换,则i:第1个元素。
//当确定以哪个字符作为开始,再决定另一部分的排列组合种类
//i仅仅是决定以谁作为排列的开始,求sub字符串每次开始,都要从start+1开 始,abc ,以b=start,swap之后:bac;PermutationHelper的功能:ac的所有排列组合(ca ac);闭区间;只输入1个字符时,str.length()=1。不是只有树型结构用树,字符串也可以是树。start=0时,a和a交换。
前中后序遍历
员工的重要性
int DFS(unordered_map<int, Employee*>& info, int id)
{
int curImpo = info[id]->importance;
for (const auto& sid : info[id]->subordinates)
{
curImpo += DFS(info, sid);
}
return curImpo;
}
int getImportance(vector<Employee*> employees, int id) {
if (employees.empty())
return 0;
unordered_map<int, Employee*> info;
for (const auto& e : employees)
{
info[e->id] = e;
}
return DFS(info, id);
}
边界: 下属为空, 每次先加第一个下属的重要性, 按照相同的操作再去加下属的第一个下属的重要性
733. 图像渲染

边界:位置是否越界,用的标记,避免重复修改,使时间复杂度不超过O(row * col)
每个点:1.染色2.上下左右搜索新的点3.判断新的点是否符合要求4.处理每一个新的点
添加链接描述
//四个方向的位置更新:顺时针更新,右下左上,方向矩阵
int nextPosition[4][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, 0 } };
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& image, int row, int col, vector<vector<int>>& book,
int sr, int sc, int oldColor, int newColor)
{
//处理当前逻辑,修改颜色
image[sr][sc] = newColor;
book[sr][sc] = 1;//标记已经修改过
//遍历每一种可能,四个方向
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k)
{
int newSr = sr + nextPosition[k][0];
int newSc = sc + nextPosition[k][1];
//判断新位置是否越界
if (newSr >= row || newSr < 0
|| newSc >= col || newSc < 0)
continue;
//如果颜色符合要求,并且之前也没有渲染过,则继续渲染:
if (image[newSr][newSc] == oldColor && book[newSr][newSc] == 0)
{
dfs(image, row, col, book, newSr, newSc, oldColor, newColor);
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> floodFill(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc, int
newColor) {
if (image.empty())
return image;
int row = image.size();
int col = image[0].size();
//建立标记
vector<vector<int>> book;
book.resize(row);
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i)
{
book[i].resize(col, 0);
}
//获取旧的颜色
int oldColor = image[sr][sc];
dfs(image, row, col, book, sr, sc, oldColor, newColor);
return image;
}
};
130. 被围绕的区域
添加链接描述
以边界上的o以及与o联通的都不算做包围,只要把边界上的o以及与之联
通的o进行特殊处理,剩下的o替换成x即可。故问题转化为,如何寻找和边界联通的o
1.首先寻找边上的每一个o,如果没有,表示所有的o都被包围
2.用渲染搜索的方法,对于边上的每一个o进行dfs进行扩散,先把边上的每一个o用特殊符号标记,比如*,#等
3.把和它相邻的o都替换为特殊符号,每一个新的位置都做相同的dfs操作
4.所有扩散结束之后,把特殊符号的位置(和边界连通)还原为o,原来为o的位置(和边界不连通)替换为x即可
int nextPosition[4][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, 0 } };
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board, int row, int col, int i, int j)
{
//当前位置设为'*'
board[i][j] = '*';
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k)
{
//向四个方向扩散
int ni = i + nextPosition[k][0];
int nj = j + nextPosition[k][1];
//判断边界
if (ni < 0 || ni >= row
|| nj < 0 || nj >= col)
continue;
//是'O'说明和边联通,继续搜索是否还有联通的
if (board[ni][nj] != '*' && board[ni][nj] != 'X')
dfs(board, row, col, ni, nj);
}
}
void solve(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
if (board.empty())
return;
//寻找边上的每一个0,如果没有,表示所有的0都被包围
int row = board.size();
int col = board[0].size();
以每一个边上的o为起点,找到和边上o联通的所有o
//寻找第一行和最后一行
for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j)
{
if (board[0][j] == 'O')
dfs(board, row, col, 0, j);
if (board[row - 1][j] == 'O')
dfs(board, row, col, row - 1, j);
}
//寻找第一列和最后一列
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i)
{
if (board[i][0] == 'O')
dfs(board, row, col, i, 0);
if (board[i][col - 1] == 'O')
dfs(board, row, col, i, col - 1);
}
替换 恢复
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j)
{
if (board[i][j] == '*')
board[i][j] = 'O';
else if (board[i][j] == 'O')
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
};

200岛屿数量
渲染的做法,尝试以每个点作为渲染的起点,可以渲染的陆地都算做一个岛屿,渲染了多少次,即深度优先算法执行了多少次
添加链接描述
int nextPosition[4][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, 0 } };
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, int row, int col, vector<vector<int>>& book,
int x, int y)
{
//处理当前逻辑
book[x][y] = 1;
//遍历每一种可能,四个方向
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k)
{
int nX = x + nextPosition[k][0];
int nY = y + nextPosition[k][1];
//判断新位置是否越界
if (nX >= row || nX < 0
|| nY >= col || nY < 0)
continue;
//如果是陆地,并且之前也没有渲染(访问)过,则继续渲染
if (grid[nX][nY] == '1' && book[nX][nY] == 0)
{
dfs(grid, row, col, book, nX, nY);
}
}
}
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
if (grid.empty())
return 0;
int ret = 0;
int row = grid.size();
int col = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> book;
book.resize(row);
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i)
book[i].resize(col, 0);
//以每一个网格点为渲染起点开始
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j)
{
if (grid[i][j] == '1' && book[i][j] == 0)
{
++ret;
dfs(grid, row, col, book, i, j);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
};
广度优先
可以找到1条路径,但不能保证是最优;前面的点没有搜索完,后面的点(在队内)是不会搜索的;新增的点在队尾,在队头获取点,
Bfs()
{
1. 建立起始步骤,队列初始化
2. 遍历队列中的每一种可能,whlie(队列不为空)
{
通过队头元素带出下一步的所有可能,并且依次入队
{
判断当前情况是否达成目标:按照目标要求处理逻辑
}
继续遍历队列中的剩余情况
}
}
迷宫问题:

员工的重要性
int getImportance(vector<Employee*> employees, int id) {
int res = 0;
queue<int> q;
//初始化队列
q.push(id);
//把员工信息保存在map中,方便查询
unordered_map<int, Employee*> m;
for (auto e : employees)
m[e->id] = e;
//遍历队列
while (!q.empty()) {
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
res += m[t]->importance;
for (int num : m[t]->subordinates) {
q.push(num);
}
}
return res;
}
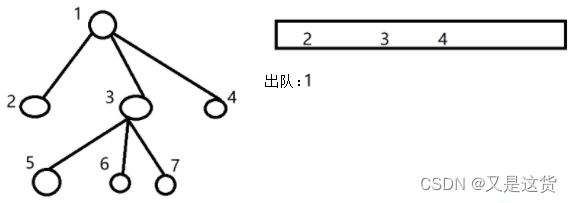

994. 腐烂的橘子

右下角的橘子被隔离,永远不会坏,返回-1
深度优先:最短时间没办法确定,走的路径不是最短的;广度优先:有最短路径,递进式,由近及远的腐烂;同1批橘子在同1分钟变坏,
添加链接描述
找到所有的腐烂橘子,入队,用第一批带出新一批腐烂的橘子每以匹橘子都会在一分钟之内腐烂, 所以此题可以转化为求BFS执行的大循环的次数
step的更新需要有一个标记,只有新的腐烂的橘子加入,step才能自加
最后BFS执行完之后,说明所有可以被腐烂的都完成了,再去遍历grid, 如何还有
值为1的,说明没有办法完全腐烂,返回 - 1, 如果没有,则返回step
int orangesRotting(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
//用pair存放位置
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
int row = grid.size();
int col = grid[0].size();
//已经腐烂的位置入队
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j)
{
if (grid[i][j] == 2)
q.push(make_pair(i, j));
}
}
//可以蔓延的方向
static int nextP[4][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, 0 } };
int step = 0;
while (!q.empty())
{
int n = q.size();
int flag = 0;
//用当前这一批已经腐烂的橘子带出下一批要腐烂的橘子
//故要遍历队列中的所有位置
while (n--)
{
auto Curpos = q.front();
q.pop();
//当前位置向四个方向蔓延
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
int nx = Curpos.first + nextP[i][0];
int ny = Curpos.second + nextP[i][1];
//如果位置越界或者是空格,或者已经是腐烂的位置,则跳过
if (nx >= row || nx < 0
|| ny >= col || ny < 0
|| grid[nx][ny] != 1)
continue;
//标记有新的被腐烂
flag = 1;
grid[nx][ny] = 2;
q.push(make_pair(nx, ny));
}
}
//如果有新的腐烂,才++
if (flag)
++step;
}
//判断是否还有无法腐烂的
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j)
{
if (grid[i][j] == 1)
return -1;
}
}
return step;
}
127. 单词接龙
127. 单词接龙
1beginWord带出转换一个字母之后所有可能的结果
2.每一步都要把队列中上一步添加的所有单词转换一遍,最短的转换肯定在这些单词当中, 所有这些词的转换只能算一次转换,因为都是上一步转换出来的,这里对于每个单词的每个位置都可以用26个字母进行转换,1个单词1次转换的可能有:单词的长度 * 26,可能改变第1个字符,可能改变第2个字符……
3.把转换成功的新词入队,进行下一步的转换
4.最后整个转换的长度就和BFS执行的次数相同
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
//hash表的查询效率最高
unordered_set<string> wordDict(wordList.begin(), wordList.end());
//标记单词是否已经访问过,访问过的不再访问
unordered_set<string> visited;
visited.insert(beginWord);
//初始化队列
queue<string> q;
q.push(beginWord);
int res = 1;
while (!q.empty()){
int nextSize = q.size();
//每一步都要把队列中上一步添加的所有单词转换一遍
//最短的转换肯定在这些单词当中, 所有这些词的转换只能算一次转换
//因为都是上一步转换出来的
while (nextSize--){
string curWord = q.front();
q.pop();
//尝试转换当前单词的每一个位置
for (int i = 0; i < curWord.size(); i++){
string newWord = curWord;
//每一个位置用26个字母分别替换
for (auto ch = 'a'; ch <= 'z'; ch++){
newWord[i] = ch;
//词典中没有此单词或者已经访问过(它的转换已经遍历过,无需再次遍历),则 跳过
if (!wordDict.count(newWord) || visited.count(newWord))
continue;
//转换成功,则在上一步转换的基础上+1
if (newWord == endWord)
return res + 1;
//还没有转换成功,则新的单词入队
visited.insert(newWord);做标记:新单词转换过
q.push(newWord);
}
}
}
res++;
}
//转换不成功,返回0
return 0;
}
752. 打开转盘锁
752. 打开转盘锁
深度优先不适合解此题,递归深度太大,会导致栈溢出,
int openLock(vector<string>& deadends, string target) {
// 哈希表的查找更快,拷贝到哈希表中
unordered_set<string> deadendsSet(deadends.begin(), deadends.end());
//如果"0000"在死亡字符串中,则永远到达不了
if (deadendsSet.find("0000") != deadendsSet.end())
return -1;
//初始化队列
queue<string> que;要搜索的字符串
que.push("0000");
//加标记,已经搜索过的字符串不需要再次搜索
unordered_set<string> book;
book.insert("0000");
int step = 0;
while (!que.empty()) {
int n = que.size();
//从上一步转换之后的字符串都需要进行验证和转换
//并且只算做一次转换,类似于层序遍历,转换的步数和层相同
//同一层的元素都是经过一步转换得到的
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string curStr = que.front();
que.pop();
if (curStr == target) return step;
//四位密码锁,每个位置每次都可以转一次
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
string newStr1 = curStr, newStr2 = curStr;
//当前位置可以向前或者向后拨一位
newStr1[j] = newStr1[j] == '9' ? '0' : newStr1[j] + 1;
newStr2[j] = newStr2[j] == '0' ? '9' : newStr2[j] - 1;
不在死亡数组中且没有访问过:可以使用的新密码
if (deadendsSet.find(newStr1) == deadendsSet.end()
&& book.find(newStr1) == book.end()) {
que.push(newStr1);
book.insert(newStr1);
}
if (deadendsSet.find(newStr2) == deadendsSet.end()
&& book.find(newStr2) == book.end()) {
que.push(newStr2);
book.insert(newStr2);
}
}
}
step++;
}
return -1;
}
























 1172
1172

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








