Q1:
公共自行车租借预测
自行车分享系统(bike sharing systems)较传统的自行车租借存在巨大的优势.它避免了注册、租借和归还等繁琐的过程,用户可以在线上完成所有相关操作.同时,自行车的行驶时长和路线等信息也可
以完整记录下来.
本题提供一份公共自行车租借数据集[36].请根据城市当天的天气、温度、湿度和风速等环境信息对自行车的租借数量进行预测.
Q2:
个人信用风险评估
在很多国家,政府机构会密切监控货款业务,银行需要明确解释申请者的贷款申请被拒绝或者批准的原因,这种可解释性对于贷款申请者也是很重要的,在贷款申请被银行拒绝时,申请者需要知道为什么自己的信用级别不符合银行的要求.
为什么自己的信用级别不符合银行的要求.
通过构建自动化的信用评分模型,以在线方式进行即时的信贷审批能够为银行节约很多人工成本.
数据集共有1000个贷款样本,每个样本包含20个相关特征和1个表示贷款是否违约的特征"default”.本章我们介绍的逻辑回归和决策树模型具有很好的可解释性.
请使用逻辑回归或者决策树算法建立个人信用风险评估模型.
Q3:
到了夏天,女士们热爱裙装.不同的款式和颜色搭配,可以让女士穿出不一样的风采,透出与众不同的魅力,本案例的数据集包含了裙装的款式,用料,颜色,大小,价格等方面的信息、销售人员可以根据这些信息,决定是否把某个具体型号的裙装推荐给客户,数据集一共有14个特征,501个样本.
本题要求依据裙装数据集,使用高斯混合模型对是否推荐裙装做判别.由于数据集特征均为名义型特征,需要对数据集作数据预处理,如特征编码等.
A1:
利用最小二乘法进行拟合,以此来做多元线性回归。通过得到线性回归的系数,来构建多元回归方程,从而将预测的数据代入自变量以后进行预测。
具体来说是:首先进行数据预处理,将离散型数据转化为one-hot编码,再进行OLS的拟合,将拟合的系数取出,构建方程,即可预测想要的数据。
这个是hour.csv的结果
==============================================================================
coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Intercept 3642.5000 433.334 8.406 0.000 2791.148 4493.852
temp 3228.9000 2454.526 1.315 0.189 -1593.395 8051.195
atemp 3623.0118 2770.730 1.308 0.192 -1820.514 9066.537
hum -2714.7015 468.416 -5.795 0.000 -3634.978 -1794.425
windspeed -3990.7544 865.630 -4.610 0.000 -5691.419 -2290.090
==============================================================================
Omnibus: 7.532 Durbin-Watson: 0.455
Prob(Omnibus): 0.023 Jarque-Bera (JB): 5.772
Skew: 0.153 Prob(JB): 0.0558
Kurtosis: 2.580 Cond. No. 81.7
这个是day.csv的结果
==============================================================================
coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Intercept 3642.5000 433.334 8.406 0.000 2791.148 4493.852
temp 3228.9000 2454.526 1.315 0.189 -1593.395 8051.195
atemp 3623.0118 2770.730 1.308 0.192 -1820.514 9066.537
hum -2714.7015 468.416 -5.795 0.000 -3634.978 -1794.425
windspeed -3990.7544 865.630 -4.610 0.000 -5691.419 -2290.090
==============================================================================
Omnibus: 7.532 Durbin-Watson: 0.455
Prob(Omnibus): 0.023 Jarque-Bera (JB): 5.772
Skew: 0.153 Prob(JB): 0.0558
Kurtosis: 2.580 Cond. No. 81.7
A2:对应Q2的算法
利用决策树C4.5的方法进行计算。通过选取最优特征来构建决策树,而最优特征的选取也取决于信息增益率,即信息增益除以当前根节点的信息熵。
由于数据中含有缺失值,以及连续型数值,所以无法使用ID3算法。而且也无法使用函数包进行计算,所以这里需要自己调用写好的C4.5针对性算法。
具体过程:将缺省值替换为我的C4.5可以检测到的值,并且对数据插入一列权值,使得我的算法能够正常运行,并且还需要自己手动添加特征属性,即每个特征的离散型和连续型情况。
最后将构建好的决策树剪枝,然后再打印出来。

因为纸张宽度有限,只能展示部分效果,具体结果请自行在python内检查。
A3:
利用高斯混合模型得到软分类,然后对软分类进行一个ROC检测
具体做法:对数据进行预处理(one-hot)编码后进一步处理完整数据(拼接方法)再将完整数据划分为训练集和测试集,对训练集样本进行高斯混合模型的计算,再对构建好的模型代入测试集判断正误。
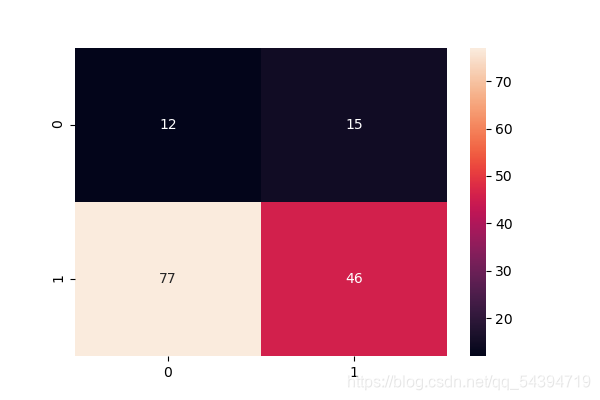
得到如下结果:
Accuracy: 0.3867
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.13 0.44 0.21 27
1 0.75 0.37 0.50 123
accuracy 0.39 150
macro avg 0.44 0.41 0.35 150
weighted avg 0.64 0.39 0.45 150
- 实验代码
D1:
基于小时的多元线性拟合
import pandas as pd
from statsmodels.formula.api import ols
import random
data_day = pd.read_csv('hour.csv')
data_day = data_day.drop(['instant'], axis=1)
random.seed(123) #设立随机数种子
a = random.sample(range(len(data_day)),round(len(data_day)*0.3))
data_day_test = []
for i in a:
data_day_test.append(data_day.iloc[i])
data_day_test = pd.DataFrame(data_day_test)
data_day_train = data_day.drop(a)
for i in [data_day_test,data_day_train]:
i.index = range(i.shape[0])
lm = ols('cnt~temp+atemp+hum+windspeed',data=data_day_train).fit()
print(lm.summary())
基于每日的多元线性拟合
import pandas as pd
from statsmodels.formula.api import ols
import random
data_day = pd.read_csv('day.csv')
data_day = data_day.drop(['instant'], axis=1)
random.seed(123) #设立随机数种子
a = random.sample(range(len(data_day)),round(len(data_day)*0.3))
data_day_test = []
for i in a:
data_day_test.append(data_day.iloc[i])
data_day_test = pd.DataFrame(data_day_test)
data_day_train = data_day.drop(a)
for i in [data_day_test,data_day_train]:
i.index = range(i.shape[0])
lm = ols('cnt~temp+atemp+hum+windspeed',data=data_day_train).fit()
print(lm.summary())
D2:
import C45
import treePlotter
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# 读取数据文件
data = pd.read_csv('credit.csv',).replace('unknown', 'N')
data = data.fillna(method= 'pad')
# 设定权重
one = np.ones((999,1))
labels = data.columns.values.tolist()
dataSet_test = data[999:].values.tolist()
data = data[0:999].values.tolist()
data = np.array(data)
data = data.reshape((-1, 21))
result = data[:, 20]
result = result.reshape(999,1)
data = data[:, :20]
x = np.c_[data, one]
x = np.c_[x, result]
x = x.tolist()
labelProperties = [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
classList = [1, 2]
# 构建决策树
trees = C45.createTree(x, labels, labelProperties)
# 利用验证集对决策树剪枝
C45.postPruningTree(trees, classList, x, dataSet_test, labels, labelProperties)
# 绘制决策树
treePlotter.createPlot(trees)
from math import log
import operator
import os
import re
from numpy import inf
import copy
# 计算信息熵
def calcShannonEnt(dataSet, labelIndex):
# type: (list) -> float
numEntries = 0 # 样本数(按权重计算)
labelCounts = {}
for featVec in dataSet: # 遍历每个样本
if featVec[labelIndex] != 'N':
weight = float(featVec[-2])
numEntries += weight
currentLabel = featVec[-1] # 当前样本的类别
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): # 生成类别字典
labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += weight # 数据集的倒数第二个值用来标记样本权重
shannonEnt = 0.0
for key in labelCounts: # 计算信息熵
prob = float(labelCounts[key]) / numEntries
shannonEnt = shannonEnt - prob * log(prob, 2)
return shannonEnt
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value, LorR='N'):
"""
type: (list, int, string or float, string) -> list
划分数据集
axis:按第几个特征划分
value:划分特征的值
LorR: N 离散属性; L 小于等于value值; R 大于value值
"""
retDataSet = []
featVec = []
if LorR == 'N': # 离散属性
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] == value:
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis + 1:])
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
elif LorR == 'L':
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] != 'N':
if float(featVec[axis]) < value:
retDataSet.append(featVec)
elif LorR == 'R':
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] != 'N':
if float(featVec[axis]) > value:
retDataSet.append(featVec)
return retDataSet
def splitDataSetWithNull(dataSet, axis, value, LorR='N'):
"""
type: (list, int, string or float, string) -> list
划分数据集
axis:按第几个特征划分
value:划分特征的值
LorR: N 离散属性; L 小于等于value值; R 大于value值
"""
retDataSet = []
nullDataSet = []
featVec = []
totalWeightV = calcTotalWeight(dataSet, axis, False) # 非空样本权重
totalWeightSub = 0.0
if LorR == 'N': # 离散属性
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] == value:
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis + 1:])
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
elif featVec[axis] == 'N':
reducedNullVec = featVec[:axis]
reducedNullVec.extend(featVec[axis + 1:])
nullDataSet.append(reducedNullVec)
elif LorR == 'L':
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] != 'N':
if float(featVec[axis]) < value:
retDataSet.append(featVec)
elif featVec[axis] == 'N':
nullDataSet.append(featVec)
elif LorR == 'R':
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] != 'N':
if float(featVec[axis]) > value:
retDataSet.append(featVec)
elif featVec[axis] == 'N':
nullDataSet.append(featVec)
totalWeightSub = calcTotalWeight(retDataSet, -1, True) # 计算此分支中非空样本的总权重
for nullVec in nullDataSet: # 把缺失值样本按权值比例划分到分支中
nullVec[-2] = float(nullVec[-2]) * totalWeightSub / totalWeightV
retDataSet.append(nullVec)
return retDataSet
def calcTotalWeight(dataSet, labelIndex, isContainNull):
"""
type: (list, int, bool) -> float
计算样本集对某个特征值的总样本树(按权重计算)
:param dataSet: 数据集
:param labelIndex: 特征值索引
:param isContainNull: 是否包含空值的样本
:return: 返回样本集的总权重值
"""
totalWeight = 0.0
for featVec in dataSet: # 遍历每个样本
weight = float(featVec[-2])
if isContainNull is False and featVec[labelIndex] != 'N':
totalWeight += weight # 非空样本树,按权重计算
if isContainNull is True:
totalWeight += weight # 总样本数,按权重计算
return totalWeight
def calcGain(dataSet, labelIndex, labelPropertyi):
"""
type: (list, int, int) -> float, int
计算信息增益,返回信息增益值和连续属性的划分点
dataSet: 数据集
labelIndex: 特征值索引
labelPropertyi: 特征值类型,0为离散,1为连续
"""
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet, labelIndex) # 计算根节点的信息熵
featList = [example[labelIndex] for example in dataSet] # 特征值列表
uniqueVals = set(featList) # 该特征包含的所有值
newEntropy = 0.0
totalWeight = 0.0
totalWeightV = 0.0
totalWeight = calcTotalWeight(dataSet, labelIndex, True) # 总样本权重
totalWeightV = calcTotalWeight(dataSet, labelIndex, False) # 非空样本权重
if labelPropertyi == 0: # 对离散的特征
for value in uniqueVals: # 对每个特征值,划分数据集, 计算各子集的信息熵
if value != 'N':
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, labelIndex, value)
totalWeightSub = 0.0
totalWeightSub = calcTotalWeight(subDataSet, labelIndex, True)
prob = totalWeightSub / totalWeightV
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet, labelIndex)
else: # 对连续的特征
uniqueValsList = list(uniqueVals)
if 'N' in uniqueValsList:
uniqueValsList.remove('N')
sortedUniqueVals = sorted(uniqueValsList) # 对特征值排序
listPartition = []
minEntropy = inf
if len(sortedUniqueVals) == 1: # 如果只有一个值,可以看作只有左子集,没有右子集
totalWeightLeft = calcTotalWeight(dataSet, labelIndex, True)
probLeft = totalWeightLeft / totalWeightV
minEntropy = probLeft * calcShannonEnt(dataSet, labelIndex)
else:
for j in range(len(sortedUniqueVals) - 1): # 计算划分点
partValue = (float(sortedUniqueVals[j]) + float(
sortedUniqueVals[j + 1])) / 2
# 对每个划分点,计算信息熵
dataSetLeft = splitDataSet(dataSet, labelIndex, partValue, 'L')
dataSetRight = splitDataSet(dataSet, labelIndex, partValue, 'R')
totalWeightLeft = 0.0
totalWeightLeft = calcTotalWeight(dataSetLeft, labelIndex, True)
totalWeightRight = 0.0
totalWeightRight = calcTotalWeight(dataSetRight, labelIndex, True)
probLeft = totalWeightLeft / totalWeightV
probRight = totalWeightRight / totalWeightV
Entropy = probLeft * calcShannonEnt(dataSetLeft, labelIndex) + \
probRight * calcShannonEnt(dataSetRight, labelIndex)
if Entropy < minEntropy: # 取最小的信息熵
minEntropy = Entropy
newEntropy = minEntropy
gain = totalWeightV / totalWeight * (baseEntropy - newEntropy)
return gain
def calcGainRatio(dataSet, labelIndex, labelPropertyi):
"""
type: (list, int, int) -> float, int
计算信息增益率,返回信息增益率和连续属性的划分点
dataSet: 数据集
labelIndex: 特征值索引
labelPropertyi: 特征值类型,0为离散,1为连续
"""
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet, labelIndex) # 计算根节点的信息熵
featList = [example[labelIndex] for example in dataSet] # 特征值列表
uniqueVals = set(featList) # 该特征包含的所有值
newEntropy = 0.0
bestPartValuei = None
IV = 0.0
totalWeight = 0.0
totalWeightV = 0.0
totalWeight = calcTotalWeight(dataSet, labelIndex, True) # 总样本权重
totalWeightV = calcTotalWeight(dataSet, labelIndex, False) # 非空样本权重
if labelPropertyi == 0: # 对离散的特征
for value in uniqueVals: # 对每个特征值,划分数据集, 计算各子集的信息熵
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, labelIndex, value)
totalWeightSub = 0.0
totalWeightSub = calcTotalWeight(subDataSet, labelIndex, True)
if value != 'N':
prob = totalWeightSub / totalWeightV
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet, labelIndex)
prob1 = totalWeightSub / totalWeight
IV -= prob1 * log(prob1, 2)
else: # 对连续的特征
uniqueValsList = list(uniqueVals)
if 'N' in uniqueValsList:
uniqueValsList.remove('N')
# 计算空值样本的总权重,用于计算IV
totalWeightN = 0.0
dataSetNull = splitDataSet(dataSet, labelIndex, 'N')
totalWeightN = calcTotalWeight(dataSetNull, labelIndex, True)
probNull = totalWeightN / totalWeight
if probNull > 0.0:
IV += -1 * probNull * log(probNull, 2)
sortedUniqueVals = sorted(uniqueValsList) # 对特征值排序
listPartition = []
minEntropy = inf
if len(sortedUniqueVals) == 1: # 如果只有一个值,可以看作只有左子集,没有右子集
totalWeightLeft = calcTotalWeight(dataSet, labelIndex, True)
probLeft = totalWeightLeft / totalWeightV
minEntropy = probLeft * calcShannonEnt(dataSet, labelIndex)
IV = -1 * probLeft * log(probLeft, 2)
else:
for j in range(len(sortedUniqueVals) - 1): # 计算划分点
partValue = (float(sortedUniqueVals[j]) + float(
sortedUniqueVals[j + 1])) / 2
# 对每个划分点,计算信息熵
dataSetLeft = splitDataSet(dataSet, labelIndex, partValue, 'L')
dataSetRight = splitDataSet(dataSet, labelIndex, partValue, 'R')
totalWeightLeft = 0.0
totalWeightLeft = calcTotalWeight(dataSetLeft, labelIndex, True)
totalWeightRight = 0.0
totalWeightRight = calcTotalWeight(dataSetRight, labelIndex, True)
probLeft = totalWeightLeft / totalWeightV
probRight = totalWeightRight / totalWeightV
Entropy = probLeft * calcShannonEnt(
dataSetLeft, labelIndex) + probRight * calcShannonEnt(dataSetRight, labelIndex)
if Entropy < minEntropy: # 取最小的信息熵
minEntropy = Entropy
bestPartValuei = partValue
probLeft1 = totalWeightLeft / totalWeight
probRight1 = totalWeightRight / totalWeight
IV += -1 * (probLeft1 * log(probLeft1, 2) + probRight1 * log(probRight1, 2))
newEntropy = minEntropy
gain = totalWeightV / totalWeight * (baseEntropy - newEntropy)
if IV == 0.0: # 如果属性只有一个值,IV为0,为避免除数为0,给个很小的值
IV = 0.0000000001
gainRatio = gain / IV
return gainRatio, bestPartValuei
# 选择最好的数据集划分方式
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet, labelProperty):
"""
type: (list, int) -> int, float
:param dataSet: 样本集
:param labelProperty: 特征值类型,1 连续, 0 离散
:return: 最佳划分属性的索引和连续属性的划分值
"""
numFeatures = len(labelProperty) # 特征数
bestInfoGainRatio = 0.0
bestFeature = -1
bestPartValue = None # 连续的特征值,最佳划分值
gainSum = 0.0
gainAvg = 0.0
for i in range(numFeatures): # 对每个特征循环
infoGain = calcGain(dataSet, i, labelProperty[i])
gainSum += infoGain
gainAvg = gainSum / numFeatures
for i in range(numFeatures): # 对每个特征循环
infoGainRatio, bestPartValuei = calcGainRatio(dataSet, i, labelProperty[i])
infoGain = calcGain(dataSet, i, labelProperty[i])
if infoGainRatio > bestInfoGainRatio and infoGain > gainAvg: # 取信息增益高于平均增益且信息增益率最大的特征
bestInfoGainRatio = infoGainRatio
bestFeature = i
bestPartValue = bestPartValuei
return bestFeature, bestPartValue
# 通过排序返回出现次数最多的类别
def majorityCnt(classList, weightList):
classCount = {}
for i in range(len(classList)):
if classList[i] not in classCount.keys():
classCount[classList[i]] = 0.0
classCount[classList[i]] += round(float(weightList[i]),1)
# python 2.7
# sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.iteritems(),
# key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(),
key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
if len(sortedClassCount) == 1:
return (sortedClassCount[0][0],sortedClassCount[0][1],0.0)
return (sortedClassCount[0][0], sortedClassCount[0][1], sortedClassCount[1][1])
# 创建树, 样本集 特征 特征属性(0 离散, 1 连续)
def createTree(dataSet, labels, labelProperty):
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet] # 类别向量
weightList = [example[-2] for example in dataSet] # 权重向量
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): # 如果只有一个类别,返回
totalWeiht = calcTotalWeight(dataSet,0,True)
return (classList[0], round(totalWeiht,1),0.0)
#totalWeight = calcTotalWeight(dataSet, 0, True)
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: # 如果所有特征都被遍历完了,返回出现次数最多的类别
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat, bestPartValue = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet,
labelProperty) # 最优分类特征的索引
if bestFeat == -1: # 如果无法选出最优分类特征,返回出现次数最多的类别
return majorityCnt(classList, weightList)
if labelProperty[bestFeat] == 0: # 对离散的特征
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat]
myTree = {bestFeatLabel: {}}
labelsNew = copy.copy(labels)
labelPropertyNew = copy.copy(labelProperty)
del (labelsNew[bestFeat]) # 已经选择的特征不再参与分类
del (labelPropertyNew[bestFeat])
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
uniqueValue = set(featValues) # 该特征包含的所有值
uniqueValue.discard('N')
for value in uniqueValue: # 对每个特征值,递归构建树
subLabels = labelsNew[:]
subLabelProperty = labelPropertyNew[:]
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(
splitDataSetWithNull(dataSet, bestFeat, value), subLabels,
subLabelProperty)
else: # 对连续的特征,不删除该特征,分别构建左子树和右子树
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat] + '<' + str(bestPartValue)
myTree = {bestFeatLabel: {}}
subLabels = labels[:]
subLabelProperty = labelProperty[:]
# 构建左子树
valueLeft = 'Y'
myTree[bestFeatLabel][valueLeft] = createTree(
splitDataSetWithNull(dataSet, bestFeat, bestPartValue, 'L'), subLabels,
subLabelProperty)
# 构建右子树
valueRight = 'N'
myTree[bestFeatLabel][valueRight] = createTree(
splitDataSetWithNull(dataSet, bestFeat, bestPartValue, 'R'), subLabels,
subLabelProperty)
return myTree
# 测试算法
def classify(inputTree, classList, featLabels, featLabelProperties, testVec):
firstStr = list(inputTree.keys())[0] # 根节点
firstLabel = firstStr
lessIndex = str(firstStr).find('<')
if lessIndex > -1: # 如果是连续型的特征
firstLabel = str(firstStr)[:lessIndex]
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr]
featIndex = featLabels.index(firstLabel) # 跟节点对应的特征
classLabel = {}
for classI in classList:
classLabel[classI] = 0.0
for key in secondDict.keys(): # 对每个分支循环
if featLabelProperties[featIndex] == 0: # 离散的特征
if testVec[featIndex] == key: # 测试样本进入某个分支
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict': # 该分支不是叶子节点,递归
classLabelSub = classify(secondDict[key], classList, featLabels,
featLabelProperties, testVec)
for classKey in classLabel.keys():
classLabel[classKey] += classLabelSub[classKey]
else: # 如果是叶子, 返回结果
for classKey in classLabel.keys():
if classKey == secondDict[key][0]:
classLabel[classKey] += secondDict[key][1]
else:
classLabel[classKey] += secondDict[key][2]
elif testVec[featIndex] == 'N': # 如果测试样本的属性值缺失,则进入每个分支
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict': # 该分支不是叶子节点,递归
classLabelSub = classify(secondDict[key], classList, featLabels,
featLabelProperties, testVec)
for classKey in classLabel.keys():
classLabel[classKey] += classLabelSub[key]
else: # 如果是叶子, 返回结果
for classKey in classLabel.keys():
if classKey == secondDict[key][0]:
classLabel[classKey] += secondDict[key][1]
else:
classLabel[classKey] += secondDict[key][2]
else:
partValue = float(str(firstStr)[lessIndex + 1:])
if testVec[featIndex] == 'N': # 如果测试样本的属性值缺失,则对每个分支的结果加和
# 进入左子树
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict': # 该分支不是叶子节点,递归
classLabelSub = classify(secondDict[key], classList, featLabels,
featLabelProperties, testVec)
for classKey in classLabel.keys():
classLabel[classKey] += classLabelSub[classKey]
else: # 如果是叶子, 返回结果
for classKey in classLabel.keys():
if classKey == secondDict[key][0]:
classLabel[classKey] += secondDict[key][1]
else:
classLabel[classKey] += secondDict[key][2]
elif float(testVec[featIndex]) <= partValue and key == 'Y': # 进入左子树
if type(secondDict['Y']).__name__ == 'dict': # 该分支不是叶子节点,递归
classLabelSub = classify(secondDict['Y'], classList, featLabels,
featLabelProperties, testVec)
for classKey in classLabel.keys():
classLabel[classKey] += classLabelSub[classKey]
else: # 如果是叶子, 返回结果
for classKey in classLabel.keys():
if classKey == secondDict[key][0]:
classLabel[classKey] += secondDict['Y'][1]
else:
classLabel[classKey] += secondDict['Y'][2]
elif float(testVec[featIndex]) > partValue and key == 'N':
if type(secondDict['N']).__name__ == 'dict': # 该分支不是叶子节点,递归
classLabelSub = classify(secondDict['N'], classList, featLabels,
featLabelProperties, testVec)
for classKey in classLabel.keys():
classLabel[classKey] += classLabelSub[classKey]
else: # 如果是叶子, 返回结果
for classKey in classLabel.keys():
if classKey == secondDict[key][0]:
classLabel[classKey] += secondDict['N'][1]
else:
classLabel[classKey] += secondDict['N'][2]
return classLabel
# 存储决策树
def storeTree(inputTree, filename):
import pickle
fw = open(filename, 'w')
pickle.dump(inputTree, fw)
fw.close()
# 读取决策树, 文件不存在返回None
def grabTree(filename):
import pickle
if os.path.isfile(filename):
fr = open(filename)
return pickle.load(fr)
else:
return None
# 测试决策树正确率
def testing(myTree, classList, data_test, labels, labelProperties):
error = 0.0
for i in range(len(data_test)):
classLabelSet = classify(myTree, classList, labels, labelProperties, data_test[i])
maxWeight = 0.0
classLabel = ''
for item in classLabelSet.items():
if item[1] > maxWeight:
classLabel = item[0]
if classLabel != data_test[i][-1]:
error += 1
return float(error)
# 测试投票节点正确率
def testingMajor(major, data_test):
error = 0.0
for i in range(len(data_test)):
if major[0] != data_test[i][-1]:
error += 1
# print 'major %d' %error
return float(error)
# 后剪枝
def postPruningTree(inputTree, classSet, dataSet, data_test, labels, labelProperties):
firstStr = list(inputTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr]
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
weightList = [example[-2] for example in dataSet]
featkey = copy.deepcopy(firstStr)
if '<' in firstStr: # 对连续的特征值,使用正则表达式获得特征标签和value
featkey = re.compile("(.+<)").search(firstStr).group()[:-1]
featvalue = float(re.compile("(<.+)").search(firstStr).group()[1:])
labelIndex = labels.index(featkey)
temp_labels = copy.deepcopy(labels)
temp_labelProperties = copy.deepcopy(labelProperties)
if labelProperties[labelIndex] == 0: # 离散特征
del (labels[labelIndex])
del (labelProperties[labelIndex])
for key in secondDict.keys(): # 对每个分支
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict': # 如果不是叶子节点
if temp_labelProperties[labelIndex] == 0: # 离散的
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, labelIndex, key)
subDataTest = splitDataSet(data_test, labelIndex, key)
else:
if key == 'Y':
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, labelIndex, featvalue,
'L')
subDataTest = splitDataSet(data_test, labelIndex,
featvalue, 'L')
else:
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, labelIndex, featvalue,
'R')
subDataTest = splitDataSet(data_test, labelIndex,
featvalue, 'R')
if len(subDataTest) > 0:
inputTree[firstStr][key] = postPruningTree(secondDict[key], classSet,
subDataSet, subDataTest,
copy.deepcopy(labels),
copy.deepcopy(
labelProperties))
if testing(inputTree, classSet, data_test, temp_labels,
temp_labelProperties) <= testingMajor(majorityCnt(classList, weightList),
data_test):
return inputTree
return majorityCnt(classList,weightList)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction', \
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction', \
va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args)
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else:
numLeafs += 1
return numLeafs
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
thisDepth = getTreeDepth(secondDict[key]) + 1
else:
thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth:
maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0] - cntrPt[0]) / 2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1] - cntrPt[1]) / 2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString)
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree)
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs)) / 2.0 / plotTree.totalw, plotTree.yOff)
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key], cntrPt, str(key))
else:
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalw
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops)
plotTree.totalw = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xOff = -0.5 / plotTree.totalw
plotTree.yOff = 1.0
plotTree(inTree, (0.5, 1.0), '')
plt.show()
D3:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn.metrics as metrics
from sklearn.mixture import GaussianMixture
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
data = pd.read_csv('dress-recommendation.csv')
# 确定字符型标签
dummpy_list = ['Style', 'Price', 'Size', 'Season', 'NeckLine', 'SleeveLength', 'waiseline','Material',
'FabricType','Decoration','Pattern Type']
# 将所有字符型数据进行one-hot编码处理
transfer_list = [pd.get_dummies(data[[feature]], prefix = feature+'_') for feature in dummpy_list]
transfer_list.append(data[['Rating','Recommendation']])
# 拼接数据
new_data = pd.concat(transfer_list, axis = 1)
def evaluate(pred, test_y):
# 输出分类的准确率
print("Accuracy: %.4f" % (metrics.accuracy_score(test_y, pred)))
# 输出衡量分类效果的各项指标
print(metrics.classification_report(test_y, pred))
# 更直观的,我们通过seaborn画出混淆矩阵
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
colorMetrics = metrics.confusion_matrix(test_y, pred)
# 坐标y代表test_y,即真实的类别,坐标x代表估计出的类别pred
sns.heatmap(colorMetrics, annot=True, fmt='d', xticklabels=[0, 1], yticklabels=[0, 1])
plt.show()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(new_data.iloc[:,:-1], new_data['Recommendation'], test_size = .3, random_state = 0)
cov_type = ['full', 'tied', 'diag', 'spherical']
model_list = [GaussianMixture(n_components = 2, covariance_type = cov_name, init_params='random', max_iter=20) for cov_name in cov_type]
# 标签去重
reco_label = np.unique(y_train)
#取纵轴上的平均值
mean_list = np.array([X_train[y_train == value].mean(axis = 0) for value in reco_label])
for gmm_model in model_list:
gmm_model.means_ = mean_list
gmm_model.fit(X_train)
y_pred = gmm_model.predict(X_test)
evaluate(y_test, y_pred)























 2382
2382

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








