
"y"字符串常量,组成是 {‘y’,‘\0’} "aaa"字符串常量 'aaa'报错 'a'字符常量 ’\7'转义字符

常量表达式(const experssion):是指(1)值不会改变 并且 (2)在编译过程就能得到计算结果的表达式。字面量属于常量表达式,用常量表达式初始化的const对象也是常量表达式。
一个对象(或表达式)是不是常量表达式由它的数据类型和初始值共同决定。
const int a =1; //常量表达式
cosnt int b=a+1; //常量表达式
int c=2; //初始值是字面值常量,当c数据类型是普通int
const int d=fun(); //fun()值要在运行时得到,d不是字面值常量

字符串的原理是 一个字符数组中所有的元素组成,只能说字符数组组成了一个字符串
char a[10]; //一维字符数组
char b[5][10]; //二维字符数组
①字符串连接函数:strcat()
char str1={"hello"};
char str2'
gets(str2);
strcat(str1,str2);
puts(str1);
string s1,s2,s;
s=s1+s2;
②字符串复制函数strcpy()
char str1={"hello"};
char str2={"world"};
strcpy(str1,str2);
puts(str1);
string s1,s2,s;
s=s1;
③字符串比较函数strcmp()
两个字符从第一个字符开始比较,若相同进行下一个字符的比较,直到得到结果
返回值:若str1 和 str2 相同,则返回 0;若str1 大于str2,则返回大于 0 的 值;若 str1 小于 str2,则返回小于 0 的值。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
char str1={"hello "};
char str2={“world”};
printf("%d",strcmp(str1, str2));
return 0;
}
string s1,s2,s;
si==s2; 返回值相等为0
s1>=s2;
s1>s2;
s[i] // 访问串下标为i的字符
④字符串测长函数strlen()
char类型字符串用strlen()
string 类型字符串用get.length()
#include<string>
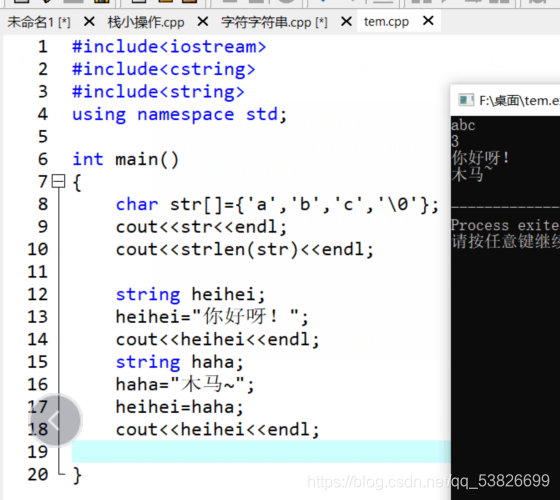
char str[]={'a','b','c','\0'} 或者 char *str={'a','b','c','\0'}
//strlen(str)=3 记得一定要加\0 否则结果错误
string str;
str="abcd";
cout<<getlength(str)<<endl;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
void fun1()
{
cout<<"直接用cin来操作字符"<<endl;
char ch;
cin>>ch;
cout<<ch<<endl;
}
void fun2()
{
cout<<"用cin.get来操作字符"<<endl;
char ch;
ch=cin.get();
cout<<ch<<endl;
}
void fun3()
{
cout<<"直接用cin来操作字符串"<<endl;
char ch[10];
cin>>ch;
cout<<ch<<endl;
}
void fun4()
{
cout<<"用cin.get来操作字符串"<<endl;
char ch[10];
cin.get(ch,20,'#');//第一个是字符串名 第二是控制数量 第三个是终止符(可以省略第三个,终止符可自定)
cout<<ch<<endl;
}
void fun5()
{
cout<<"用cin.getline来操作字符串"<<endl;
char ch[10];
cin.getline(ch,20,'#');//第一个是字符串名 第二是控制数量 第三个是终止符(可以省略第三个,终止符可自定)
cout<<ch<<endl;
}
int main()
{
fun1();
cin.ignore();//这个就是把缓冲区的字符清理掉防止影响下面的东西
fun2();
cin.ignore();
fun3();
cin.ignore();
fun4();
cin.ignore();
cin.get();//吃掉回车
fun5();
cin.ignore();
}

p==&(*p) p[1]=*(p+1) &p[1]=p+1 *p=p[0]

*p[2]=p[2][ ] &(*p[0])=p[0] p=&&p[0][0]=&p[0] **p=p[0][0]
.
带参构造函数必须要严格按照声明的类型

1.静态数据成员的定义形式:static 类型名 变量名。
2.静态数据成员不属于任何一个对象,它是属于类的,故它能被所有对象共享。
3.静态数据成员不能用参数初始化表初始化,它一般是在类外进行初始化的,一般形式为:数据类型名 类名::静态数据成员名=初值。
4.静态数据成员的引用:对象名.数据成员名,也可以通过类名类引用。


释放的是动态的内存空间(对象数组还有动态指针)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class student
{
private:
string name;
string num;
public:
student(string a="no",string b="no"):name(a),num(b){}
void say(){
cout<<"I am a student"<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
student d("xiaoming","101");
// new student a; 不能创建和释放
int n;
int *a;
a=(int *) malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
int *b;
b=new int(n); //自动创建构造函数的空间
int *c;
c=new int[n];
free(a);
delete b;
// delete c;
delete[] c;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class people
{
private:
string name;
string id;
public:
people(string a="haahha",string b="345"):name(a),id(b){}
virtual void say(){
cout<<"I am a person"<<endl;
}
//虚函数:“我变的不重要了55555555555555……”
};
class student: virtual public people //虚基类
{
private:
int score;
public:
student(string a="no",string b="haha",int c=0):people(a,b),score(c){}
void say()
{
cout<<"I am a student"<<endl;
}
};
class teacher: virtual public people
{
public:
teacher(string a="no",string b="haha"):people(a,b){}
void say()
{
cout<<"I am a teacher"<<endl;
}
};
class assistant:public teacher,public student
{
public:
assistant(string a="a",string b="b"):teacher(a,b),student(a,b){}
void say()
{
cout<<"I am a assistant"<<endl;
}
};
void fun(class people &a)
{
a.say();
a.people::say(); //虚函数:“我又变的重要了!!”
}
int main(void)
{
student a("张杰宁","101",150);
teacher b("李坤璘","222");
assistant c("胖达","666");
// a.people::say();
// a.student::say();
// b.people::say();
fun(a);
fun(b); //类型转化
fun(c);
}


动态:多态
运算符重载与函数模板都属于静态联编
联编:多个类继承派生联系在一起(虚函数、虚基类和抽象类)
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
const double PI=3.14;
class shape
{
public:
virtual double area()=0;
virtual void say()=0;
};
class circle:public shape
{
private:
int x;
int y;
double r;
public:
circle(int a=0,int b=0,double c=0):x(a),y(b),r(c){}
double area()
{
return PI*r*r;
}
void say(){cout<<"the fucking area is "<<area()<<endl;}
};
class rectangle:public shape
{
private:
int x;
int y;
public:
rectangle(int xx=0,int yy=0):x(xx),y(yy){}
double area()
{
return x*y;
}
void say(){cout<<"the fucking area is "<<area()<<endl;}
};
void fun(shape &a)
{
a.say();
a.shape::say();
}
void fun1(shape &a)
{
cout<<a.area()<<endl;
}
int main()
{
circle a(1,1,2);
rectangle b(2,3);
fun(a);
fun1(a);
fun(b);
fun1(b);
}
//char ch[2];
//strcpy(ch,"abc");
//char *sh[10];
//strcpy(sh[1],"bcd");



赋值:char *p2; p[2]="abc" strcpy(p[2],"abc"); //地址
初始化: *p[ ]={"abc"}


内存决定



#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Clock
{
private:
int hour=0;
int minute=0;
int second=0;
public:
void set(int hour,int minute,int second)
{
Clock::hour=hour;
Clock::minute=minute;
second=second;
}
void Set(int hour,int minute,int second)
{
this->hour=hour;
this->minute=minute;
this->second=second;
}
void show()
{
cout<<hour<<':'<<minute<<':'<<second<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Clock a;
a.set(1,1,1);
a.show();
a.Set(2,2,2);
a.show();
}


#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class student
{
private:
string name;
int score;
static double sum; //C艹禁止在类内给静态成员赋初值
static double average;
static int num;
public:
void set(string name,double score)
{
this->name=name;
this->score=score;
num++;
}
void Sum(){sum+=score;}
static double get_ave(){return sum/num;} //其使用的数据成员必须都是静态
};
//student::num=0; //Error:私有数据成员
int student::num=0;
double student::sum=0; //必须赋初值,且重新定义可以骗过编译器
int main()
{
student *s;
s=new student[5];
string name;
double score;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
cin>>name>>score;
s[i].set(name,score);
s[i].Sum();
}
cout<<"平均分为:"<<student::get_ave()<<endl; //调用静态成员函数方式
delete[] s;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<fstream> //文件流
#include<sstream> //string流
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
fstream fp;
fp.open("aaa.txt",ios::in); //可读
fp.open("aaa.txt",ios::out); //可写
fstream fp("abc.txt",ios::in);
ifstream fp; //可读
fp.open("aaa.txt");
ifstream fp("abc.txt");
ofstream fp; //可写
fp.open("aaa.txt");
ofstream fp("abc.txt");
//逐个读取字符并输出
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++)
{
char a; //自动跳过空格
fp>>a;
cout<<a<<endl;
}
//读取全部字符串并输出
char b[20];
fp>>b;
fp.getline(b,300); //读到299个字符
cout<<b<<endl;
while(fp.getline(b,100))
{
cout<<b<<endl;
}
//读取一行字符串并输出
string c;
getline(fp,c,'#'); //一行的内容或者到终止符
cout<<c;
while(getline(fp,c))
{
cout<<c<<endl;
}
//读取整型数据并输出
int d;
while(fp>>d)
{
cout<<d<<endl;
}
//
string e;
int sum=0,a;
while(getline(fp,e))
{
sum=0;
for(stringstream jb(c);jb>>a;)
{
sum=sum+a;
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
string f;
char g[10][50];
int i=0;
getline(fp,f);
for(stringstream ab(f);ab>>g[i];)
{
// i=a.length();
// for(;i>=0;i--)
// {
// cout<<a[i];
// }
i++;
}
for(i=i-1;i>=0;i--)
{
cout<<g[i]<<" ";
}
}






 本文详细介绍了C++中的字符串基础知识,包括字符串连接、复制、比较和长度测量函数的使用。同时,讲解了常量表达式的概念及其应用,以及字符数组的一维和二维表示。此外,还探讨了动态内存管理和多态性在C++中的实现,包括动态内存分配、析构和虚函数。最后,展示了文件输入输出操作,包括读取字符、字符串和整型数据的方法。
本文详细介绍了C++中的字符串基础知识,包括字符串连接、复制、比较和长度测量函数的使用。同时,讲解了常量表达式的概念及其应用,以及字符数组的一维和二维表示。此外,还探讨了动态内存管理和多态性在C++中的实现,包括动态内存分配、析构和虚函数。最后,展示了文件输入输出操作,包括读取字符、字符串和整型数据的方法。
















 4541
4541

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








