目录
一、概念&&特性
1、有序表
2、多层级链表
3、每个节点层级具有随机性
4、时间复杂度为O(logN)
二、数据结构图
如下,是一个四层级的跳表结构。

如果我们想找到值 17 这个节点,搜寻路径为:
1、从左上角 即 head 的最高有效层级开始往右往下查找(查找路径就像二维空间下的 ”下楼梯“ 一样)
2、逐层级往下查找
层级4:head -> 6 -> NULL,跳到节点6下一个层级
层级3:6 -> 25,25>17 了,继续跳到节点6下一个层级
层级2:6 -> 9 -> 17。找到节点 17,不需要再继续往下跳了。
三、复杂度 O(logN)
从上图可以看到,每个节点的 层级不是固定,是随机的,这是构造复杂度O(logN) 的一个算法实现。
1、普通链表的复杂度为 O(n),设计跳表就是为了将复杂度降低到 O(logN)
2、有序数组利用二分法查找,复杂度为 O(logN)。有序链表的因为结构本质原因,即使是有序链表,但不能根据下标索引直接跳跃定位节点,其复杂度还是 O(n)
3、结合有序数组二分法查找思想,构建多层级跳表思路如下:
①、在起点、中间、终点使用指针链接起来
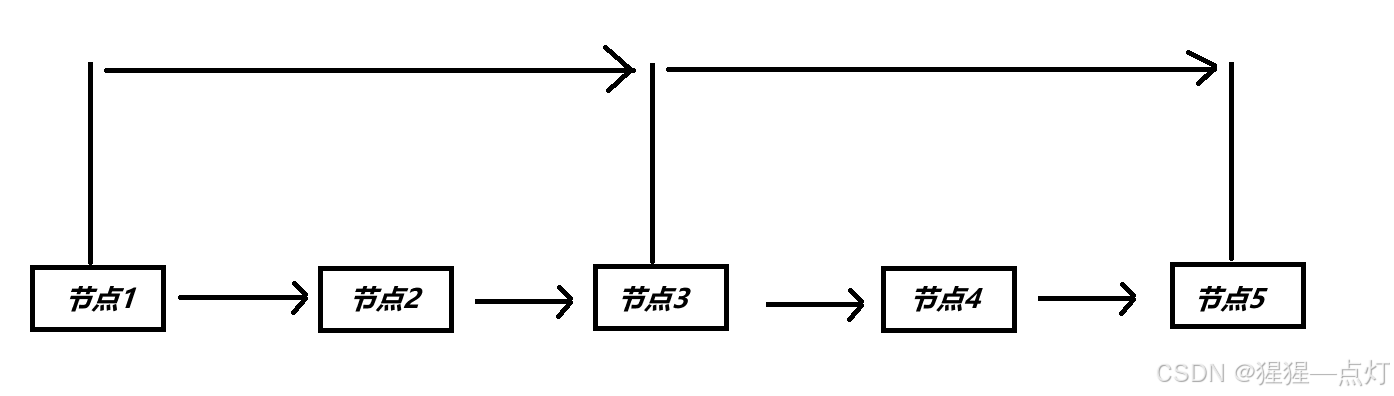
②、经过步骤1之后,被分为左、右两大块结构体
a、处理左结构体,按照步骤1一样的操作

b、处理右结构体,按照步骤1一样的操作

③、这样就能通过二分法查找了。但存在一个问题,当链表新添加一个节点时,已经构建的层级指针结构被破坏不适用,需要重新生成新的层级指针。
4、这当然是不能被接受的。于是,我们转变了设计方式,把层级设定成每个节点都是随机的,从层级1开始生成,可能生成最终层级为 n。
生成层级过程:
层级1生成,
层级2开始生成:生成概率为 1/2。(如果没生成,流程不再往下走)
层级3开始生成:生成概率为 1/2。(如果没生成,流程不再往下走)
...
层级n开始生成:生成概率为 1/2。
函数实现:
// 随机生成节点的层数
int randomLevel()
{
int level = 1;
while (rand() % 2 && level < MAX_LEVEL) {
level++;
}
return level;
}四、跳表代码实现
1、结构体设计
#define MAX_LEVEL 16 // 最大层数
// 跳表节点
typedef struct SkipListNode {
int value; // 节点值
struct SkipListNode* next[MAX_LEVEL]; // 每层的指针
} SkipListNode;
// 跳表结构
typedef struct SkipList {
SkipListNode* head; // 头节点
int level; // 当前跳表的最大层数
} SkipList;2、接口设计
// 创建一个新的跳表节点
SkipListNode* createNode(int value, int level);
// 初始化跳表
SkipList* initSkipList();
// 随机生成节点的层数
int randomLevel();
// 插入一个值到跳表中
void insert(SkipList* list, int value);
// 查找一个值在跳表中是否存在
int search(SkipList* list, int value);
// 删除一个值从跳表中
void delete(SkipList* list, int value);
// 打印跳表
void printSkipList(SkipList* list);3、接口实现
// 创建一个新的跳表节点
SkipListNode* createNode(int value, int level)
{
int i = 0;
SkipListNode* newNode = (SkipListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SkipListNode));
newNode->value = value;
for (i = 0; i < level; i++) {
newNode->next[i] = NULL;
}
return newNode;
}
// 初始化跳表
SkipList* initSkipList()
{
SkipList* list = (SkipList*)malloc(sizeof(SkipList));
list->head = createNode(-1, MAX_LEVEL); // 创建头节点,值为-1
list->level = 0;
return list;
}
// 随机生成节点的层数
int randomLevel()
{
int level = 1;
while (rand() % 2 && level < MAX_LEVEL) {
level++;
}
return level;
}
// 插入一个值到跳表中
void insert(SkipList* list, int value)
{
int i = 0;
SkipListNode* update[MAX_LEVEL]; // 用于记录每层的前驱节点
SkipListNode* current = list->head;
// 找到每层的插入位置
for (i = list->level - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
while (current->next[i] != NULL && current->next[i]->value < value) {
current = current->next[i];
}
update[i] = current;
}
// 找到插入位置
current = current->next[0];
// 如果值已存在,直接返回
if (current != NULL && current->value == value) {
printf("Value %d already exists in the skip list.\n", value);
return;
}
// 创建新节点
int newLevel = randomLevel();
if (newLevel > list->level) {
for (i = list->level; i < newLevel; i++) {
update[i] = list->head;
}
list->level = newLevel;
}
SkipListNode* newNode = createNode(value, newLevel);
// 更新指针
for (i = 0; i < newLevel; i++) {
newNode->next[i] = update[i]->next[i];
update[i]->next[i] = newNode;
}
printf("Value %d inserted successfully.\n", value);
}
// 查找一个值在跳表中是否存在
int search(SkipList* list, int value) {
int i = 0;
SkipListNode* current = list->head;
for (i = list->level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (current->next[i] != NULL && current->next[i]->value < value) {
current = current->next[i];
}
}
current = current->next[0];
if (current != NULL && current->value == value) {
printf("Value %d \033[32mfound\033[0m in the skip list.\n", value);
return 1;
} else {
printf("Value %d \033[31mnot found\033[0m in the skip list.\n", value);
return 0;
}
}
// 删除一个值从跳表中
void delete(SkipList* list, int value) {
int i = 0;
SkipListNode* update[MAX_LEVEL];
SkipListNode* current = list->head;
// 找到每层的前驱节点
for (i = list->level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (current->next[i] != NULL && current->next[i]->value < value) {
current = current->next[i];
}
update[i] = current;
}
current = current->next[0];
// 如果值不存在,直接返回
if (current == NULL || current->value != value) {
printf("Value %d not found in the skip list.\n", value);
return;
}
// 更新指针
for (i = 0; i < list->level; i++) {
if (update[i]->next[i] != current) {
break;
}
update[i]->next[i] = current->next[i];
}
// 释放节点
free(current);
// 更新最大层数
while (list->level > 1 && list->head->next[list->level - 1] == NULL) {
list->level--;
}
printf("Value %d deleted successfully.\n", value);
}
// 打印跳表
void printSkipList(SkipList* list) {
int i = 0;
printf("Skip List:\n");
// for (i = 0; i < list->level; i++) {
for (i = list->level; i >= 0; i--) {
SkipListNode* current = list->head->next[i];
printf("Level %d: ", i);
while (current != NULL) {
printf("%d ", current->value);
current = current->next[i];
}
printf("\n");
}
}4、接口测试
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int main() {
srand(time(NULL)); // 初始化随机数种子
SkipList* list = initSkipList();
insert(list, 3);
insert(list, 6);
insert(list, 7);
insert(list, 9);
insert(list, 12);
insert(list, 19);
insert(list, 17);
insert(list, 26);
insert(list, 21);
insert(list, 25);
printSkipList(list);
search(list, 19);
search(list, 18);
delete(list, 19);
delete(list, 18);
printSkipList(list);
return 0;
}测试结果:

























 657
657

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








