一、基本概念
文件夹(folder)
目录(director)
文件路径(path)
绝对路径(absolute path)
快捷方式(shortcut)
软连接(soft link)
二、文件划分
我们通常将文件划分为 文本文件 和 二进制文件。
三、java中如何操作文件
主要是通过File这个类来进行操作。其具体属性和方法如下所示:
| 修饰符及类型 | 属性 | 说明 |
| static String | pathSeparator | 依赖于系统的路径分隔符,String类型的表示 |
| static char | pathSeparator | 依赖于系统的路径分隔符,char类型的表示 |
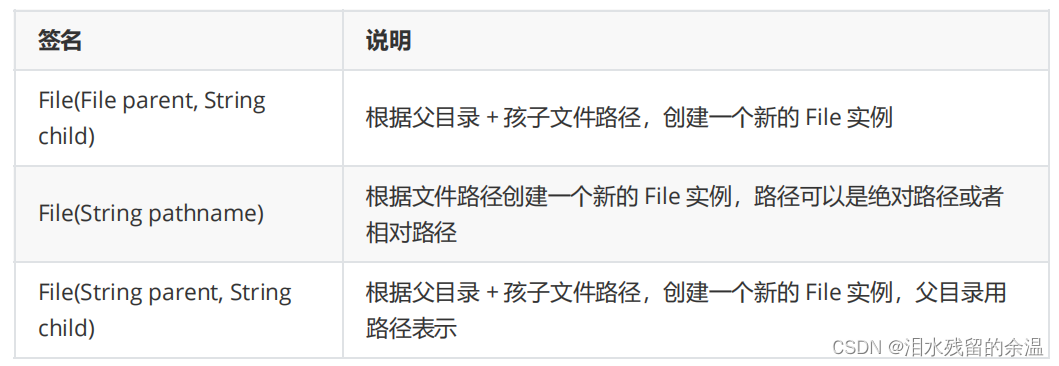

四、示例
//第一种read
public class demo1 {
//1.一次read一个字符
// public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// //创建reader对象的过程,其实就是在打开文件
// Reader reader = new FileReader("test.txt");
// while (true){
// //返回读到的字符的编码
// int c = reader.read();
// if (c == -1){
// break;
// }
// char ch = (char) c;
// System.out.print(ch);
// }
//
// }
// public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// Reader reader = new FileReader("test.txt");
// try {
// while (true) { //如果文件内容特别长,超出了数组范围,此处就会循环读,保证读完
// char[] cbuf = new char[1024]; //填不满也没关系
// //返回的数字表示读到字符的个数,如果为-1则表示读取完毕
// int n = reader.read(cbuf);
// if (n == -1) {
// break;
// }
// System.out.println("n = " + n);
// for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// System.out.println(cbuf[i]);
// }
// }
// }finally {
// //用finally
// reader.close(); //如果这么写,还是有风险,上面如果有个地方发出异常,close就执行不到了
// }
// }
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//try with resources,在try()中定义的变量,会在代码块结束的时候,自动调用其中的close方法,无论正常结束还是抛出异常
//要求写入对象,必须实现Closeable接口才行。流对象都可以这么写
try (Reader reader = new FileReader("test.txt")){
while (true) { //如果文件内容特别长,超出了数组范围,此处就会循环读,保证读完
char[] cbuf = new char[1024]; //填不满也没关系
//返回的数字表示读到字符的个数,如果为-1则表示读取完毕
int n = reader.read(cbuf);
if (n == -1) {
break;
}
System.out.println("n = " + n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println(cbuf[i]);
}
}
}
}
}
public class demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Reader reader = new FileReader("test.txt");
char[] cbuf = new char[10];
int read = reader.read(cbuf);
}
}
public class demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (Writer writer = new FileWriter("test.txt",true)){
writer.write("你好");
}
}
}
//inputStream
public class demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args){
try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("test.txt")){
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int n = inputStream.read(buffer);
System.out.println("n = " + n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print((char)buffer[i]);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//outputStream
public class demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("test.txt",true)){
String s = "你好世界";
outputStream.write(s.getBytes());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
//字节流转化为字符流,使用scanner转换
public class demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("test.txt")){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(inputStream);
//使用scanner读取后续数据
String next = scanner.next();
System.out.println(next);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
//把字节流转化成字符流
public class demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("test.txt")){
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(outputStream);
//写入内容
writer.println("hello");
writer.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
//示例1
//扫描指定目录,并找到名称中包含指定字符的所有普通文件(不包含目录),并且后续询问用户是否要
//删除该文件
public class demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.先让用户输入一个要扫描的目录
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要扫描的路径:");
String path = sc.next();
//检查路径是否有问题
File rootPath = new File(path);
if (!rootPath.isDirectory()){
System.out.println("您输入的扫描目录有误!");
return ;
}
//2.再让用户输入一个查询关键词
Scanner key = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要查询的关键词:");
String word = sc.next();
//3.可以进行递归的扫描了
scanDir(rootPath,word);
}
private static void scanDir(File rootPath, String word) {
//1.先列出rootPath中所有的文件和目录
File[] files = rootPath.listFiles();
//空目录,直接返回
if (files == null){
return;
}
//2.遍历这里的每个元素,针对不同类型进行不同处理
for (File file : files) {
//加个日志,方便查看当前递归的执行过程
System.out.println("当前扫描的文件" + file.getAbsoluteFile());
if (file.isFile()){
//如果是文件
//检查文件是否要删除,并执行删除动作
checkDelete(file,word);
}else{
//否则,是目录
//需要递归的再判定子目录里包含的内容
scanDir(file,word);
}
}
}
private static void checkDelete(File file, String word) {
if (!file.getName().contains(word)){
//不包含,直接结束
return;
}
//需要删除
System.out.println("当前文件为:" + file.getAbsoluteFile() + ",请确认是否需要删除(Y/N)");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String choice = scanner.next();
if (choice.equals("Y") || choice.equals("y")){
file.delete();
System.out.println("删除完毕!");
} else {
//如果输入其他值,都会取消删除
System.out.println("取消删除!");
}
}
}




 本文介绍了Java中文件和目录的基本概念,如文本文件与二进制文件的区别,以及如何通过File类进行文件操作,包括使用FileReader、FileWriter、InputStream、OutputStream等进行读写,以及递归扫描目录和删除文件的示例。
本文介绍了Java中文件和目录的基本概念,如文本文件与二进制文件的区别,以及如何通过File类进行文件操作,包括使用FileReader、FileWriter、InputStream、OutputStream等进行读写,以及递归扫描目录和删除文件的示例。
















 977
977

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








