本文主要包含以下几个方面:
1、递归算法的学习心得;
2、常见的递归算法使用场景
3、几个常见的递归算法代码(逆置链表,斐波拉契数列,螺旋矩阵);
开门见山:
在很长一段时间中我都没弄懂递归到底是如何去工作的,最近几天我一直在学习递归,对其有了一些领悟,希望对您有所帮助。我觉得学习递归以下两个观念是比较重要的:
1、如果你要求解的目标是f(n),那么你可以默认f(n - 1)已经被求解出来了,可以直接使用;
2、多练习几道递归解法的题目,看一下别人是如何去递归的,如何使用return以及在何处使用return的;
一般来说,能够用递归解决的问题应该满足以下3个条件:
(1)需要解决的问题可以转化为一个或多个子问题来求解,而这些子问题的求解方法与原问题完全相同,只是在数量规模上不同。
(2)递归调用的次数必须是有限的。
(3)必须有结束递归的条件来终止递归。
这3个条件想必你也是了解的,不做赘述。
在什么时候使用递归呢?
一般来说有以下三个情况经常用到递归:
1、该问题的定义是递归的:
例如:
求 n! ;
求斐波拉契数列;
2、该问题的数据结构是递归的:
例如:
单链表;
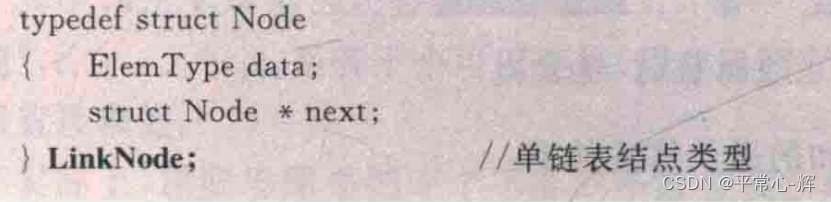
二叉树;
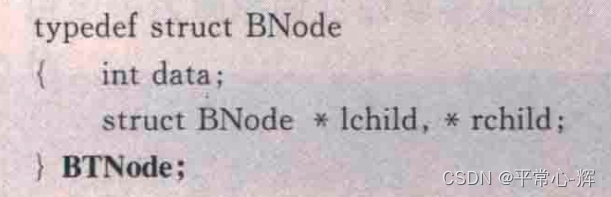
3、问题的求解方法是递归的:
例如:
汉诺塔问题:
赋上几个递归例子的代码:
1、斐波拉契数列:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
//斐波拉契数列
int fib(int n){
if(n == 1 || n == 2){
return 1;
}
return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
int main(){
int n;
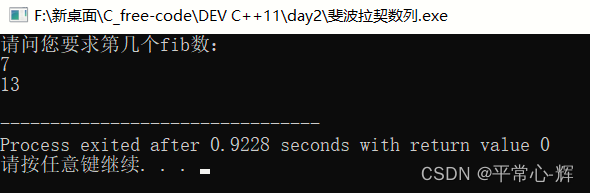
cout <<"请问您要求第几个fib数:"<<endl;
cin >>n;
int result = fib(n);
cout <<result<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行截图:
2、递归法-逆置单链表:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
//Definition for singly-linked list.
struct Node
{
int data;
Node* next;
};
//尾插法创建单链表
Node * CreateNode(int n)
{
Node *head = NULL, *pnew = NULL, *ptail = NULL; //创建表头、表尾和新插入结点并初始化
int num, i=1;
while(i <= n)
{
pnew = new Node;
cout << "输入第" << i << "个结点:" << endl;
cin>>num;
pnew->data = num;
pnew->next = NULL;
if(head == NULL)
head = pnew;
else
{
ptail->next = pnew;
}
ptail = pnew;
i++;
}
pnew = NULL;
delete pnew;
return head;
}
//打印单链表
void PrintNode(Node *head, int n)
{
Node *p;
p = head;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
//递归-反转单链表
Node* reverse(Node* head){
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL){
return head;
}
Node *p = reverse(head->next);
//关键步骤:
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return p;
}
int main()
{
int n; //结点个数
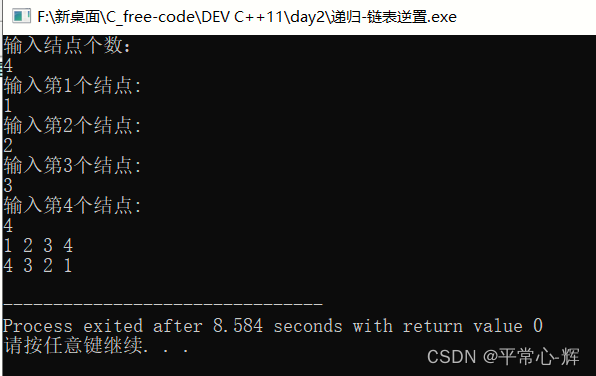
cout << "输入结点个数:" << endl;
cin>>n;
Node *head;
//创建单链表
head = CreateNode(n);
PrintNode(head,n);
//反转
head = reverse(head);
PrintNode(head,n);
return 0;
}
运行截图:
3、螺旋矩阵:
//[问题描述]创建n阶螺旋矩阵并输出,输入描述:输入包含多个测试用例,每个测试用例为一行,
//包含一个正整数n(l≤nK50),以输入0表示结束。输出描述:每个测试用例输出n行,每行包括n个整数﹐整数之间用一个空格分隔。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int num = 1;
void luox(int n,vector<vector<int>>& a,int left,
int right,int top,int bottom){
if(left <= right && top <= bottom){
for(int i = left ; i <= right;i++){
a[top][i] = num;
num++;
}
for(int i = top + 1 ; i <= bottom;i++){
a[i][right] = num;
num++;
}
for(int i = right - 1 ; i >= left ;i--){
a[bottom][i] = num;
num++;
}
for(int i = bottom - 1 ; i > top;i--){
a[i][left] = num;
num++;
}
}
if(num > n*n){
return;
}
luox(n,a,left+1,right-1,top+1,bottom-1);
}
//打印矩阵
void prt(vector<vector<int>>& a){
int len = a.size();
for(int i = 0 ; i < len ;i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < len ;j++){
cout<<setw(5)<<a[i][j] <<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
int main(){
int n ;
cout <<"请输入一个正整数n(1<= n <= 50):"<<endl;
cin>>n;
vector<vector<int>> a(n, vector<int>(n));
int left = 0, right = n - 1, top = 0, bottom = n - 1;
luox(n,a,left,right,top,bottom);
cout<<"结果为:" <<endl;
prt(a);
return 0;
}
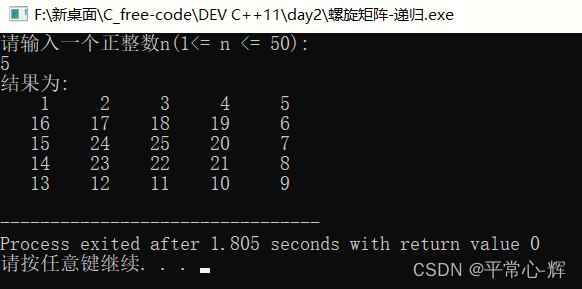
运行截图:
以上便是本文的全部,希望对您有所帮助。如果本文有不正确之处,希望您能不吝指教,共同进步。





 本文深入探讨了递归算法的基本概念、使用场景及常见问题,包括斐波那契数列、链表逆置及螺旋矩阵生成等实例代码。
本文深入探讨了递归算法的基本概念、使用场景及常见问题,包括斐波那契数列、链表逆置及螺旋矩阵生成等实例代码。
















 2924
2924

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








