Java数据结构基础–单链表
单链表定义:
(1)单链表是一种链式存取的数据结构,用一组地址任意的存储单元存放线性表中的数据元素。
(1)链表中的数据是以结点来表示的,每个结点的构成:
元素(数据元素的映象) + 指针(指示后继元素存储位置),
(3)元素就是存储数据的存储单元,指针就是连接每个结点的地址数据。

结点类实现:
public class Node {
Object data;//元素
private Node next;//指针
}
- 定义结点类 Node
- Object data:存放元素数据。
- Node next :存放后续结点(指针),无后续结点时为空。
带头结点链表的实现(完整代码):
package linknode;
public class LinkNode {
public class Node {
Object data;//存放数据
private Node next;//下一个节点(指针)
public Node(Object data, Node next) {//双参数构造函数
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(Object data) {//单参数构造函数
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
private Node first = new Node(null,null);//定义头节点
public int Length() {//获取单链表长度(不包含头节点)
Node p = first.next;
int count = 0;
while (p != null) {
p = p.next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
public boolean Search(Object data) {// 判断是否存在某元素
Node current = first.next;
while (current.data.equals(null)) {
if (current.data.equals(data)) {
return true;
} else {
current = current.next;
}
}
return false;
}
public Node Locate(int i) {// 下标查找对应节点
if (i < 0) {
System.out.println("数值越界");
return null;
}
Node current = first;
int k = 0;
while (current != null && k < i) {
current = current.next;
k++;
}
return current;
}
public Object getData(int i) {// 索引获取对应值
if (i <= 0) {
System.out.println("数值越界");
return null;
}
Node current = Locate(i);
if (current == null) {
System.out.println("数值越界");
return null;
}
return current.data;
}
public boolean setData(int i, Object x) {// 修改值
if (i <= 0) {
System.out.println("数值越界");
return false;
}
Node current = Locate(i);
if (current == null) {
System.out.println("数值越界");
return false;
} else
current.data = x;
return true;
}
public boolean Insert(int i, Object x) {//在第i个节点后插入新节点
Node current = Locate(i);
if (current == null) {
return false;
}
Node newNode = new Node(x);
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
return true;
}
public boolean Remove(int i) {//删除某元素
Node current = Locate(i-1);
if(current == null||current.next == null) {
System.out.println("数值越界");
return false;
}
Node del = current.next;
current.next = del.next;
return true;
}
public void addFront(Object x) {//前插法建立单链表
Node newNode = new Node(x);
newNode.next = first.next;
first.next = newNode;
}
public void addtRear(Object x) {
Node newNode = new Node(x);
Node last = first;
while(last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
last.next = newNode;
}
@Override
public String toString() {//重载输出函数
Node current = first.next;
String result = "";
while(current != null) {
result += current.data+"-->";
current = current.next;
}
result +="null";
return result;
}
}
函数解析:
1. 单链表类:
public class LinkNode {
public class Node {
Object data;//存放数据
private Node next;//下一个节点(指针)
}
private Node first = new Node(null,null);//定义头节点
}
- 单链表作为一个整体,包含了0个或者多个节点。而带头结点的单链表至少包含一个节点(头节点==》Node first)。
- LinkNode(单链表类)定义了Node类,用于创建节点。
- 初始单链表:

单链表长度Length():
public int Length() {//获取单链表长度(不包含头节点)
Node p = first.next;
int count = 0;
while (p != null) {//当前节点下一个不为空;
p = p.next;//当前节点后移
count++;//数量加一;
}
return count;//返回时当前节点指向空
}

判断是否存在某元素Search(Object data):
public boolean Search(Object data) {
Node current = first.next;//从头节点的下一个节点开始寻找(头节点不存储数据)
while (current.data.equals(null)) {//当前节点数据部分为null,即已经指向最后一个节点的后续节点,遍历结束
if (current.data.equals(data)) {
return true;//当前节点数据与寻找数据相等,寻找成功
} else {
current = current.next;//当前节点后移
}
}
return false;//
}
与判断单链表长度类似,先定义一个节点指向第一个存储数据的节点,之后不断将节点后移,直到解决问题则退出。
下标查找对应节点Locate(int i) :
public Node Locate(int i) {
if (i < 0) {
System.out.println("数值越界");
return null;
}
Node current = first;//指向头节点
int k = 0;//存储下标
while (current != null && k < i) {
current = current.next;//节点后移
k++;//下标记录加一
}
return current;
}
与上面两个函数略有不同,此处定义一个节点指向头节点,而非第一个存储数据节点。也是通过节点后移解决问题。
索引获取对应值getData(int i)
public Object getData(int i) {//i--索引下标
if (i <= 0) {
System.out.println("数值越界");
return null;
}
Node current = Locate(i);//下标查找对应节点
if (current == null) {
System.out.println("数值越界");
return null;
}
return current.data;
}
直接调用函数Locate(i)获取节点,在获取该节点数据部分
修改值setData(int i, Object x)
public boolean setData(int i, Object x) {//i--下标,x--修改后的值
if (i <= 0) {
System.out.println("数值越界");
return false;
}
Node current = Locate(i);//下标查找对应节点
if (current == null) {//判断该节点数据是否存在
System.out.println("数值越界");
return false;
} else
current.data = x;//获取并赋值
return true;
}
利用Locate()函数获取对应节点,获取该节点数据并重新赋值。
在第i个节点后插入新节点Insert(int i, Object x):
public boolean Insert(int i, Object x) {//i--插入位置,x--插入数据
Node current = Locate(i);//获取插入操作中被移动节点
if (current == null) {
return false;
}
Node newNode = new Node(x);//定义插入节点
newNode.next = current.next;//插入节点的后续结点指向被移动节点的后续结点
current.next = newNode;//被移动的后续结点指向插入节点
return true;
}
 首先改变插入节点的后续结点指向。如果先改变current的后续结点,则会丢失插入节点应该指向的节点的信息。
首先改变插入节点的后续结点指向。如果先改变current的后续结点,则会丢失插入节点应该指向的节点的信息。
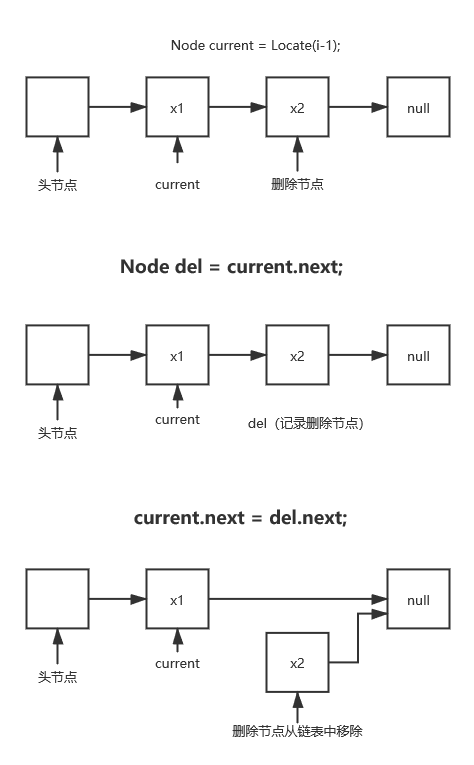
删除某元素Remove(int i):
public boolean Remove(int i) {
Node current = Locate(i-1);//获取删除节点的前一个结点,改变后续结点指向即可
if(current == null||current.next == null) {
System.out.println("数值越界");
return false;
}
Node del = current.next;//记录删除节点,为了获取删除节点的后续节点
current.next = del.next;//改变指向,删除节点前驱为无
return true;
}
前插法建立单链表addFront(Object x):
public void addFront(Object x) {//在链表的最前端添加
Node newNode = new Node(x);//建立新节点
newNode.next = first.next;//新节点后续指向头节点后续
first.next = newNode;//改变新节点后续为新增节点
}

后插法建立单链表addtRear(Object x):
public void addtRear(Object x) {
Node newNode = new Node(x);
Node last = first;//定义一个新节点指向头指针
while(last.next != null) {//节点后移,找到最后一个节点
last = last.next;
}
last.next = newNode;//最后一个节点的后续节点为新增节点
}
原理和前插基本相同,先找到最后存储数据节点,改变其后续指向即可。
运行结果
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkNode link = new LinkNode();
link.addFront(4);
link.addFront(3);
link.addFront(2);
link.addFront(1);
link.addtRear(6);
System.out.println(link);
link.Insert(4, 5);
System.out.println(link);
link.Remove(6);
System.out.println(link);
System.out.println(link.Length());
System.out.println(link.Locate(6));
}

本文对你有帮助,点个赞鼓励鼓励吧。蟹蟹。欢迎留言。








 本文详细介绍了Java中单链表的实现方式,包括结点类的定义、带头结点链表的实现,以及各种操作如长度获取、元素搜索、值修改、插入删除等的代码解析。
本文详细介绍了Java中单链表的实现方式,包括结点类的定义、带头结点链表的实现,以及各种操作如长度获取、元素搜索、值修改、插入删除等的代码解析。
















 894
894

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








