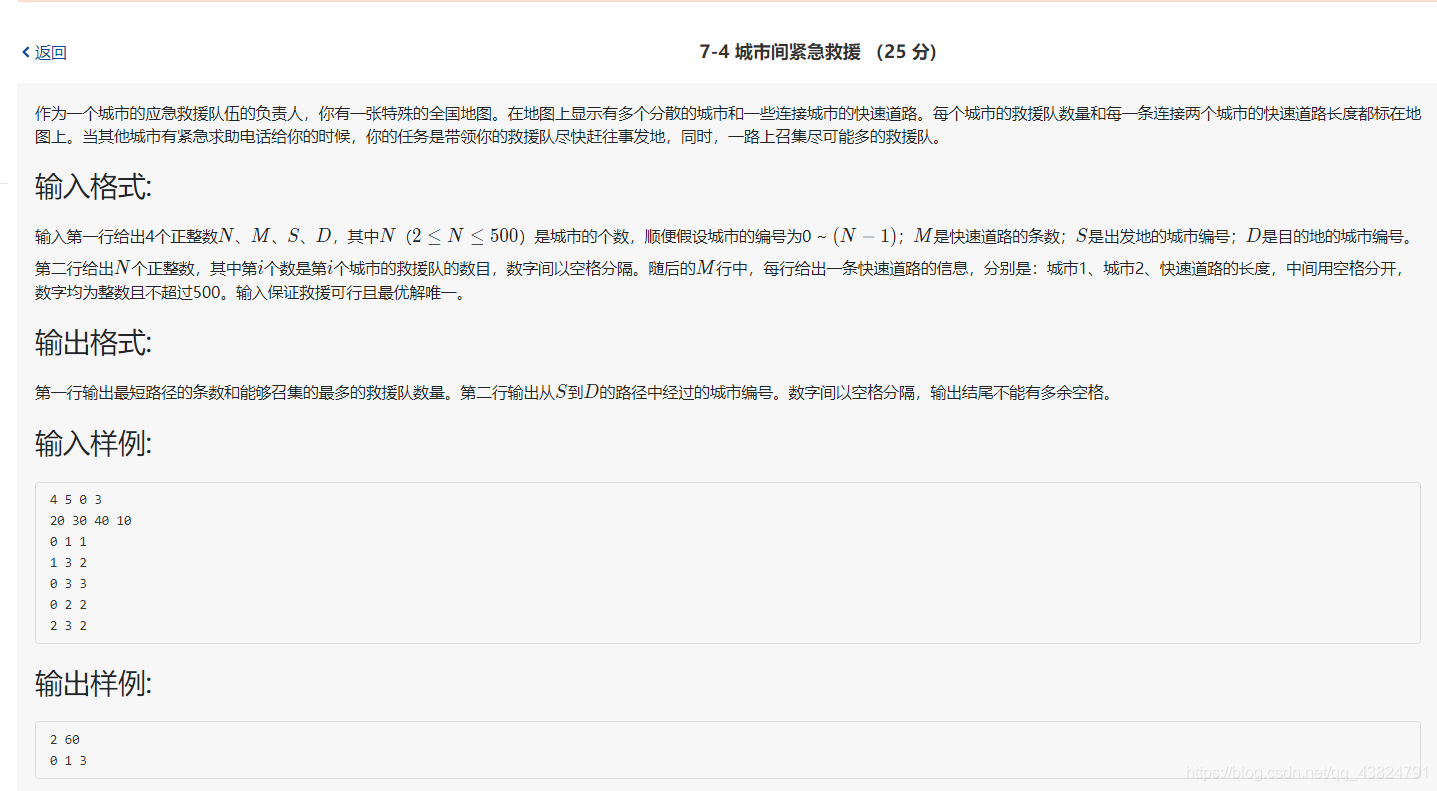
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f
int N, M, S, D;// N 城市个数, M 道路条数, S出发点, D 终点
int pre[1111];//储存到达i城市的上一个城市编号(该城市是到达i城市的最近且救援人数最多)
int num[1111];//到达该城市的最短路径条数
int peo[1111];//储存该城市的 救援人数
int abpeo[1111];//储存到达该城市的救援人数
int Gra[1111][1111];//图的存储
void Dijkstra()
{
memset(pre, -1, sizeof(pre));//初始化为-1****表示前面没有城市
int i;
/*********距离的初始化****/
int dis[1111];
for(i = 0;i < N;i++) dis[i] = Gra[S][i];
dis[S] = 0;




 本文探讨了如何利用Dijkstra算法解决城市间紧急救援的最短路径问题,通过1.1版的实现,提高了救援效率和决策准确性。
本文探讨了如何利用Dijkstra算法解决城市间紧急救援的最短路径问题,通过1.1版的实现,提高了救援效率和决策准确性。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 277
277

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








