一、解释一个启动命令
经常启动metastore 以及hiveserver2这两个服务,命令有点长,为了长期使用,可以编写一个命令:
#!/bin/bash
# hive 服务控制脚本,可以控制 Hive 的 metastore 和 hiveserver2 服务的启停
# 使用方式: hive-server-manager.sh [start|stop|status] [metastore|hiveserver2]
# - start : 一键开启metastore和hiveserver2服务,也可以指定服务开启
# - stop : 一键停止metastore和hiveserver2服务,也可以指定服务停止
# - status : 一键查看metastore和hiveserver2服务,也可以指定服务查看
help_info() {
echo "+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------+"
echo "| 本脚本可以一键控制 Hive 的 metastore 和 hiveserver2 服务 |"
echo "| 使用方式: hive-server-manager.sh [start|stop|status] [metastore|hiveserver2] |"
echo "+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------+"
echo "| 第一个参数用来指定操作命令,可以选择 开始(start)、停止(stop)、状态查看(status) |"
echo "| 第二个参数用来指定操作的服务,可以选择 metastore、hiveserver2,默认为全部 |"
echo "+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------+"
echo "| - start : 一键开启metastore和hiveserver2服务,也可以指定服务开启 |"
echo "| - stop : 一键停止metastore和hiveserver2服务,也可以指定服务停止 |"
echo "| - status : 一键查看metastore和hiveserver2服务,也可以指定服务查看 |"
echo "+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------+"
exit -1
}
# 获取操作命令
op=$1
# 获取操作的服务
server=$2
# 检查参数是否正确
if [ ! $op ]; then
help_info
elif [ $op != "start" -a $op != "stop" -a $op != "status" ]; then
help_info
fi
# 检查进程状态
metastore_pid=`ps aux | grep org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.HiveMetaStore | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}'`
hiveserver2_pid=`ps aux | grep proc_hiveserver2 | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}'`
# 检查日志文件夹的存在情况,如果不存在则创建这个文件夹
log_dir=/var/log/my_hive_log
if [ ! -e $log_dir ]; then
mkdir -p $log_dir
fi
# 开启服务
start_metastore() {
# 检查是否开启,如果未开启,则开启 metastore 服务
if [ $metastore_pid ]; then
echo "metastore 服务已经开启,进程号: $metastore_pid,已跳过"
else
nohup hive --service metastore >> $log_dir/metastore.log 2>&1 &
echo "metastore 服务已经开启,日志输出在 $log_dir/metastore.log"
fi
}
start_hiveserver2() {
# 检查是否开启,如果未开启,则开启 hiveserver2 服务
if [ $hiveserver2_pid ]; then
echo "hiveserver2 服务已经开启,进程号: $hiveserver2_pid,已跳过"
else
nohup hive --service hiveserver2 >> $log_dir/hiveserver2.log 2>&1 &
echo "hiveserver2 服务已经开启,日志输出在 $log_dir/hiveserver2.log"
fi
}
# 停止服务
stop_metastore() {
if [ $metastore_pid ]; then
kill -9 $metastore_pid
fi
echo "metastore 服务已停止"
}
stop_hiveserver2() {
if [ $hiveserver2_pid ]; then
kill -9 $hiveserver2_pid
fi
echo "hiveserver2 服务已停止"
}
# 查询服务
status_metastore() {
if [ $metastore_pid ]; then
echo "metastore 服务已开启,进程号: $metastore_pid"
else
echo "metastore 服务未开启"
fi
}
status_hiveserver2() {
if [ $hiveserver2_pid ]; then
echo "hiveserver2 服务已开启,进程号: $hiveserver2_pid"
else
echo "hiveserver2 服务未开启"
fi
}
# 控制操作
if [ ! $server ]; then
${op}_metastore
${op}_hiveserver2
elif [ $server == "metastore" ]; then
${op}_metastore
elif [ $server == "hiveserver2" ]; then
${op}_hiveserver2
else
echo "服务选择错误"
help_info
fi
上传,赋予权限:
[root@bigdata01 ~]# cd /usr/local/bin
[root@bigdata01 bin]# chmod u+x hive-server-manager.sh 
[root@bigdata01 bin]# hive-server-manager.sh status metastore
metastore 服务已开启,进程号: 119769
[root@bigdata01 bin]# hive-server-manager.sh status
metastore 服务已开启,进程号: 119769
hiveserver2 服务未开启二、分区
1、为什么要分区?
为了提高sql的查询效率
比如:
select * from orders where create_date='20230826';
假如数据量比较大,这个sql就是全表扫描,速度肯定慢。
可以将数据按照天进行分区,一个分区就是一个文件夹,当你查询20230826的时候只需要去20230826这个文件夹中取数据即可,不需要全表扫描,提高了查询效率。总结:
1)分区表实际上就是对应一个HDFS文件系统上的独立的文件夹。
2)该文件夹下是该分区所有的数据文件。
3)Hive中的分区就是分目录,把一个大的数据集根据业务需要分割成小的数据集。
4)在查询时通过WHERE子句中的表达式选择查询所需要的指定的分区,这样的查询效率会提高很多2、如何分区
根据业务需求而定,不过通常以年、月、日、小时、地区等进行分区
3、语法
create table tableName(
.......
.......
)
partitioned by (colName colType [comment '...'],...)分区就是在hdfs上创建文件夹,为了提高查询效率而已
4、分区实战
1)一级分区(分区字段只有一个)
create table if not exists part1(
id int,
name string,
age int
)
partitioned by (dt string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
lines terminated by '\n';由上面可以知道,dt字段不在普通字段里面,是一个伪列,但是可以当做普通字段使用。
搞两份数据user1.txt 和 user3.txt
user1.txt
1,zhangsan,21
2,lisi,25
3,wangwu,33
user2.txt
4,zhaoliu,38
5,laoyan,36
6,xiaoqian,12加载数据:建表的时候有ed,不建表的时候的sql不加ed.
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/user1.txt' into table part1 partition(dt='2023-08-25');
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/user3.txt' into table part1 partition(dt='2023-08-26');查看数据:发现分区字段列也查询出来了。

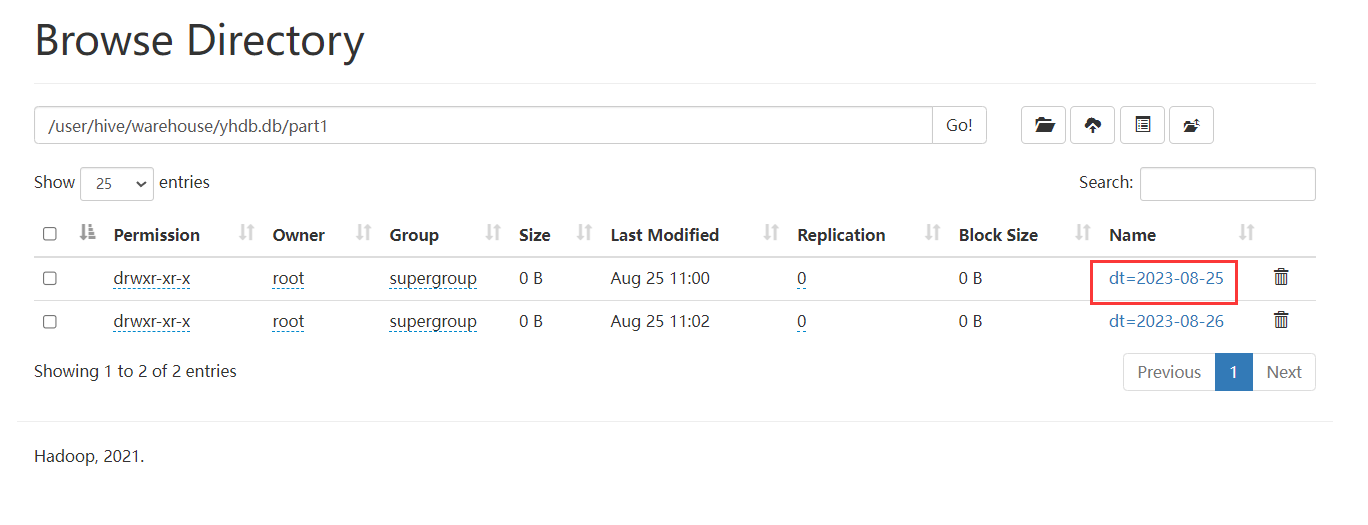

以上创建的是一级分区,只有一个分区字段,但是有两个分区 dt=20230825 和 dt=20230826
2)二级分区【分区字段有两个】
create table if not exists part2(
id int,
name string,
age int
)
partitioned by (year string,month string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ',';load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/user1.txt' into table part2 partition(year='2023',month='03');
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/user3.txt' into table part2 partition(year='2023',month=04);
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/user3.txt' into table part2 partition(year='2023',month="05");
3) 三级分区【三级目录】
建表:
create table if not exists part3(
id int,
name string,
age int
)
partitioned by (year string,month string,day string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ',';加载数据:
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/user1.txt' into table part3 partition(year='2023',month='08',day='01');
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/user3.txt' into table part3 partition(year='2023',month='08',day='31'); 


4)测试分区字段的大小写
在hive中,分区字段名是不区分大小写的,不过字段值是区分大小写的。我们可以来测试一下
新建表:
create table if not exists part4(
id int,
name string,
age int
)
partitioned by (year string,month string,DAY string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',' ;新创建的分区表没有数据的话,是不会有文件夹的。

导入数据:
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/user1.txt' into table part4 partition(year='2018',month='03',DAy='21');
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/user3.txt' into table part4 partition(year='2018',month='03',day='AA');
5)分区数据的查询
单个分区查询:
select * from part1 where dt='2018-03-21';查询多个分区:
select * from part1 where dt='2023-08-25' union select * from part1 where dt='2023-08-26';
使用union 整个SQL语句进行了MR任务
select * from part1 where dt='2023-08-25' or dt='2023-08-26';6)查看分区的数量
语法:
show partitions tableName
eg:
show partitions part4;
分区和分区字段的区别:
分区:比如year=2018/month=03/day=21 这是一个分区
分区字段:创建表的时候,有多少个分区字段就是多少级分区。
创建表的时候 partitioned by (year string,month string,day string) 表示创建一个拥有3级分区的表,目前如果没有数据的,是一个分区都没有的。7)添加分区
1、创建空数据的分区
-- 单分区
alter table part3 add partition(year='2023',month='05',day='02');
-- 多分区
alter table part3 add partition(year='2023',month='05',day='03') partition(year='2023',month='05',day='04');
一下子添加多个分区,partition 之间没有符号!2)添加分区,并且带有数据
单分区带数据
alter table part3 add partition(year='2023',month='05',day='05') location '/user/hive/warehouse/yhdb.db/part1/dt=2023-08-25';
hive (yhdb)> select * from part3 where year='2023' and month='05' and day='05';
OK
part3.id part3.name part3.age part3.year part3.month part3.day
1 zhangsan 21 2023 05 05
2 lisi 25 2023 05 05
3 wangwu 33 2023 05 05
Time taken: 0.431 seconds, Fetched: 3 row(s)多分区带数据
alter table part3 add
partition(year='2020',month='05',day='06') location '/user/hive/warehouse/yhdb.db/part1/dt=2023-08-25'
partition(year='2020',month='05',day='07') location '/user/hive/warehouse/yhdb.db/part1/dt=2023-08-25';8) 删除分区
删除一个分区:
alter table part3 drop partition(year='2023',month='05',day='05');
删除多个分区,中间有逗号
alter table part3 drop partition(year='2023',month='05',day='02'),partition(year='2023',month='05',day='03');9)查看表设计
desc formatted part3;
5、让分区关联数据的三种方式【重点】
(1)方式一:上传数据后修复
create table if not exists part5(
id int,
name string,
age int
)
partitioned by (year string,month string,day string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ',';在hdfs上创建文件夹:
hive (yhdb)> dfs -mkdir -p /user/hive/warehouse/yhdb.db/part5/year=2023/month=08/day=28;
上传数据
hive (yhdb)> dfs -put /home/hivedata/user1.txt /user/hive/warehouse/yhdb.db/part5/year=2023/month=08/day=28;
查询数据发现没有数据,原因是partition的元数据没有在mysql中,修复一下:
msck repair table part5;
hive (yhdb)> msck repair table part5;
OK
Partitions not in metastore: part5:year=2023/month=08/day=28
Repair: Added partition to metastore part5:year=2023/month=08/day=28
Time taken: 0.623 seconds, Fetched: 2 row(s)
通过修复的日志,可以看出,修复操作其实是在part5这个表的元数据中,添加了分区的数据。
再次测试,发现就有数据了!
select * from part5;(2)方式二:上传数据后添加分区
在hdfs上创建文件夹:
hive (yhdb)> dfs -mkdir -p /user/hive/warehouse/yhdb.db/part5/year=2023/month=08/day=27;
上传数据
hive (yhdb)> dfs -put /home/hivedata/user1.txt /user/hive/warehouse/yhdb.db/part5/year=2023/month=08/day=27;
创建一个分区:
alter table part5 add partition(year='2023',month='08',day='27');
先创建一个分区,会不会产生文件夹呢?会!
创建一个分区表,会不会产生文件夹呢?不会!
你也可以先创建分区,在分区的文件夹里面,上传数据!
alter table part5 add partition(year='2023',month='08',day='26');
添加分区之后就有了文件夹:/user/hive/warehouse/yhdb.db/part5/year=2023/month=08/day=26
在这个文件夹里面上传数据:
dfs -put /home/hivedata/user1.txt /user/hive/warehouse/yhdb.db/part5/year=2023/month=08/day=26;(3) 方式三:创建文件夹后load数据到分区
dfs -mkdir -p /user/hive/warehouse/yhdb.db/part5/year=2023/month=08/day=25;
load一下数据:
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/user1.txt' into table
part5 partition(year='2023',month='08',day='25');
这种方式其实没必要,因为不创建文件夹,load数据到分区表也会自动创建的。6、分区的种类
静态分区:先创建分区,再加载数据
动态分区:直接加载数据,根据数据动态创建分区
混合分区:分区字段有静态的,也有动态的。
动态分区的玩法:
(1)开启动态分区功能(默认true,开启)
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true;
(2)设置为非严格模式(动态分区的模式,默认strict,表示必须指定至少一个分区为静态分区,nonstrict模式表示允许所有的分区字段都可以使用动态分区。)
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict;
(3)在所有执行MR的节点上,最大一共可以创建多少个动态分区。默认1000
set hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions=1000;
(4)在每个执行MR的节点上,最大可以创建多少个动态分区。
该参数需要根据实际的数据来设定。比如:源数据中包含了一年的数据,即day字段有365个值,那么该参数就需要设置成大于365,如果使用默认值100,则会报错。
set hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions.pernode=100;
创建一个dongtai.txt,添加如下数据:
10703007267488 usa 2014-05-01
10101043505096 usa 2014-05-01
10103043509747 china 2014-05-02
10103043501575 china 2014-05-02
10104043514061 china 2014-05-01
创建普通的表,将数据加载进去:
-- 创建表
create table order_partition
(
order_no string,
type string,
order_time string
) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
-- 加载数据
load data local inpath "/home/hivedata/dongtai.txt" into table order_partition;
接着按照需求,创建动态分区表
create table order_dynamic_partition
(
order_no string
)
partitioned by(type String, `time` String)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
导入数据:效果就是按照type和time 两个字段的数据,动态的创建分区:
一定不要使用load加载数据,要从普通表中查询数据插入到动态表:
insert overwrite table order_dynamic_partition partition (type, `time`)
select order_no, type, order_time from order_partition;
hive (yhdb)> show partitions order_dynamic_partition;
OK
partition
type=china/time=2014-05-01
type=china/time=2014-05-02
type=usa/time=2014-05-01
Time taken: 0.254 seconds, Fetched: 3 row(s)
思考:order_no, type, order_time 能过换成*
insert overwrite table order_dynamic_partition partition (type, `time`)
select * from order_partition;
虽然没有报错,但是不建议:
因为动态分区是由规律的:动态分区数据必须是查询数据的后几位。
insert overwrite table order_dynamic_partition partition (type, `time`)
select order_no, type, order_time from order_partition;
动态分区需要依赖于两个字段的数据,这两个数据必须是最后两个,而且必须数据要照应.
也就是说,不管select 有多少个字段,最后两个字段必须照应,否则有问题!混合分区的玩法:
--创建一个分区表
create table dy_part2(
id int,
name string
)
partitioned by (year string,month string,day string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
-- 要想往分区表内动态加载数据,必须有普通表
create table temp_part2(
id int,
name string,
year string,
month string,
day string
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
编写一个数据文件:temp_part2.txt
1,廉德枫,2019,06,25
2,刘浩(小),2019,06,25
3,王鑫,2019,06,25
5,张三,2019,06,26
6,张小三,2019,06,26
7,王小四,2019,06,27
8,夏流,2019,06,27
加载数据到普通表中:
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/temp_part2.txt' into table temp_part2;
将普通表的数据动态加载到分区表:
- 错误用法:
insert into dy_part2 partition (year='2019',month,day)
select * from temp_part2;
会报错:
FAILED: SemanticException [Error 10044]: Line 1:12 Cannot insert into target table because column number/types are different 'day': Table insclause-0 has 4 columns, but query has 5 columns.
- 正确用法:
insert into dy_part2 partition (year='2019',month,day)
select id,name,month,day from temp_part2;
hive (yhdb)> show partitions dy_part2;
OK
partition
year=2019/month=06/day=25
year=2019/month=06/day=26
year=2019/month=06/day=27
Time taken: 0.163 seconds, Fetched: 3 row(s)
四、分桶
分桶的重要性没有分区那么重要。
1、分桶的意义
数据分区可能导致有些分区,数据过多,有些分区,数据极少。分桶是将数据集分解为若干部分(数据文件)的另一种技术。
分区和分桶其实都是对数据更细粒度的管理。当单个分区或者表中的数据越来越大,分区不能细粒度的划分数据时,我们就采用分桶技术将数据更细粒度的划分和管理。
分桶其实跟我们MR中的分区是一样的。
2、分桶的原理
与MapReduce中的HashPartitioner的原理一模一样
MapReduce:使用key的hash值对reduce的数量进行取模(取余)
hive:使用分桶字段的hash值对分桶的数量进行取模(取余)。针对某一列进行分桶存储。每一条记录都是通过分桶字段的值的hash对分桶个数取余,然后确定放入哪个桶。
MapReduce: Key 单词 reduce的数量是3个,最后形成3个。
hello --> hello 进行hash算法 --> 得到的hash值对3取模(0 1 2)
MapReduce假如不指定分区,是否有分区呢?答案是有,使用默认分区HashPartitioner。
Hive --> 假如 我指定分桶字段为 id , 桶的数量为 3个,就是hash(id) % 3 = 0 1 2
桶是一个个的文件,分区是一个个的文件夹。3、分桶有啥好处?
分区的意义:提高查询效率
分桶的意义:将每一个分区的数据进行切分,变成一个个小文件,然后进行抽样查询(从一堆数据中找一些数据进行分析)。在进行多表联查的时候,可以提高效率(hive优化的时候再提)。4、分桶的实战
创建分桶的表:
create table stu_bucket(id int, name string)
clustered by(id)
into 4 buckets
row format delimited fields terminated by ' ';
设置reduce的数量:
注意:
想要将表创建为4个桶,需要将hive中mapreduce.job.reduces参数设置为>=4或设置为-1;
通过 set mapreduce.job.reduces ; 可以查看参数的值
hive (yhdb)> set mapreduce.job.reduces;
mapreduce.job.reduces=-1
hive (yhdb)> set mapreduce.job.reduces=-1;
reduces = -1 表示让系统自行决定reduce的数量。加载数据
建议:不要使用load直接加载!
使用:创建普通表,加载普通表的数据到分桶表。
数据:student.txt
1001 ss1
1002 ss2
1003 ss3
1004 ss4
1005 ss5
1006 ss6
1007 ss7
1008 ss8
1009 ss9
1010 ss10
1011 ss11
1012 ss12
1013 ss13
1014 ss14
1015 ss15
1016 ss16
建议不要使用load直接加载,但是可以尝试一下:
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/student.txt' into table stu_bucket;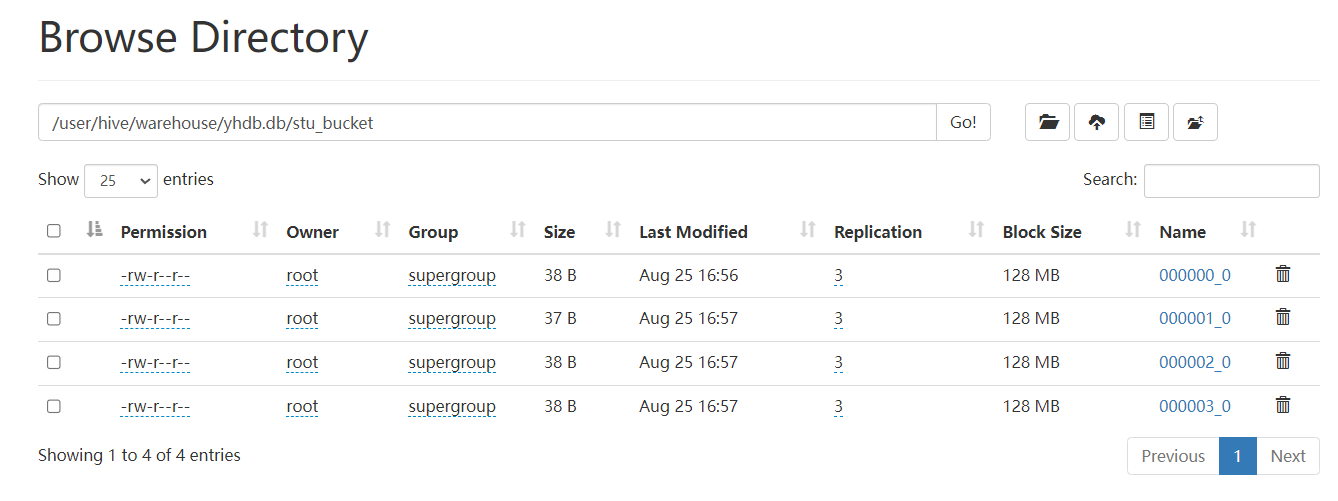

如上所示:Hive的分桶采用对分桶字段的值进行哈希,然后除以桶的个数求余的方式决定该条记录存放在哪个桶当中。
1、reduce=-1 让job自行决定开启多少个reduce,或者设置数量大于等于桶的数量。
2、建议关闭本地模式:
官方建议使用 创建临时表加载数据:使用insert将数据插入到分桶表
hive(yhdb)> truncate table stu_bucket;(删除表内数据,不删表结构,因此只能删内表)
hive(yhdb)> create table temp_stu(id int, name string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ' ';
hive(yhdb)> load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/student.txt' into table temp_stu;
hive(yhdb)> insert into table stu_bucket select * from temp_stu cluster by (id);
5、分桶的查询
语法: tablesample(bucket x out of y on sno)
select * from stu_bucket;
select * from stu_bucket tablesample(bucket 1 out of 1);
查询第一桶
select * from stu_bucket tablesample(bucket 1 out of 4 on id);
查询第一桶和第三桶
select * from stu_bucket tablesample(bucket 1 out of 2 on id);
查询第二桶和第四桶的数据
select * from stu_bucket tablesample(bucket 2 out of 2 on id);
查询对8取余的第一桶的数据:
select * from stu_bucket tablesample(bucket 1 out of 8 on id);其他查询:
查询前三条
select * from stu_bucket limit 3;
select * from stu_bucket tablesample(3 rows);
查询百分比的数据
select * from stu_bucket tablesample(13 percent);大小的百分比所占的那一行。
查询固定大小的数据
select * from stu_bucket tablesample(68b); 单位(K,KB,MB,GB...)
固定大小所占的那一行。
随机抽三行数据
select * from stu_bucket order by rand() limit 3;6、总结(重要)
定义阶段:
clustered by (id); ---指定表内的字段进行分桶。
sorted by (id asc|desc) ---指定数据的排序规则,表示咱们预期的数据是以这种规则进行的排序
举例:
create table stu_bucket2(id int, name string)
clustered by(id) sorted by(id desc)
into 4 buckets
row format delimited fields terminated by ' ';
sorted by 指定分桶表中的每一个桶的排序规则导入数据阶段:
cluster by (id)
--指定getPartition以哪个字段来进行hash,并且排序字段也是指定的字段,排序是以asc排列
--相当于distribute by (id) sort by (id)
insert into table stu_bucket select * from student cluster by (id);
想当于:
insert into table stu_bucket select * from student distribute by (id) sort by (id) ;
distribute by (id) -- 指定getPartition以哪个字段来进行hash
sort by (name asc | desc) --指定排序字段
-- 区别:distribute by 这种方式可以分别指定getPartition和sort的字段总结:
分区使用的是表外字段,分桶使用的是表内字段
分桶更加细粒度的管理数据,更多的是使用来做抽样、join
cluster 和 clusted 的区别:一个是导入数据的时候调用的,一个是创建表的时候使用的。
sort by 和 sorted by 区别:sort by 是导入数据的时候,sorted by 是分桶排序规则指定的时候
distribute by 和 cluster by 的区别:前一个是分区,后一个是分区并排序。
partition by 和 partitioned by 的区别:partition by 一般和开窗函数一起使用,partitioned by 建表的时候一起使用。








 本文围绕Hive展开,先解释了启动metastore和hiveserver2服务的命令。重点介绍了分区,包括分区原因、方法、语法、实战操作,如一级到三级分区创建、分区数据查询等,还提及让分区关联数据的三种方式及分区种类。此外,阐述了分桶的意义、原理、好处、实战和查询等内容。
本文围绕Hive展开,先解释了启动metastore和hiveserver2服务的命令。重点介绍了分区,包括分区原因、方法、语法、实战操作,如一级到三级分区创建、分区数据查询等,还提及让分区关联数据的三种方式及分区种类。此外,阐述了分桶的意义、原理、好处、实战和查询等内容。

















 6466
6466

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










