- 中缀表达式计算主要方法
1)利用后缀表达式和栈
2)利用表达式树
- 中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式
- 后缀表达式的特点
- 数字的顺序与中缀一样
- 运算顺序根据从左到有遇到运算符的顺序进行
- 中缀表达式转换成后缀表达式的核心思想:
比较相邻的两个运算符,优先级高的先算。 - 转换的过程——主要用到一个运算符栈opor
1.假设中缀表达式exp用string类型存储,则在遍历exp的过程中,如果遇到了数字符,则将连续的数字符末尾加上‘#’后添加到后缀表达式postexp中(加入‘#’的作用主要是为了区分出不同的数字)
2.如果遇到的是运算符op2,则和栈顶元素op1比较优先级,如果高于op1,则直接将op2进栈;如果低于或等于op2,则可以将栈中‘(’(如果有)之前所有高于或等于op2的运算符退栈,加入到postexp中。(opor中的运算符退栈就说明它已经可以开始计算了)
3.如果遇到‘(’,进栈,遇到‘)’,则可以退栈运算符到postexp中,直到遇到‘(’为之。(细节注意:‘(’不用加入到postexp中)
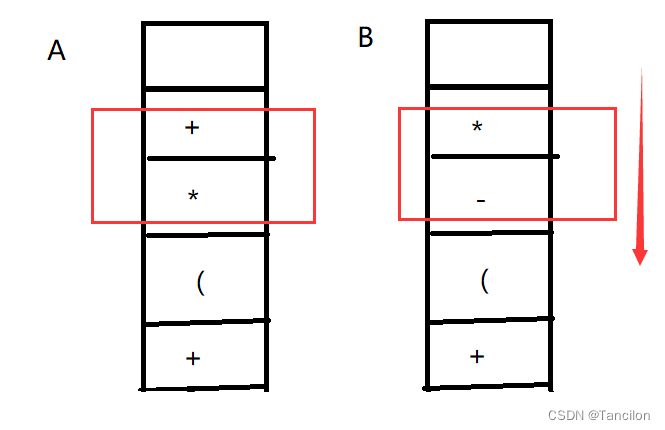
疑问:为什么第三步可以直接就简单地把栈中所有‘(’以上的运算符都弹出?
理解:
当遇到‘)’时,栈中会有A情况吗?
答案应该是否定的,因为此处“+”的运算符优先级要低于‘x’号,所以会在第2步中就将‘x’退栈,所以当遇到‘)’运算符时,‘(’以上的运算符优先级应该是从上到下逐渐递减的,所以我们可以直接全部弹出。
- 转换代码如下
void trans()
{
stack<char> opor;
int i = 0;
while (i < expr.length()) // 扫描expr表达式
{
if(expr[i] == ' ' || expr[i] == '=')
{
++ i;
continue;
}
else if (expr[i] == '(')
opor.push(expr[i]);
else if (expr[i] == ')') //遇到')'退栈运算符
{
while (!opor.empty() && opor.top() != '(')
{
char tmp = opor.top(); opor.pop();
postexp += tmp;
}
opor.pop();
}
else if (expr[i] == '+' || expr[i] == '-')
{
if (!opor.empty() && opor.top() != '(')
{
char tmp = opor.top();
postexp += tmp;
opor.pop();
opor.push(expr[i]);
}
else
opor.push(expr[i]);
}
else if (expr[i] == '*' || expr[i] == '/')
{
if (!opor.empty() && (opor.top() == '*' ||opor.top() == '/'))
{
char tmp = opor.top();
postexp += tmp;
opor.pop();
opor.push(expr[i]);
}
else
opor.push(expr[i]);
}
else //处理数字
{
while(expr[i] >= '0' && expr[i] <= '9')
{
postexp += expr[i];
++ i;
}
postexp += "#"; //符号作用:区别两个不同的数字
continue;
}
++ i;
}
while (!opor.empty()) //注意最后还得考虑栈中是否还有符号
{
char tmp = opor.top();
opor.pop();
postexp += tmp;
}
}
- 利用表达式树求中缀表达式的值
- 建立步骤如下
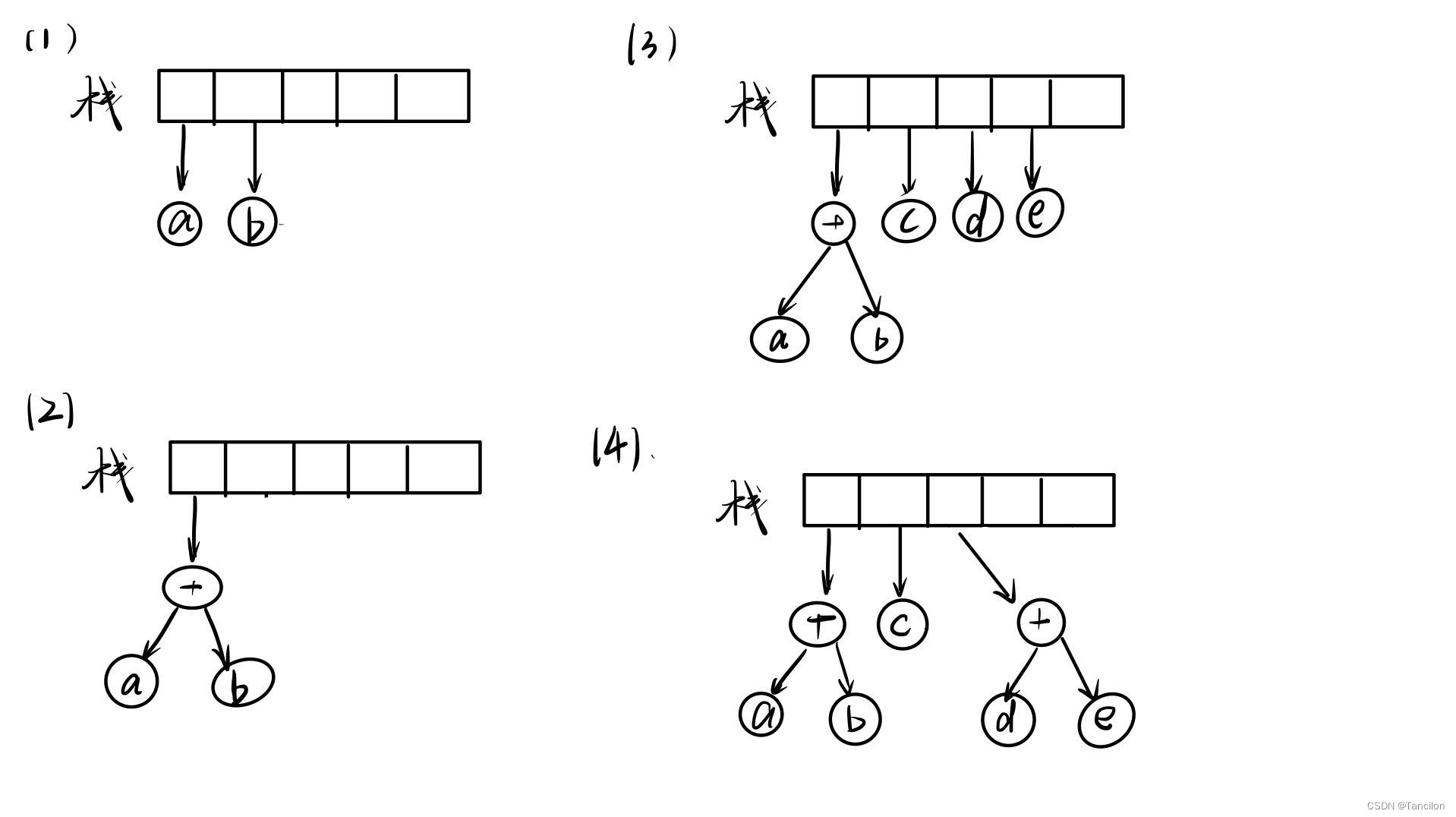
读入一个符号:
->如果是操作数,则建立一个单节点树并将指向他的指针推入栈中;
->如果是运算符,就从栈中弹出指向两棵树T1和T2的指针(T1先弹出)并形成一棵新树,树根为该运算符,它的左、右子树分别指向T2和T1,然后将新树的指针压入栈中。
对于一个后缀表达式 ab+cde+** 则部分建立过程如图所示
- 例题描述
从标准输入中读入一个整数算术运算表达式,如24 / ( 1 + 2 + 36 / 6 / 2 - 2) * ( 12 / 2 / 2 )= ,计算表达式结果,并输出。
【输入形式】
从键盘输入一个以=结尾的整数算术运算表达式。操作符和操作数之间可以有空格分隔。
【输出形式】
首先在屏幕上输出表达式树根、左子节点及右子节点上的运算符或操作数,中间由一个空格分隔,最后有一个回车(如果无某节点,则该项不输出)。然后输出表达式计算结果。
【样例输入】
24 / ( 1 + 2 + 36 / 6 / 2 - 2) * ( 12 / 2 / 2 ) =
【样例输出】
* / /
18
- 完整代码展示
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
class TreeNode{
public:
int data;
char opor;
TreeNode *lchild, *rchild;
TreeNode(): data(-1), opor('$'), lchild(NULL), rchild(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int d, char o)
{
data = d;
opor = o;
lchild = rchild = NULL;
}
};
string expr, postexp;
void trans()
{
stack<char> opor;
int i = 0;
while (i < expr.length()) // 扫描expr表达式
{
if(expr[i] == ' ' || expr[i] == '=')
{
++ i;
continue;
}
else if (expr[i] == '(')
opor.push(expr[i]);
else if (expr[i] == ')') //遇到')'退栈运算符
{
while (!opor.empty() && opor.top() != '(')
{
char tmp = opor.top(); opor.pop();
postexp += tmp;
}
opor.pop();
}
else if (expr[i] == '+' || expr[i] == '-')
{
if (!opor.empty() && opor.top() != '(')
{
char tmp = opor.top();
postexp += tmp;
opor.pop();
opor.push(expr[i]);
}
else
opor.push(expr[i]);
}
else if (expr[i] == '*' || expr[i] == '/')
{
if (!opor.empty() && (opor.top() == '*' ||opor.top() == '/'))
{
char tmp = opor.top();
postexp += tmp;
opor.pop();
opor.push(expr[i]);
}
else
opor.push(expr[i]);
}
else //处理数字
{
while(expr[i] >= '0' && expr[i] <= '9')
{
postexp += expr[i];
++ i;
}
postexp += "#"; //符号作用:区别两个不同的数字
continue;
}
++ i;
}
while (!opor.empty()) //注意最后还得考虑栈中是否还有符号
{
char tmp = opor.top();
opor.pop();
postexp += tmp;
}
}
void creatTree() //建立表达式树
{
stack<TreeNode*> solu;
int i = 0;
while (i < postexp.length())
{
if (postexp[i] >= '0' && postexp[i] <= '9')
{
int tmp = 0;
while(postexp[i] >= '0' && postexp[i] <= '9')
{
tmp = tmp * 10 + postexp[i] - '0';
++ i;
}
TreeNode* p;
p = new TreeNode(tmp, '$'); //叶子节点opor成员赋值‘$'
solu.push(p);
}
else
{
TreeNode *n1, *n2, *p;
n2 = solu.top(); solu.pop();
n1 = solu.top(); solu.pop();
int data = 0;
switch (postexp[i])
{
case '+':
data = n2->data + n1->data;
break;
case '-':
data = n1->data - n2->data;
break;
case '*':
data = n1->data * n2->data;
break;
case '/':
data = n1->data / n2->data;
break; // 每一个case后记得加break!!!
default:
break;
}
p = new TreeNode(data, postexp[i]);
p->lchild = n2;
p->rchild = n1;
solu.push(p);
}
++ i;
}
TreeNode* root = solu.top();
(root->opor == '$') ? cout << root->data << " " : cout << root->opor << " ";
if (root->rchild != NULL)
(root->rchild->opor == '$') ? cout << root->rchild->data << " " : cout << root->rchild->opor << " ";
if (root->lchild != NULL)
(root->lchild->opor == '$') ? cout << root->lchild->data << " " : cout << root->lchild->opor << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << root->data << endl;
}
int main()
{
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
getline(cin, expr); // 细节注意:若题中有空格,则需要直接读一整行,直接cin>>expr是不可以的
trans(); // 中缀表达式转后缀
creatTree();
return 0;
}

























 3189
3189

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










