MPI环境搭建可以看这篇博客:
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_42683011/article/details/109231798
MPI基础结构:
一个HelloWorld程序:
#include <mpi.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
int main (int argc, char **argv){
int myid, numprocs;
int namelen;
char processor_name[MPI_MAX_PROCESSOR_NAME];
int initFlag=false;
MPI_Initialized(&initFlag);
fprintf(stdout, "%s\n",initFlag?"true":"false");
MPI_Init (&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank (MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size (MPI_COMM_WORLD, &numprocs);
MPI_Get_processor_name (processor_name, &namelen);
fprintf (stdout, "Hello World! Process %d of %d on %s\n", myid, numprocs, processor_name);
MPI_Finalize ();
return 0;
}

基本框架&常用函数讲解:
- 初始化MPI系统:
MPI_Init (&argc, &argv);
-
通常为第一个调用的MP
I函数,除 MPI_Initialized 外
-
在C接口中,MPI系统通过argc和argv得到命令行参数,并且会把MPI系统专用的参数删除,留下用户的解释参数
-
检测MPI系统是否已经初始化
int MPI_Initialized(int *flag)- 唯一可在 MPI_Init 前使用的函数
- 已经调用MPI_Init,返回flag=true,否则flag=false
-
得到通信器的进程数和进程在通信器中的标号
int MPI_Comm_size(MPI_Comm comm, int *size); //进程数 int MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_Comm comm, int *rank); //进程号-
MPI_Comm:
这个是MPI通信器, 两进程通过通信器进行通信MPI_COMM_WORLD通信器将所有的进程都包括在内
-
-
退出MPI系统
int MPI_Finalize(void)- 每个进程都必须调用,使用后不准许调用任何MPI函数
- 若不执行MPI退出函数,进程可能被悬挂
- 用户在调用该函数前,应确保非阻塞通讯结束
-
异常终止MPI系统:
int MPI_Abort(MPI_Comm comm, int errorcode);- 在出现了致命错误而希望异常终止MPI程序时执行
- MPI系统会设法终止comm通信器中所有进程
- 整型参数errorcode,将被作为进程的退出码返回给系统
-
获取处理器名称:
int MPI_Get_processor_name(char *name, int *resultlen)- 在返回的name中存储所在处理器的名称
应提供参数name不少于MPI_MAX_PROCESSOR_NAME个字节的存储空间 - resultlen存放返回名字所占字节
- 在返回的name中存储所在处理器的名称
-
获取MPI版本号:
int MPI_Get_version(int *version, int *subversion)- 若 mpi 版本号为2.0,则返回的version=2,subversion=0
-
获取wtime:
double MPI_Wtime(void); double MPI_Wtick(void);- 返回调用时刻的墙上时间,用浮点数表示秒数
经常用来计算程序运行时间 - MPI_WTICK 则返回MPI_WTIME 函数的时钟精度==(分度值)==,也是以秒为单位
例如,假设 MPI_WTIME 使用的硬件时钟计数器每1/1000 秒增加1,则 MPI_WTICK 的返回值为 10-3,表示用函数 MPI_WTIME 得到的时间精度为干分之一秒。
- 返回调用时刻的墙上时间,用浮点数表示秒数
点对点通信:
阻塞式点对点通信:
消息的发送&接收都将被阻塞, 仅仅当操作完成后才继续线程执行
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#define n 1024
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myrank, nprocs, namelen;
double a[n]={0}, b[n]={0};
MPI_Status status;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myrank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &nprocs);
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
a[i]=myrank;
b[i]=0;
}
MPI_Send(a,n,MPI_DOUBLE, (myrank+1)%nprocs, 99, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Recv(b, n, MPI_DOUBLE, (myrank-1+nprocs)%nprocs, 99, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
printf("b[0]=%f in process %d\n",b[0], myrank);
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}

常用函数:
- 消息发送
int MPI_Send(void *buf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype,
int dest, int tag, MPI_Comm comm);
- buf: 所要发送消息数据的首地址
- count: 发送消息数组元素的个数。不是字节数,而是指定数据类型的个数
- datatype: 发送消息的数据类型。可是原始数据类型,或为用户自定义类型
- dest: 接收消息的进程编号。取值范围是 0~np-1,或MPI_PROC_NULL (np是comm中的进程总数)
- tag: 消息标签。取值范围是 0~MPI_TAG_UB,用来区分消息
- comm: 通信器
返回条件:
- 发送数据被MPI系统存入系统缓存,此时不要求接收操作收到发送数据
- 不缓存,则数据被接收到接收缓冲区
- 消息接收:
int MPI_Recv(void *buf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype,
int source, int tag, MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Status *status);
-
buf: 接收消息数据的首地址
-
count: 接收消息数组元素的最大个数。是接受缓存区的大小,表示接受上界,具体接受长度可用MPI_Get_count 获得
-
datatype: 接收消息的数据类型
-
source: 发送消息的进程编号。取值范围是 0~np-1,或MPI_PROC_NULL和MPI_ANY_SOURCE
-
tag: 消息标签。取值范围是 0~MPI_TAG_UB,或MPI_ANY_TAG
-
comm: 通信器
-
status: 接收消息时返回的状态:
在使用时需要预先申请内存:

但用户仅能使用后三个域
-
查询接收到的消息长度:
int MPI_Get_count(MPI_Status status, MPI_Datatype datatype, int *count);该函数在count中返回数据类型的个数,即消息的长度
- status:接收消息时返回的状态
- datatype:接收消息的数据类型
- count:接收消息数组元素的个数
消息传递成功的条件:
- 发送进程需指定一个有效的目标接收进程
- 接收进程需指定一个有效的源发送进程
- 接收和发送消息的进程要在同一个通信器内
- 接收和发送消息的 tag 要相同
- 接收缓存区要足够大
阻塞式点对点通信有可能导致死锁
后头还有这个, 先放着:
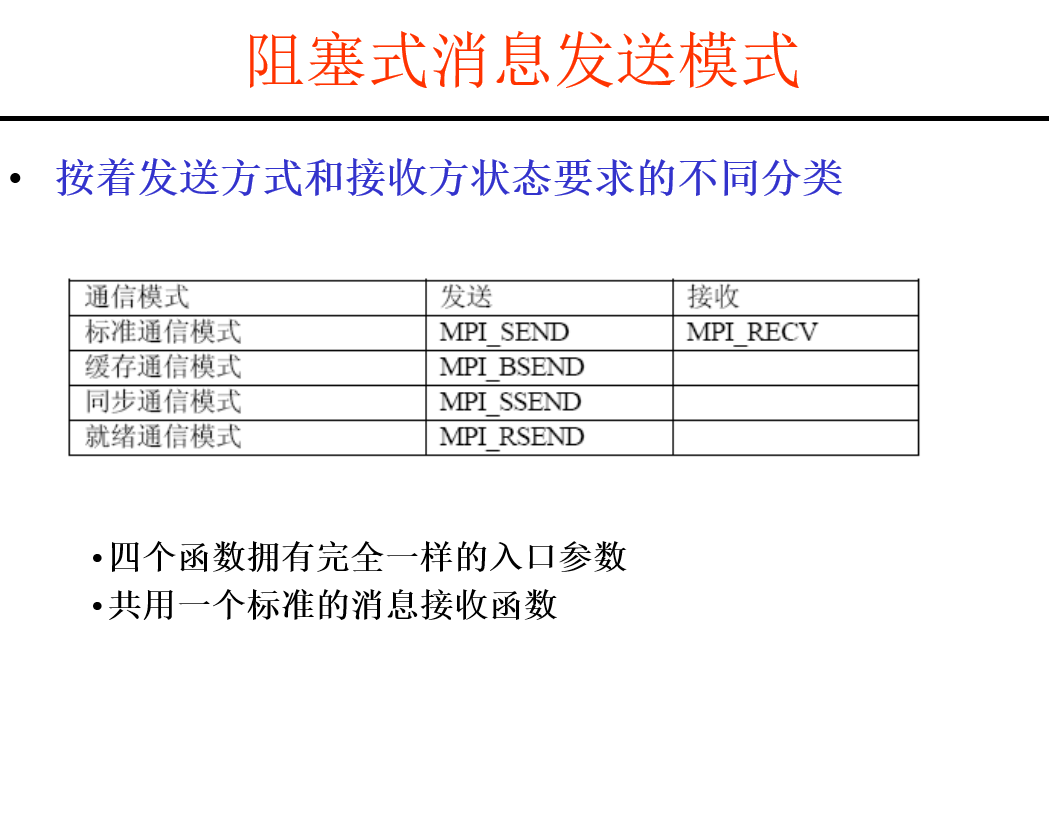
非阻塞式点对点通信:

常用函数:
-
发送:
int MPI_Isend (void *buf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, int dest, int tag, MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Request *request)- 该函数仅提交了一个消息发送请求,并立即返回
- MPI系统会在后台完成消息发送
- 函数为该发送操作创建了一个请求,通过request变量返回
- request可供之后(查询和等待)函数使用
几个参数大致同上
-
接收
int MPI_Irecv(void *buf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, int source, int tag, MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Request *request)- 该函数仅提交了一个消息接收请求,并立即返回
- MPI系统会在后台完成消息的接收
- 函数为该接收操作创建了一个请求,通过request变量返回
- request可供之后查询和等待函数使用
-
等待&检测一个通信请求完成:
int MPI_Wait (MPI_Request *request, MPI_Status *status) int MPI_Test (MPI_Request *request, int *flag, MPI_Status *status)- MPI_Wait阻塞等待通信函数完成后返回
MPI_Test检测某通信,不论其是否完成,都立刻返回。如果通信完成,则flag=true - 当等待或检测的通信完成时,通信请求request被设置成MPI_REQUEST_NULL
- 考察接收请求,status返回与MPI_Recv一样;发送请求,则不确定
- MPI_Test返回时,当flag=false, status不被赋值
- MPI_Wait阻塞等待通信函数完成后返回
持久通信:
这玩意暂时不做要求
数据类型:
| MPI数据类型 | 对应的C数据类型 |
|---|---|
| MPI_INT | int |
| MPI_FLOAT | float |
| MPI_DOUBLE | double |
| MPI_SHORT | short |
| MPI_LONG | long |
| MPI_CHAR | char |
| MPI_UNSIGNED_CHAR | unsigned char |
| MPI_UNSIGNED_SHORT | unsigned short |
| MPI_UNSIGNED | unsigned |
| MPI_UNSIGNED_LONG | unsigned long |
| MPI_LONG_DOUBLE | long double |
| MPI_BYTE | |
| MPI_PACKED |
定义:
这个还是直接看PPT更好点

理解这里对于后头的自定义数据类型有必要性的帮助
MPI中自定义数据类型由于需要保证地址对界, 所以通常不是连续存放的, 进行地址偏移的时候需要注意
获取变量的实际地址:
int MPI_Address(&a, &address);
获取到a的实际地址, 并储存在address中
这玩意对于基本数据类型, 与&a作用相同, 但是主要是用于在Fortran中解决地址的问题
解决自定义数据类型中对界产生的偏移问题?
输出:

数据类型常用函数
这部分有些函数很迷, 先放着
数据类型查询函数:
int MPI_Type_size(MPI_Datatype datatype, int *size);
int MPI_Type_extent(MPIDatatype datatype, MPI_Aint *extent);
int MPI_Type_ub(MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Aint *displacement);
int MPI_Type_lb(MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Aint *displacement);
分别返回数据类型的大小, 域和上下界
MPI_Aint 为存放地址或位移的变量, 实际上就是地址专用变量, 为long int
-
size为数据类型中数据部分所占用的大小, 等于所有基本数据类型大小之和
相当于sizeof, 只不过sizeof对于自定义数据类型无法使用 -
extent为数据类型实际占用的大小(包括中间对界用的空白)
很迷…啊, 应该只是单个元素?
-
ub-lb=extent
如果没有指定ub & lb, 这俩默认lb=0, ub=extent
例程
MPI_Type_vector()详见下头
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
#define maxbuf 200
#define len 10
#define mp 5
struct data{
double value;
char str;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myid, np;
int root=0;
int startWtime=0;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np);
printf ("Process %d of %d is running.\n",myid,np);
if(myid==root){
startWtime=MPI_Wtime();
}
//--------------------------------------------
//代码部分:
MPI_Aint address1;
int a=1;
MPI_Datatype newType1, newType2;
int size1, size2;
MPI_Aint extent1=0, ub1=0, lb1=0;
MPI_Aint extent2=0, ub2=0, lb2=0;
MPI_Type_contiguous(3, MPI_INT, &newType1);
MPI_Type_commit(&newType1);
MPI_Type_size(newType1, &size1);
MPI_Type_extent(newType1, &extent1);
MPI_Type_ub(newType1, &ub1);
MPI_Type_lb(newType1, &lb1);
MPI_Type_vector(2,3,1,newType1, &newType2);
MPI_Type_commit(&newType2);
MPI_Type_size(newType2,&size2);
MPI_Type_extent(newType2,&extent2);
MPI_Type_ub(newType2,&ub2);
MPI_Type_lb(newType2,&lb2);
if(myid == 0) {
printf(
"size = %d\n"
"entent = %ld\n"
"ub = %ld\n"
"lb = %ld\n"
,size1, extent1, ub1, lb1);
putchar('\n');
printf(
"size = %d\n"
"entent = %ld\n"
"ub = %ld\n"
"lb = %ld\n"
,size2, extent2, ub2, lb2);
putchar('\n');
}
//--------------------------------------------
//Wait for other process to complete the work
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf("Used %lfs.\n",MPI_Wtime()-startWtime);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
输出:

解释:
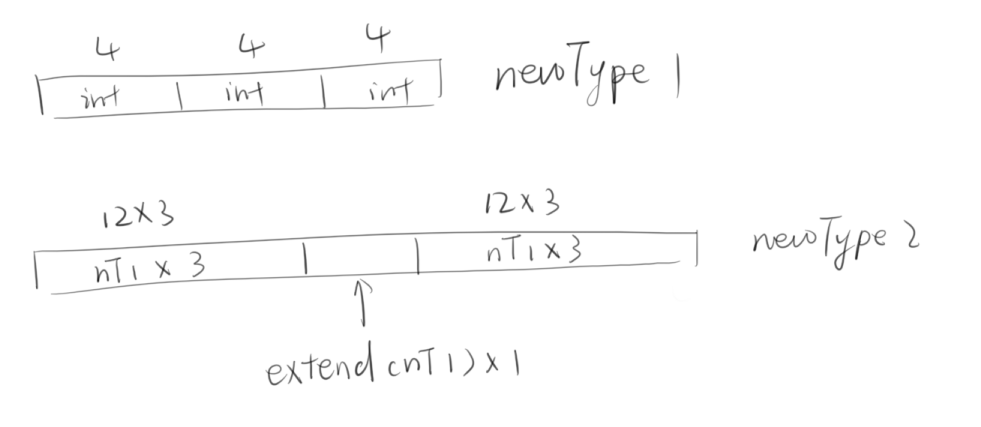
数据类型创建函数:
int MPI_Type_contiguous(int count, MPI_Datatype oldtype, MPI_Datatype *newytpe);
创建一个连续存放的数据类型
新数据类型newtypecount个老数据类型oldtype按域(extent)连续存放构成.
例程:
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
#define maxbuf 200
#define len 10
#define mp 5
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myid, np;
int displs[mp], counts[mp];
int root=0;
int startWtime=0;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np);
printf ("Process %d of %d is running.\n",myid,np);
if(myid==root){
startWtime=MPI_Wtime();
}
//--------------------------------------------
//代码部分:
MPI_Datatype cmplx;
MPI_Status sta;
float a[10]={0};
MPI_Type_contiguous(2, MPI_FLOAT, &cmplx);
MPI_Type_commit(&cmplx);
if(myid==0){
for(int i=0;i<10;++i){
a[i]=i+1.0;
}
MPI_Send(a, 5, cmplx, 1, 99, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}else if(myid==1){
MPI_Recv(a, 5, cmplx, 0, 99, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &sta);
for(int i=0;i<10;++i){
printf("%f\n",a[i]);
}
}
//--------------------------------------------
//Wait for other process to complete the work
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf("Used %lfs.\n",MPI_Wtime()-startWtime);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
本例程相当于注册了一个由俩MPI_FLOAT类型组成的自定义数据类型
输出:

int MPI_Type_vector(int count, int blocklength, int stride,
MPI_Datatype oldtype, MPI_Datatype *newtype);
新数据类型newtype由count个数据块构成,每个数据块由blocklength个连续存放的oldtype构成,相邻两个数据块的位移相差stride x extent(oldtype)个字节.
使用效果详见上头
int MPI_Type_struct(int count, int *array_of_blocklengths,
MPI_Aint *array_of_displacements, MPI_Datatype *array_of_types,
MPI_Datatype *newtype);
新数据类型newtype由count个数据块构成, 第i个数据块包含了array_of_blocklengths[i]个连续存放, 类型为array_of_types[i]的数据, 字节位移为array_of_displacements[i]
例程:
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
#define maxbuf 200
#define len 10
#define mp 5
struct data{
double value;
char str;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myid, np;
int root=0;
int startWtime=0;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np);
printf ("Process %d of %d is running.\n",myid,np);
if(myid==root){
startWtime=MPI_Wtime();
}
//--------------------------------------------
//代码部分:
MPI_Aint address1;
int a=1;
MPI_Datatype newType1, newType2, newType3;
int size1, size2, size3;
MPI_Aint extent1=0, ub1=0, lb1=0;
MPI_Aint extent2=0, ub2=0, lb2=0;
MPI_Aint extent3=0, ub3=0, lb3=0;
MPI_Type_contiguous(3, MPI_INT, &newType1);
MPI_Type_commit(&newType1);
MPI_Type_size(newType1, &size1);
MPI_Type_extent(newType1, &extent1);
MPI_Type_ub(newType1, &ub1);
MPI_Type_lb(newType1, &lb1);
MPI_Type_vector(3,3,3,newType1, &newType2);
MPI_Type_commit(&newType2);
MPI_Type_size(newType2,&size2);
MPI_Type_extent(newType2,&extent2);
MPI_Type_ub(newType2,&ub2);
MPI_Type_lb(newType2,&lb2);
int count3=3;
int blength3[count3]={1,2,3};
MPI_Datatype types3[count3]={MPI_INT, MPI_CHAR, MPI_DOUBLE};
MPI_Aint disp3[count3]={1,2,3};
MPI_Type_struct(count3, blength3, disp3, types3, &newType3);
MPI_Type_commit(&newType3);
MPI_Type_size(newType3,&size3);
MPI_Type_extent(newType3,&extent3);
MPI_Type_ub(newType3,&ub3);
MPI_Type_lb(newType3,&lb3);
if(myid == 0) {
printf(
"size = %d\n"
"extent = %ld\n"
"ub = %ld\n"
"lb = %ld\n"
,size1, extent1, ub1, lb1);
putchar('\n');
printf(
"size = %d\n"
"extent = %ld\n"
"ub = %ld\n"
"lb = %ld\n"
,size2, extent2, ub2, lb2);
putchar('\n');
printf(
"size = %d\n"
"extent = %ld\n"
"ub = %ld\n"
"lb = %ld\n"
,size3, extent3, ub3, lb3);
putchar('\n');
}
//--------------------------------------------
//Wait for other process to complete the work
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf("Used %lfs.\n",MPI_Wtime()-startWtime);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
输出:
Running tool: MPI_Tool
Process 0 of 2 is running.
size = 12
extent = 12
ub = 12
lb = 0size = 108
extent = 108
ub = 108
lb = 0size = 30
extent = 32
ub = 33
lb = 1Process 1 of 2 is running.
Used 0.789576s.Done.
数据类型的使用:
注册
int MPI_Type_commit(MPI_Datatype *datatype);
相当于后头的自定义运算, 需要进行绑定注册
注册后的数据类型可以像原生数据类型一样使用
释放:
int MPI_Type_free(MPI_Datatype datatype);
例程:
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
#define maxbuf 200
#define len 10
#define mp 5
struct data{
double value;
char str;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myid, np;
int displs[mp], counts[mp];
int root=0;
int startWtime=0;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np);
printf ("Process %d of %d is running.\n",myid,np);
if(myid==root){
startWtime=MPI_Wtime();
}
//--------------------------------------------
//代码部分:
int lens[3]={1,1,1};
int size1;
struct data tst[4];
MPI_Datatype newType, type[3]={MPI_DOUBLE, MPI_CHAR, MPI_UB};
MPI_Aint IA, IB, EX , disp[3], size2;
MPI_Status status;
if(myid==0){
for(int i=0;i<4;++i){
tst[i].value=1.0;
tst[i].str='a';
}
}
printf("The Process %d of %d is running. \n",myid,np);
MPI_Address(&tst[0], &IA);
MPI_Address(&tst[0].str, &IB);
disp[0]=0;
disp[1]=IB-IA;
disp[2]=16;
MPI_Type_struct(3, lens, disp, type, &newType);
MPI_Type_commit(&newType);
MPI_Type_size(newType, &size1);
MPI_Type_extent(newType, &size2);
if(myid==0){
printf("The size of Data Tyep is %d, the extent of DataType is %d, "
"the size of tst is %ld. \n", size1, size2, sizeof(tst));
}
if(myid==0){
MPI_Ssend(tst, 4, newType, 1, 99, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}else if(myid==1){
MPI_Recv(tst, 4, newType, 0, 99, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
}
MPI_Type_free(&newType);
if(myid==1){
printf("The values are %f and %c. \n",tst[3].value, tst[3].str);
}
//--------------------------------------------
//Wait for other process to complete the work
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf("Used %lfs.\n",MPI_Wtime()-startWtime);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
输出:

int MPI_Get_elements(MPI_Status *status, MPI_Datatype datatype, int *count);
与MPI_Get_count相似, 但是返回的是消息中所包含的MPI原始数据类型的个数,
其返回的如果不等于MPI_UNDEFINED的话, 则必然是MPI_Get_count的整数倍
例程:
这个码现在就是很迷, 报浮点错误, 到时候在其他环境中试试
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
#define maxbuf 200
#define len 10
#define mp 5
struct data{
double value;
char str;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myid, np;
int root=0;
int startWtime=0;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np);
printf ("Process %d of %d is running.\n",myid,np);
if(myid==root){
startWtime=MPI_Wtime();
}
//--------------------------------------------
//代码部分:
int lens[3]={1,1,1};
int count1, count2;
struct data tst[3];
MPI_Datatype newType, type[3]={MPI_DOUBLE, MPI_CHAR, MPI_UB};
MPI_Aint IA, IB, EX , disp[3], size;
MPI_Status status;
if(myid==0){
for(int i=0;i<3;++i){
tst[i].value=1.0+i;
tst[i].str='a'+i;
}
}
printf("The Process %d of %d is running. \n",myid,np);
MPI_Address(&tst[0], &IA);
MPI_Address(&tst[0].str, &IB);
MPI_Type_extent(MPI_DOUBLE, &EX);
disp[0]=0;
disp[1]=IB-IA;
disp[2]=EX;
MPI_Type_struct(3, lens, disp, type, &newType);
MPI_Type_commit(&newType);
MPI_Type_extent(newType, &size);
if(myid==0){
printf("The Extent of Data Type is %ld.\n", size);
}
if(myid==0){
MPI_Ssend(tst, 3, newType, 1, 99, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}else if(myid==1){
MPI_Recv(tst, 3, newType, 0, 99, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
MPI_Get_count(&status, newType, &count1);
//这句加上会报浮点错误, 不知道咋回事
MPI_Get_elements(&status, newType, &count2);
}
MPI_Type_free(&newType);
if(myid==1){
printf("The values are %lf and %c. \n",tst[1].value, tst[1].str);
printf("The count is %d, the elements is %d. \n",count1, count2);
}
//--------------------------------------------
//Wait for other process to complete the work
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf("Used %lfs.\n",MPI_Wtime()-startWtime);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
数据的打包和拆包:
常用函数:
int MPI_Pack(void *inbuf, int incount, MPI_Datatype datatype, void *outbuf,
int outsize, int *position, MPI_Comm comm);
将缓冲区inbuf中incount个datatype的数据进行打包后存放到outbuf中
- outsize用于检测打包后的数据是否越界
- position为打包缓冲区中的位移, 指向缓冲区中数据末尾的下一个位置(尾指针), 其应该被初始化为0
- 打包后的数据类型为MPI_PACKED
- buf为char类型, pos为字节指针
int MPI_Unpack(void *inbuf, int insize, int *position, void *outbuf,
int outcount, MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Comm comm);
为打包的逆操作
从inbuf中解析outcount个datatype数据到outbuf中
int MPI_Pack_size(int incount, MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Comm comm , int *size);
获得打包后的数据大小, 主要用于预测打包后的数据大小, 以设定outbuf的大小
例程:
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
struct data{
double value;
char str;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myid, np;
int root=0;
int startWtime=0;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np);
printf ("Process %d of %d is running.\n",myid,np);
if(myid==root){
startWtime=MPI_Wtime();
}
//--------------------------------------------
//代码部分:
const int MAX=12, MAXBUFF=200, len=MAX;
int iData[MAX]={0};
double dData[MAX]={0};
char buf[MAXBUFF]={0};
int count1, count2;
MPI_Pack_size(len, MPI_INT, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &count1);
MPI_Pack_size(len, MPI_DOUBLE, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &count2);
printf("count1= %d, count2= %d \n",count1, count2);
int pos=0;
MPI_Status status;
if(myid==0 && np>1){
for(int i=0;i<len;++i){
iData[i]=i;
dData[i]=i;
}
MPI_Pack(iData, len, MPI_INT, buf, MAXBUFF, &pos, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Pack(dData, len, MPI_DOUBLE, buf, MAXBUFF, &pos, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Send(buf, pos, MPI_PACKED, 1, 99, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}else if(myid==1){
MPI_Recv(buf, MAXBUFF, MPI_PACKED, 0, 99, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
int cc=0;
MPI_Get_count(&status, MPI_PACKED, &cc);
printf("RecvNum= %d\n",cc);
MPI_Unpack(buf, MAXBUFF, &pos, iData, len, MPI_INT, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Unpack(buf, MAXBUFF, &pos, dData, len, MPI_DOUBLE, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
printf("Process %d recved the data: \n",myid);
for(int i=0;i<len;++i){
printf("%d ",iData[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
for(int i=0;i<len;++i){
printf("%lf ",dData[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
//--------------------------------------------
//Wait for other process to complete the work
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf("Used %lfs.\n",MPI_Wtime()-startWtime);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
输出:

聚合通信:

常用函数:
进程同步:
int MPI_Barrier(MPI_Comm comm);
Barrier栅栏
用于进程间的同步, 即一个进程调用该函数后, 需要等待通信器内所有进程调用该函数返回
广播:
int MPI_Bcase(void *buffer, int count, MPI_Datatype, int root, MPI_Comm comm);
参数:

用于指定的root进程向通信器内的所有进程发送数据, 其余非root进程用指定的buffer接收数据
对于SPMD而言, 实际上就相当于将root进程的buffer信息发送给所有的其他非root进程, 以完成buffer的同步
例程:
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#define maxbuf 200
#define len 10
#define mp 5
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myid, np, ia[len], iga[maxbuf], i;
int displs[mp], counts[mp];
int root=0;
int startWtime=0;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np);
printf ("Process %d of %d is running.\n",myid,np);
if(myid==root){
startWtime=MPI_Wtime();
}
//--------------------------------------------
//代码部分:
int data=0;
if(myid==root){
data=114514;
}
MPI_Bcast(&data, 1, MPI_INT, root, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
printf("Process %d got the data= %d\n",myid, data);
//--------------------------------------------
//Wait for other process to complete the work
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf("Used %lfms.\n",MPI_Wtime()-startWtime);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
输出:
Process 0 of 4 is running.
Process 0 got the data= 114514
Process 1 of 4 is running.
Process 1 got the data= 114514
Process 3 of 4 is running.
Process 2 of 4 is running.
Process 2 got the data= 114514
Process 3 got the data= 114514
Used 0.762565ms.
收集:
顺序收集函数:
int MPI_Gather(void *sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype sendtype, void *recvbuf,
int recvcount, MPI_Datatype recvtype, int root, MPI_Comm comm);
参数基本上与MPI_Gatherv相近
通信器中的所有进程(包括根进程)将sendbuf中的数据传送给根进程的recvbuf, 根进程按照进程号依次将数据存储在recvbuf, 所以这里用的是void* 的recvbuf和int的recvcount

- 发送和接收的数据类型必须相同
- 非根进程的recvbuf不使用, 但还是要提供
另一个版本的非顺序收集函数
int MPI_Gatherv(void *sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void *recvbuf,int *recvcounts, int *displs,
MPI_Datatype recvtype, int root, MPI_Comm comm);
参数:

- 每个进程发送的数据个数不同
- root进程接收数据时并不连续存放(数据个数不同), 但接收到的数据在recvbuf中是顺序存放的
例程:
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#define maxbuf 200
#define len 10
#define mp 5
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myid, np, ia[len], iga[maxbuf], i;
int displs[mp], counts[mp];
int root=0;
int startWtime=0;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np);
printf ("Process %d of %d is running.\n",myid,np);
if(myid==root){
startWtime=MPI_Wtime();
}
for(int i=0;i<len;++i){
ia[i]=i+myid*len;
}
for(int i=0; i<np; ++i){
displs[i]=20*i;
counts[i]=len;
}
//--------------------------------------------
//Gather:
MPI_Gather(ia, len, MPI_INT, iga, len, MPI_INT, root, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf("The gather values are: \n");
for(int i=0;i<np;++i){
for(int j=0;j<len;++j){
printf("%d ",iga[len*i+j]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
}
//--------------------------------------------
//Gatherv:
MPI_Gatherv(ia, len, MPI_INT, iga, counts, displs, MPI_INT, root, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf ("The gatherv values are :\n");
for(int i=0;i<np;++i){
for(int j=0;j<counts[i];++j){
printf("%d ",iga[displs[i]+j]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
}
//--------------------------------------------
if(myid==root){
printf("Used %lfms.\n",MPI_Wtime()-startWtime);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
输出结果:

另一个版本的收集:
这玩意用的不多
int MPI_Allgatherv(void *sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype datatype,
void *recvbuf, int *recvcounts, int *displs,
MPI_Datatype recvtype, MPI_Comm comm);
MPI_Allgatherv相当于以每个进程为root进程调用一次MPI_Gatherv, 总共调用np次
参数:
- sendbuf:要发送内容的起始地址
- sendcount:要发送的数量
- sendtype:要发送数据的类型
- recvbuf:接收数据要存放的单元的地址
- recvcounts:这是一个整数数组,包含从每个进程要接收的数据量,比如{0, 1} 从0号进程接收0个,从1号进程接收1个
- displs:这是一个整数数组,包含存放从每个进程接收的数据相对于recvbuf的偏移地址
- recvtype:要接收的数据类型
- comm:通信集合
散发:
int MPI_Scatter(void *sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void *recvbuf, int recvcount, MPI_Datatype datatype,
int root, MPI_Comm comm);
参数:
基本与MPI_Bcast()相似, 不做介绍了
与 MPI_Bcast()的对比, 作用一目了然, 相当于数据收集MPI_Gather()的逆操作

另一个版本的散发:
和之前Gatherv相似, 就是任意顺序
用的不多, 以后有用到再说吧
int MPI_Scatterv(void *sendbuf, int *sendcounts, int *displs,
MPI_Datatype datatype, void *recvbuf, int recvcount,
MPI_Datatype datatype, int root, MPI_Comm comm);
使用这个函数的时候, 每个进程是知道自己要多少个数据的, 所以通常配合Gather使用, 先获取每个进程所需的数据量, 然后在根据此分发
例程:
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#define maxbuf 200
#define len 10
#define mp 5
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myid, np, ia[len], iga[maxbuf], i;
int displs[mp], counts[mp];
int root=0;
int startWtime=0;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np);
printf ("Process %d of %d is running.\n",myid,np);
if(myid==root){
startWtime=MPI_Wtime();
}
//--------------------------------------------
//代码部分:
int data[np]={0};
if(myid==root){
for(int i=0;i<np;++i){
data[i]=i*10;
}
}
int recvData=0, dataNum=1;
MPI_Scatter(data, dataNum, MPI_INT, &recvData, dataNum, MPI_INT, root,
MPI_COMM_WORLD);
printf("Process %d got the data= %d\n",myid, recvData);
//--------------------------------------------
//Wait for other process to complete the work
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf("Used %lfms.\n",MPI_Wtime()-startWtime);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
输出:

全散发收集:
int MPI_Alltoall(void *sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void *recvbuf, int recvcount, MPI_Datatype recvtype,
MPI_Comm comm);
通信器中的每个进程的通信就与笛卡尔积类似, 接收每个进程(包括自身)发送的数据, 并向每个进程(包括自己)发送数据
MPI_Alltoall的具体操作是:将进程i的发送缓冲区中的第j块数据发送给进程j,进程j将接收到的来自进程i的数据块放在自身接收缓冲区的第i块位置

参数:
- sendbuf代表发送缓冲区的起始地址
- sendcount代表往每个进程发送的数量
- sendtype代表发送的数据类型
- recvbuf代表接收缓冲区的起始位置
- recvcount代表从每个进程接收的数量
- recvtype代表要接收的类型
- comm代表通信子
所以sendbuf & recvbuf的大小是sendcount * np
例程:
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define maxbuf 200
#define len 10
#define mp 5
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myid, np;
int displs[mp], counts[mp];
int root=0;
int startWtime=0;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np);
printf ("Process %d of %d is running.\n",myid,np);
if(myid==root){
startWtime=MPI_Wtime();
}
//--------------------------------------------
//代码部分:
int data[np]={0};
for(int i=0;i<np;++i){
data[i]=myid*10+i;
}
//MPI_Bcast(&data, 1, MPI_INT, root, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
int recvData[np], dataNum=1;
memset(recvData, 0, sizeof(recvData));
MPI_Alltoall(data, dataNum, MPI_INT, recvData, 1, MPI_INT, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
//output synchronization
int tag=1;
if(myid){
MPI_Status s;
MPI_Recv(data, 1, MPI_INT, myid-1, tag, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &s);
}
printf("Process %d got the data= ",myid);
for(int i=0;i<np;++i){
printf("%d ",recvData[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
if(myid!=(np-1)){
MPI_Send(data, 1, MPI_INT, myid+1, tag, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
//--------------------------------------------
//Wait for other process to complete the work
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf("Used %lfms.\n",MPI_Wtime()-startWtime);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
输出:

归约:
int MPI_Reduce(void *sendbuf, void *recvbuf, int count,
MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Op op,
int root, MPI_Comm comm);
参数:

其中sendbuf大小为count, recvbuf大小为count
MPI_Op的可用操作:

例程:
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
#define maxbuf 200
#define len 10
#define mp 5
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myid, np;
int displs[mp], counts[mp];
int root=0;
int startWtime=0;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np);
printf ("Process %d of %d is running.\n",myid,np);
if(myid==root){
startWtime=MPI_Wtime();
}
//--------------------------------------------
//代码部分:
int data[np]={0};
srand(time(0));
for(int i=0;i<np;++i){
data[i]=rand()%100;
}
//MPI_Bcast(&data, 1, MPI_INT, root, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
int recvData[np]={0}, dataNum=1;
MPI_Reduce(data, recvData, dataNum, MPI_INT, MPI_MAX, root, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
//output synchronization
int tag=1;
if(myid){
MPI_Status s;
MPI_Recv(data, 1, MPI_INT, myid-1, tag, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &s);
}
printf("Process %d hold the data= ",myid);
for(int i=0;i<np;++i){
// cout<<recvData[i]<<endl;
printf("%d ",data[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
if(myid!=(np-1)){
MPI_Send(data, 1, MPI_INT, myid+1, tag, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(!myid){
for(int i=0;i<np;++i){
printf("Process %d got the MAX data: %d\n", myid, recvData[i]);
}
}
//--------------------------------------------
//Wait for other process to complete the work
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf("Used %lfms.\n",MPI_Wtime()-startWtime);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
输出:
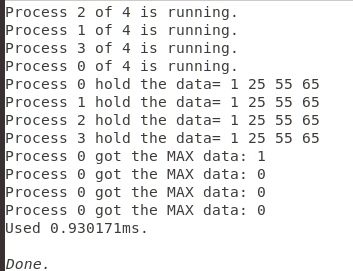
全归约:
用的少, 先放着
int MPI_Allreduce(void *sendbuf, void *recvbuf, int count,
MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Op op, MPI_Comm comm);
就比上头的reduce少了个root参数, 其余含义均相同
归约散发 等:
用的不多, 也暂时放着
int MPI_Reduce_scatter(void *sendbuf, void *recvbuf, int *recvcounts,
MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Op op, MPI_Comm comm);
自定义MPI_Op操作:
注册一个用户自定义操作函数, 使其可以像MPI自带的操作一样使用
int MPI_Op_create(MPI_User_function *func, int commute, MPI_Op *op);
参数:
- func为用户自定义的函数
- commute为一个flag, 为true时可适用交换律, 否则不适用交换律
- OP为操作
用户定义的函数必须满足结合律, 且必须具备4个参数:
typedef void MPI_User_function(void *invec, void *inoutvec, int *len,
MPI_Datatype *datatype)
- invec & inoutvec
为将要被归约的数据所在的缓冲区的首地址, 类比与sort的cmp函数 - len为归约的元素个数
- datatype为数据类型
可以认为invec和inoutvec 是函数中长度为len的数组, 归约的结果重写了inoutvec 的值。每次调用此函数都导致了对这len个元素逐个进行相应的操作
此函数中不能调用任何MPI通信函数, 否则报错
当不在使用这个操作函数时, 需要释放
int MPI_Op_free(MPI_Op *op);
例程:
几个注意点:
- 虽然User_function要求的是void* , 但是由于C的特性, 可以将参数直接定义为其他类型, 在传参时会自动发生类型转换(void* 可以转换为任意类型)
- 自定义函数的返回值也是如此, 只需要在create时强制转换为(MPI_User_function*)即可
- 所绑定的OP要事先定义
#include <cstdio>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
#define maxbuf 200
#define len 10
#define mp 5
//这里定义了一个加法
void myOpFunc(int *invec, int *inoutvec,
int *length, MPI_Datatype *datatype){
int n=*length;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
inoutvec[i]=inoutvec[i]+invec[i];
}
return ;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int myid, np;
int displs[mp], counts[mp];
int root=0;
int startWtime=0;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np);
printf ("Process %d of %d is running.\n",myid,np);
if(myid==root){
startWtime=MPI_Wtime();
}
//--------------------------------------------
//代码部分:
int data[np]={0};
srand(time(0));
for(int i=0;i<np;++i){
data[i]=rand()%100;
}
MPI_Op myOp;
MPI_Op_create((MPI_User_function*)myOpFunc, true, &myOp);
int recvData[np]={0}, dataNum=1;
MPI_Reduce(data, recvData, dataNum, MPI_INT, myOp, root, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
//output synchronization
int tag=1;
if(myid){
MPI_Status s;
MPI_Recv(data, 1, MPI_INT, myid-1, tag, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &s);
}
printf("Process %d hold the data= ",myid);
for(int i=0;i<np;++i){
// cout<<recvData[i]<<endl;
printf("%d ",data[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
if(myid!=(np-1)){
MPI_Send(data, 1, MPI_INT, myid+1, tag, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(!myid){
for(int i=0;i<np;++i){
printf("Process %d got the MAX data: %d\n", myid, recvData[i]);
}
}
//--------------------------------------------
//Wait for other process to complete the work
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid==root){
printf("Used %lfms.\n",MPI_Wtime()-startWtime);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
输出:

进程组 & 通信器:
进程组操作函数:
int MPI_Comm_group(MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Group *group);
获取通信器中的进程组, 保存到group中
int MPI_Group_size(MPI_Group group, int *size);
int MPI_Group_rank(MPI_Group group,int *rank);
俩函数分别返回 给定进程组的大小 和 进程在其中的序号, 与MPI_Comm_size & MPI_Comm_rank完全相同
int MPI_Group_translate_ranks(MPI_Group group1, int n, int *ranks1,
MPI_Group group2, int *rank2);
该函数给出group1中的进程在group2中对应的序号, n为进程的个数
int MPI_Group_compare(MPI_Group group1, MPI_Group group2, int *result);
比较俩进程组, result储存比较的结果:
- MPI_IDENT 进程与其对应的序号都完全相同
- MPI_SIMILAR 进程相同但是对应的序号不同
- MPI_UNEQUAL 其余情况都是这个
int MPI_Group_union(MPI_Group group1, MPI_Group group2, MPI_Group *group);
求进程组的并集, newgroup返回group1 & group2的并集进程组

int MPI_Group_intersection(MPI_Group group1, MPI_Group group2, MPI_Group *group);
就是求交集, 基本上和上头一样
int MPI_Group_difference(MPI_Group group1, MPI_Group group2, MPI_Group *group);
这个是求差集
以及后头的这些:




int MPI_Group_free(MPI_Group *group);
当不在使用进程组的时候可以释放
通信器操作函数:
int MPI_Comm_create(MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Group group, MPI_Comm *newcomm);

int MPI_Comm_dup(MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Comm *newcomm);

int MPI_Comm_split(MPI_Comm comm, int color, int key, MPI_Comm *newcomm);

int MPI_Comm_compare(MPI_Comm comm1, MPI_Comm comm2, int *result);

int MPI_Comm_free(MPI_Comm *comm);

//自动补齐n到np的整数倍
























 1886
1886

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








