session内置对象
request内置对象中的属性只是在当次请求中有效(经过客户端跳转之后就无效),也就是说request只代表当次请求的对象,如果要让客户端跳转之后保存的属性还有效,则可以使用session内置对象,因为该对象表示的是一个用户
经过分析用户的信息保存在request内置对象中是不合理的,应该保存到表示一个用户的内置对象中,就是session内置对象,因为session就算你客户端跳转了保存的属性还是有效的
session内置对象的类型是javax.servlet.http.HttpSession,常见的方法有:
public void serAttribute(java.lang.String name,java.lang.Object value)
保存属性
public java.lang.Object getAttribute(java.lang.String name)
根据属性名取得值(只能取得使用setAttribute()保存的数据值)
public void removeValue(java.lang.String name)
根据属性名称删除对应的值,只能删除使用setAttribute()保存的数据值
public boolean isNew()
判断当前访问的用户是否是第一次访问
public void invalidate()
销毁当前session,一般用来实现用户注销功能
public java.lang.String getID()
取得session的编号,其实这个编号和浏览器中的名字叫做JSESSIONID
和cookie的值是一样的
取得session的编号
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
System.out.println(session.getId());
}
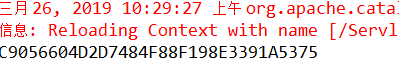
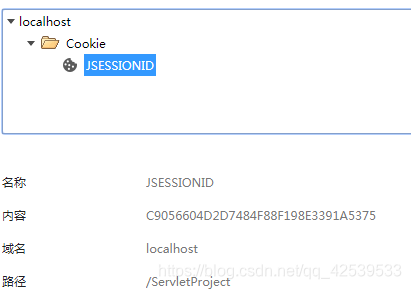
其实浏览器中的JSESSIONID,就是服务器端的session内置对象的编号的副本
判断当前的用户是否是新用户
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//取得session内置对象
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
//判断是否是新用户
boolean flag = session.isNew();
if (flag) {
System.out.println("新人,你好!");
}else {
System.out.println("来啦,老油条!");
}
}

之所以能判断是否是新用户,是因为浏览器发送请求的时候会将cookie带到服务器端,之后使用cookie中JESSIONID和服务器端比较,如果匹配上则不是新的用户,否则就是一个新用户
实现简单的登录验证
index.jsp
<body>
<form action="emp/login" method="POST">
<fieldset>
<legend>请登录</legend>
用户名<input type="text" name="username" placehodler="请输入用户名">
密码š<input type="password" name="pwd" placehodler="请输入密码">
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</fieldset>
</form>
<a href="emp/logout">注销”€</a>
</body>
emp.jsp
<body>
<h1>欢迎${name}来到首页!</h1>
</body>
package com.xie;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class EmpServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String pathInfo = req.getPathInfo();
try {
if ("/login".equals(pathInfo)) {
this.login(req, resp);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 负责登录的方法
* @param req
* @param resp
*/
public void login(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception{
String name = req.getParameter("username");
String pwd = req.getParameter("pwd");
//查询数据库中的用户名和密码和用户输入的进行对比
req.setAttribute("name", "smith");
if ("smith".equals(name)&&"1234".equals(pwd)) {
//应该跳转到欢迎页面或者首页
req.getRequestDispatcher("/emp.jsp").forward(req, resp);
}else {
//保留错误信息
req.setAttribute("msg", "用户名密码不正确!");
//重新返回登录页面再次登录
req.getRequestDispatcher("/index.jsp").forward(req, resp);
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(req, resp);
}
}
之后在单独访问emp.jsp
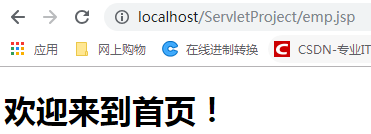
此时发现无法获取用户信息,原因的登录的时候用户名是保存在request内置对象中,只能在当次请求中取得用户名,如果此时还要取得则需要重新登录
这种登录操作最好的方式是将用户信息保存到session内置对象
将用户信息保存到session内置对象
public void login(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception{
String name = req.getParameter("username");
String pwd = req.getParameter("pwd");
//查询数据库中的用户名和密码和用户输入的进行对比
if ("smith".equals(name)&&"1234".equals(pwd)) {
//登录之后将用户信息保存到session内置对象
req.getSession().setAttribute("name", "smith");
//应该跳转到欢迎页面或者首页
req.getRequestDispatcher("/emp.jsp").forward(req, resp);
}else {
//保留错误信息
req.setAttribute("msg", "用户名密码不正确!");
//重新返回登录页面再次登录
req.getRequestDispatcher("/index.jsp").forward(req, resp);
}
}
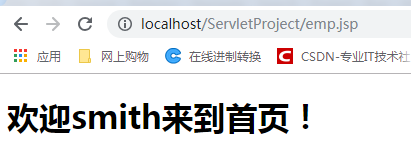
经过客户端跳转页可以取得保存在session内置对象中的信息,因为session表示的是一个用户
只要不关闭浏览器,那么session一直存在(默认30分钟),但是在做一些相关的业务操作的时候(比如删除某些信息)则首先要保证用户是登录的,此时就需要判断了
可以设置session的超时时间,可以设置为任意时间
以后就暂时将用户的信息保存到session内置对象,此时就可以实现登录验证了,在进行一些数据操作的时候需要进行登录的认证
登录判断
package com.xie;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class EmpServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String pathInfo = req.getPathInfo();
try {
if ("/login".equals(pathInfo)) {
this.login(req, resp);
}else if ("/remove".equals(pathInfo)) {
this.removeById(req, resp);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 负责登录的方法
* @param req
* @param resp
*/
public void login(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception{
String name = req.getParameter("username");
String pwd = req.getParameter("pwd");
//查询数据库中的用户名和密码和用户输入的进行对比
if ("smith".equals(name)&&"1234".equals(pwd)) {
//登录之后将用户信息保存到session内置对象
req.getSession().setAttribute("name", "smith");
//应该跳转到欢迎页面或者首页
req.getRequestDispatcher("/emp.jsp").forward(req, resp);
}else {
//保留错误信息
req.setAttribute("msg", "用户名密码不正确!");
//重新返回登录页面再次登录
req.getRequestDispatcher("/index.jsp").forward(req, resp);
}
}
/**
* 删除数据
* @param req
* @param resp
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
public void removeById(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException{
//需要判断用户是否登录,如果登录了则直接操作
if (req.getSession().getAttribute("name")==null) {//表示每有登录
System.out.println("你还没有登录!");
//跳转到登录页面
req.getRequestDispatcher("/index.jsp").forward(req, resp);
} else {
System.out.println("调用业务层代码删除数据!");
}
}
/**
* 负责注销的方法
* @param req
* @param resp
*/
public void logout(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
// req.getSession().invalidate();
System.out.println("注销成功!");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(req, resp);
}
}

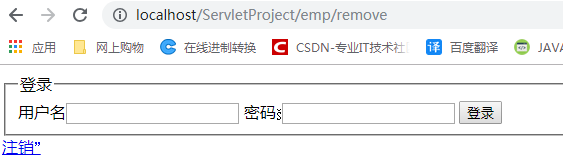
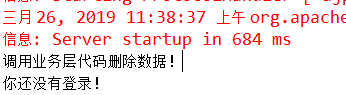
注销用户
package com.xie;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class EmpServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String pathInfo = req.getPathInfo();
try {
if ("/login".equals(pathInfo)) {
this.login(req, resp);
}else if ("/remove".equals(pathInfo)) {
this.removeById(req, resp);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 负责登录的方法
* @param req
* @param resp
* @throws IOException
* @throws ServletException
*/
public void login(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String name = req.getParameter("username");
String pwd = req.getParameter("pwd");
//查询数据库中的用户名和密码和用户输入的进行对比
if ("smith".equals(name)&&"1234".equals(pwd)) {
//登录之后将用户信息保存到session内置对象
req.getSession().setAttribute("name", "smith");
//应该跳转到欢迎页面或者首页
req.getRequestDispatcher("/emp.jsp").forward(req, resp);
}else {
//保留错误信息
req.setAttribute("msg", "用户名密码不正确!");
//重新返回登录页面再次登录
req.getRequestDispatcher("/index.jsp").forward(req, resp);
}
}
/**
* 删除数据
* @param req
* @param resp
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
public void removeById(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException{
//需要判断用户是否登录,如果登录了则直接操作
if (req.getSession().getAttribute("name")==null) {//表示每有登录
System.out.println("你还没有登录!");
//跳转到登录页面
req.getRequestDispatcher("/index.jsp").forward(req, resp);
} else {
System.out.println("调用业务层代码删除数据!");
}
}
/**
* 负责注销的方法
* @param req
* @param resp
*/
public void logout(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
//取得session对象,之后调用注销方法(销毁当前的session)
req.getSession().invalidate();
System.out.println("注销成功!");
}
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String pathInfo = req.getPathInfo();
if ("/emp".equals(pathInfo)) {
this.login(req, resp);
} else if ("/remove".equals(pathInfo)) {
this.removeById(req, resp);
}else if ("logout".equals(pathInfo)) {
this.logout(req, resp);
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(req, resp);
}
}










 本文介绍了session内置对象在用户管理中的应用,包括如何取得session编号、判断新用户、实现登录验证、保存用户信息以及登录和注销用户操作。通过示例说明了session在保持用户状态方面的优势,强调了在客户端跳转后仍能保留信息的有效性。
本文介绍了session内置对象在用户管理中的应用,包括如何取得session编号、判断新用户、实现登录验证、保存用户信息以及登录和注销用户操作。通过示例说明了session在保持用户状态方面的优势,强调了在客户端跳转后仍能保留信息的有效性。
















 709
709

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








