说明:禁止转载,对源码的要求是禁止把这个东西原封不动或非常小量改动后用于课程设计(我很建议你自己动手实现,你会做的比我更好),源码仅供学习参考,思路仅供参考,仍有不足,欢迎评论指出。
3.1 总体功能设计
实现二进制堆的查找、插入、删除、合并、修改操作,及简单应用
3.2 数据结构设计
抽象数据类型的定义
typedef int T;
struct bin_node
{
T key;//值
int degree;//度
bin_node *first_child;//第一个孩子
bin_node *next;//兄弟
bin_node *parent;//父亲
bin_node() :degree(0),first_child(NULL), next(NULL), parent(NULL) {}//默认构造函数
};
3.3 函数原型设计
//查找操作
bin_node* binomial_search(bin_node* heap, T key)
{
果p的值等于key,return p;(开始p为根节点)
否则进入循环,只要p不为空
{
如果有((child = binomial_search(parent->first_child, key)) != NULL)
return child;
parent = parent->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//修改操作:修改节点的值
static void binomial_update_key(bin_node* heap, bin_node* node, T key)
{
如果key小于节点node的值,就调用
binomial_decrease_key(heap, node, key);
大于则调用
binomial_increase_key(heap, node, key);
相等则print不需要修改
}
static void binomial_increase_key(bin_node* heap, bin_node *node, T key)
{
先用search找到要修改的节点,修改key的值,然后调整
如果"当前节点" < "它的左孩子",
则在"它的孩子中(左孩子 和 左孩子的兄弟)"中,找出最小的节点;
然后将"最小节点的值" 和 "当前节点的值"进行互换
交换数据之后,再对"原最小节点"进行调整,使它满足最小堆的性质:父节点 <= 子节点
}
binomial_decrease_key{方法同increase函数}
//删除操作:删除键值为key的节点,并返回删除节点后的二项树
bin_node* binomial_delete(bin_node* heap, T key)
{
调用search函数找到节点的位置
再将被删除的节点的数据上移到它所在的二项树的根节点
while (parent != NULL) parent = node->parent;
由于根节点的孩子节点按度数递减排列,故需要调用reverse函数逆序去掉了根节点的孩子节点,使其按度数升序排列
}
static bin_node* binomial_reverse(bin_node* heap)
{
就是单链表的逆序
先让头的next为空再逐个让p的下一个节点指向p,每次循环后p后移一位
}
BinomialNode* union(bin_node h1,bin_node h2)//合并
{
bin_node *heap;
bin_node *prev_x,*x,*next_x;
heap=merge(h1,h2);//调用merge使两个二项堆的根链表合并成一个链表,合并后的新链表按照'节点的度数'单调递增排序
如果heap为空,返回空值
令prev_x为空,x=heap,next_x=x->next;
当next_x不为空时执行循环
{
如果x的深度不等于next_x的深度或(next_x不指向空且next_x的深度等于next_x的next的深度)
就令prev_x=x; x=next_x;
或者x的key值小于等于next_x的key值时
就令x->next=next_x->next;
调用link函数link(next_x,x);
否则
{
当prev_x为空时,令heap=next_x
否则让prev_x->next=next_x;
再连接link(x,next_x);
让x=next_x;
}
让next_x=x->next;
}
返回heap
}
//两个二项堆的根链表合并成一个链表,合并后的新链表按照'节点的度数'单调递增排序
static bin_node* merge(bin_node h1,bin_node h2)
{
bin_node* head=NULL;
bin_node** pos=&head;
当h1和h2都不为空时执行循环
{
如果h1的度数小于h2的度数,pos指向h1的地址,h1指向h1的next
否则pos指向h2的地址,h2指向h2的next
pos指向*pos的next的地址
}
如果h1不为空,pos指向h1的地址
否则pos指向h2的地址
返回head
}
static void link(bin_node child,bin_node heap)//将"二项堆child的根节点"设为"二项堆heap的左孩子",从而将child整合到heap中去
{
让child的根节点为heap
让child指向heap的左孩子
让heap的左孩子指向child的左孩子
heap的深度加一
}
//插入
bin_node* insert(bin_node heap,int key)
{
bin_node* node;
如果该key值已存在(通过search函数搜索)
输出该key值已存在
返回heap
创建一个为key值的节点,并赋给node
如果node为空
返回heap
否则返回将node和heap合并的根节点(通过合并函数union)
}
3.4 输入输出设计
输入输出主要是内置的测试。LPT调度这个应用在用的时候,可以很容易改成输入输出模块。
3.5 主算法设计
各模块的功能
binomial_link、binomial_union和binomial_merge函数实现合并操作,主程序调用union函数,union函数调用link和merge函数
binomial_search函数实现查找操作
binomial_update_key、 binomial_decrease_key和binomial_increase_key函数改变节点的值,主函数调用update,判断要改小还是改大节点的值,改小则调用decrease和改大则调用increase函数
binomial_insert 和make_binomial_node实现插入一个节点,主函数调用insert找到要插入节点的位置,make_binomial_node申请空间新建节点
binomial_delete、binomial_search 、binomial_reverse函数实现删除一个节点,主函数调用delete函数,delete函数调用search函数找到该节点,删除节点后,delete再调用reverse将去掉了根节点的孩子节点逆序,使其按度数升序排列
binomial_print打印节点
主函数的流程
运行bin_test()函数,新建堆a,b,c分别对插入删除合并函数通过prin函数打印测试,运行LPT(),对堆的pop()进行测试,并实现简单应用。
4.3 个人设计实现(按组员分工)
4.3.1王震
//查找
bin_node* binomial_search(bin_node* heap, T key)
{
bin_node *child;
bin_node *parent = heap;
parent = heap;
while (parent != NULL)
{
if (parent->key == key)
return parent;
else
{
if((child = binomial_search(parent->first_child, key)) != NULL)
return child;
parent = parent->next;
}
}
return NULL;
}
//修改节点的值
static void binomial_update_key(bin_node* heap, bin_node* node, T key)
{
if (node == NULL)
return ;
if(key < node->key)
binomial_decrease_key(heap, node, key);
else if(key > node->key)
binomial_increase_key(heap, node, key);
else
printf("不需要修改");
}
bin_node* make_binomial_node(T key)
{
bin_node* node;
node = (bin_node*)malloc(sizeof(bin_node));
if (node==NULL)
{
printf("申请空间失败\n");
return NULL;
}
node->key = key;
node->degree = 0;
node->parent = NULL;
node->first_child = NULL;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
//减关键字的值:将二项堆heap中的节点node的键值减少为key。
static void binomial_decrease_key(bin_node* heap, bin_node *node, T key)
{
if ((key >= node->key) || (binomial_search(heap, key) != NULL))
{
printf("修改失败,新节点%d已经存在,或者小于要修改节点的值%d", key, node->key);
return ;
}
node->key = key;
bin_node *child, *parent;
child = node;
parent = node->parent;
while(parent != NULL && child->key < parent->key)
{
swap(parent->key, child->key);
child = parent;
parent = child->parent;
}
}
//加关键字的值:将二项堆heap中的节点node的键值增加为key。
static void binomial_increase_key(bin_node* heap, bin_node *node, T key)
{
if ((key <= node->key) || (binomial_search(heap, key) != NULL))
{
printf("修改失败,新节点%d已经存在,或者大于于要修改节点的值%d", key, node->key);
return ;
}
node->key = key;
bin_node *cur, *child, *least;
cur = node;
child = cur->first_child;
while (child != NULL)
{
if(cur->key > child->key)
{
// 如果"当前节点" < "它的左孩子",
// 则在"它的孩子中(左孩子 和 左孩子的兄弟)"中,找出最小的节点;
// 然后将"最小节点的值" 和 "当前节点的值"进行互换
least = child;
while(child->next != NULL)
{
if (least->key > child->next->key)
{
least = child->next;
}
child = child->next;
}
// 交换最小节点和当前节点的值
swap(least->key, cur->key);
// 交换数据之后,再对"原最小节点"进行调整,使它满足最小堆的性质:父节点 <= 子节点
cur = least;
child = cur->first_child;
}
else
{
child = child->next;
}
}
}
//删除节点:删除键值为key的节点,并返回删除节点后的二项树
bin_node* binomial_delete(bin_node* heap, T key)
{
bin_node *node;
bin_node *parent, *prev, *pos;
if (heap==NULL)
return heap;
// 查找键值为key的节点
if ((node = binomial_search(heap, key)) == NULL)
return heap;
// 将被删除的节点的数据数据上移到它所在的二项树的根节点
parent = node->parent;
while (parent != NULL)
{
// 交换数据
swap(node->key, parent->key);
// 下一个父节点
node = parent;
parent = node->parent;
}
// 找到node的前一个根节点(prev)
prev = NULL;
pos = heap;
while (pos != node)
{
prev = pos;
pos = pos->next;
}
// 移除node节点
if (prev)
prev->next = node->next;
else
heap = node->next;
heap = binomial_union(heap, binomial_reverse(node->first_child));
free(node);
return heap;
}
static bin_node* binomial_reverse(bin_node* heap)
{
bin_node* next;
bin_node* tail = NULL;
if (!heap)
return heap;
heap->parent = NULL;
while (heap->next)
{
next = heap->next;
heap->next = tail;
tail = heap;
heap = next;
heap->parent = NULL;
}
heap->next = tail;
return heap;
}
4.3.2刘津源
//合并
bin_node* binomial_union(bin_node* h1, bin_node* h2)
{
bin_node *heap;
bin_node *prev_x, *x, *next_x;
// 将h1, h2中的根表合并成一个按度数递增的链表heap
heap = binomial_merge(h1, h2);
if (heap == NULL)
return NULL;
prev_x = NULL;
x = heap;
next_x = x->next;
while (next_x != NULL)
{
if ( (x->degree != next_x->degree)
|| ((next_x->next != NULL) && (next_x->degree == next_x->next->degree)))
{
// Case 1: x->degree != next_x->degree
// Case 2: x->degree == next_x->degree == next_x->next->degree
prev_x = x;
x = next_x;
}
else if (x->key <= next_x->key)
{
// Case 3: x->degree == next_x->degree != next_x->next->degree
// && x->key <= next_x->key
x->next = next_x->next;
binomial_link(next_x, x);
}
else
{
// Case 4: x->degree == next_x->degree != next_x->next->degree
// && x->key > next_x->key
if (prev_x == NULL)
{
heap = next_x;
}
else
{
prev_x->next = next_x;
}
binomial_link(x, next_x);
x = next_x;
}
next_x = x->next;
}
return heap;
}
static void binomial_link(bin_node* child, bin_node* heap)
{
child->parent = heap;
child->next = heap->first_child;
heap->first_child = child;
heap->degree++;
}
static bin_node* binomial_merge(bin_node* h1, bin_node* h2)
{
bin_node* head = NULL; //heap为指向新堆根结点
bin_node** pos = &head;
while (h1 && h2)
{
if (h1->degree < h2->degree)
{
*pos = h1;
h1 = h1->next;
}
else
{
*pos = h2;
h2 = h2->next;
}
pos = &(*pos)->next;
}
if (h1)
*pos = h1;
else
*pos = h2;
return head;
}
//插入操作
bin_node* binomial_insert(bin_node* heap,T key)
{
bin_node* node;
if (binomial_search(heap, key) != NULL)
{
printf("插入失败,给定的值%d已经存在\n", key);
return heap;
}
node = make_binomial_node(key);
if (node==NULL)
return heap;
return binomial_union(heap,node);
}
void bin_test()
{
bin_heap<int> a;
bin_heap<int> b;
bin_heap<int> c;
//bin_node<int> *d= new bin_node<int>[5];
//bin_node<int> *e = new bin_node<int>[5];
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i)
{
//d[0].key = i;
a.insert(i);
}
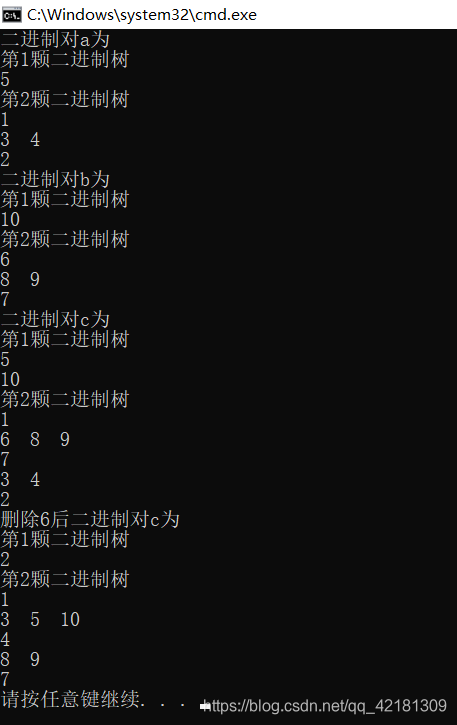
cout << "二进制对a为" << endl;
a.prin();
for (int i = 6; i <= 10; ++i)
b.insert(i);
cout << "二进制对b为" << endl;
b.prin();
c.merge(a.heap(), b.heap());
cout << "二进制对c为" << endl;
c.prin();
c.erase(6);
cout << "删除6后二进制对c为" << endl;
c.prin();
}//我通过二进制堆a,b,c分开测试功能
其中最重要的一个模块是template<class T>
void bin_heap<T>::prin ()
{
bin_node<T> *p = root;//从根节点开始
int i = 1,j = 0;
while (p != NULL)
{
cout << "第" << i << "颗二进制树" << endl;
bin_node<T> *second = p;//second代表每颗树
cout<< second->key<<endl;
second = second->first_child;//不在首节点,向下找
prin_tree(second);
/*while (second != NULL)
{
bin_node<T> *third = second;
while (third != NULL)
{
cout << third->key<<" ";
third = third->next;
}
cout << endl;
second = second->first_child;
}*/
p = p->next;
++i;
}//一颗一颗树的遍历,树按层次遍历
}
Prin函数,这里我起初看注释我是想写循环遍历的,后来发现有的节点遍历不到,所以我写了递归while (p != NULL)
{
cout << "第" << i << "颗二进制树" << endl;
bin_node<T> *second = p;//second代表每颗树
cout<< second->key<<endl;
second = second->first_child;//不在首节点,向下找
prin_tree(second);
这个递归的意思是从每棵树的第一个孩子开始,先往兄弟节点那里遍历(准确说是加入递归栈),不断遍历直到递归栈全部出来,其实我想是做层次遍历的,但这样到深层次就无法按层次,因为不同树的同一层的兄弟节点不是连在一起的,所以不是按层输出,但堆分的很明显了,也达到了检验的效果。
设计的是一个二进制堆,一个经典的应用就是LPT机器调度问题。首先何谓机器调度。假设你有m台机器,刚开始他们都是空闲的,你有n个任务,每个任务的时间是不同的,分配这m台机器,机器只有空闲的时候能够工作,并且一次只能工作一次,求最短的工作时间。
那如何模拟呢?
struct lpt_machine
{
int ma_name;
int avail;
lpt_machine(int i,int j):ma_name(i), avail(j){}
bool operator <(lpt_machine x) { return avail < x.avail; }
bool operator <=(lpt_machine x) { return avail <= x.avail; }
bool operator ==(lpt_machine x) { return avail == x.avail; }
};
void LPT()
{
bin_heap<int> c;
bin_heap<lpt_machine> machine;
int a[7] = { 2,14,4,16,6,5,3 };
int m = 3;
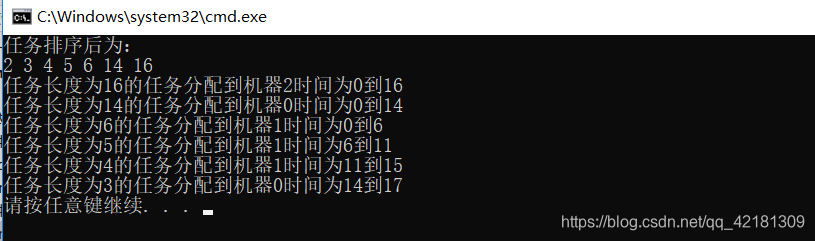
for (int i = 0; i <7; ++i)
c.insert(a[i]);
int b[7];
for (int i = 0; i <7; ++i)
{
b[i] = c.bin_pop();
cout << b[i] << ' ';
}//a任务排序
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
lpt_machine x(i, 0);
machine.insert(x);
}//初始化机器
for (int i = 6; i > 0; --i)
{
lpt_machine y = machine.bin_pop();
cout << "任务长度为" << b[i] << "的任务" << "分配到机器" << y.ma_name << "时间为" << y.avail
<< "到" << (y.avail + b[i]) << endl;
y.avail += b[i];
machine.insert(y);
}//生成调度方案
}
首先先设计一个机器的结构体,为了简单,我就没设计给它名字呢,直接给了它一个int表示名字。int a[7] = { 2,14,4,16,6,5,3 };这是我人为定义的一个任务序列,内容代表时长,机器我也初始化为3个, for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
lpt_machine x(i, 0);
machine.insert(x);
}//初始化机器
为什么用这个,因为便于检验正确性,它的正确答案应该是17
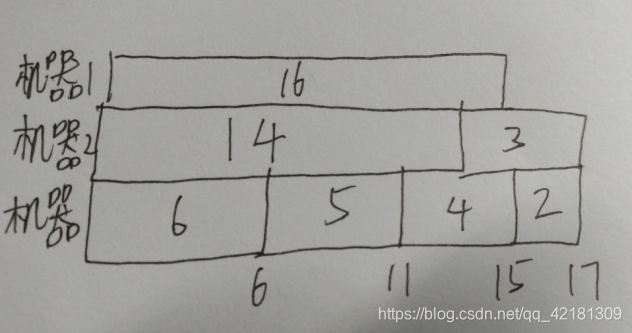
这是它一个其中的调度。然后你要做的第一件事是堆排序给任务排好顺序,然后机器是有个空闲时间的,你先给机器建立一个堆,依此把任务放进去,每次放任务进去的时候y.avail += b[i],机器的空闲时间就增加了,相当于模拟机器执行任务,然后堆顶的机器是空闲时间是最小的,直到任务调完。生成了机器调度序列。
5 测试与调试
Bin_test()
LPT()




 本文详细介绍了二进制堆的数据结构设计、算法实现及其在机器调度问题中的应用。涵盖了查找、插入、删除、合并、修改等核心操作,以及LPT机器调度问题的经典案例。
本文详细介绍了二进制堆的数据结构设计、算法实现及其在机器调度问题中的应用。涵盖了查找、插入、删除、合并、修改等核心操作,以及LPT机器调度问题的经典案例。
















 984
984

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








