http://poj.org/problem?id=3469
poj 3469 Dual Core CPU //最小割(最大流)
Dual Core CPU
Time Limit: 15000MS Memory Limit: 131072K Total Submissions: 27115 Accepted: 11691 Case Time Limit: 5000MS Description
As more and more computers are equipped with dual core CPU, SetagLilb, the Chief Technology Officer of TinySoft Corporation, decided to update their famous product - SWODNIW.
The routine consists of N modules, and each of them should run in a certain core. The costs for all the routines to execute on two cores has been estimated. Let's define them as Ai and Bi. Meanwhile, M pairs of modules need to do some data-exchange. If they are running on the same core, then the cost of this action can be ignored. Otherwise, some extra cost are needed. You should arrange wisely to minimize the total cost.
Input
There are two integers in the first line of input data, N and M (1 ≤ N ≤ 20000, 1 ≤ M ≤ 200000) .
The next N lines, each contains two integer, Ai and Bi.
In the following M lines, each contains three integers: a, b, w. The meaning is that if module a and module b don't execute on the same core, you should pay extra w dollars for the data-exchange between them.Output
Output only one integer, the minimum total cost.
Sample Input
3 1 1 10 2 10 10 3 2 3 1000Sample Output
13Source
POJ Monthly--2007.11.25, Zhou Dong
题意:求将元素划分成两个集合,元素划分到不同集合有对应的代价,且某两个元素不在同一集合也有代价。
这是一个最小割的问题。(可以用最大流跑出来)
将顶点连接到源点和汇点,并将且某两个元素不在同一集合有代价的元素连接起来。
如图
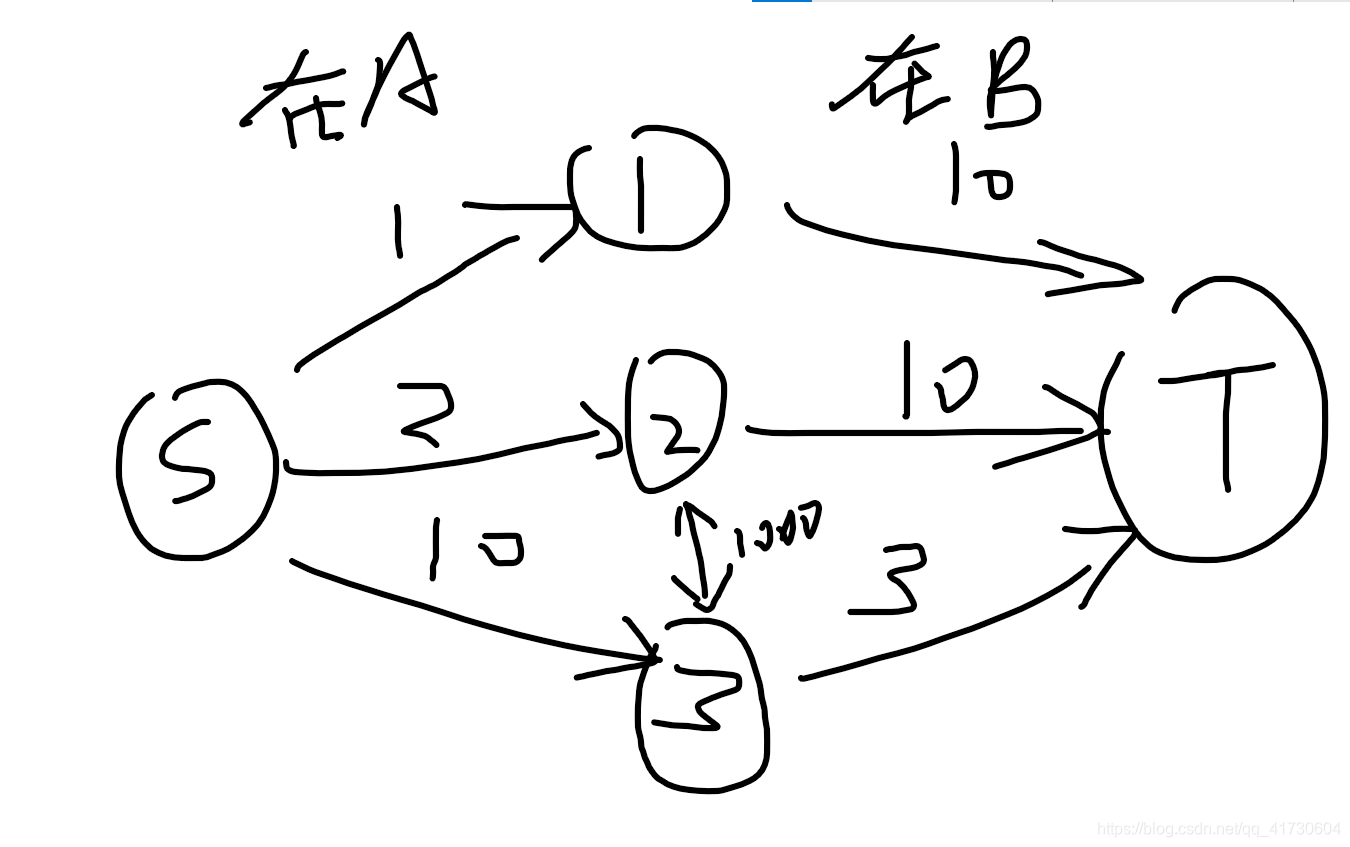
如果已经划分好两个集合,那么此时的最小割肯定也包含两个集合中间的连接线(当然需要双向边),那么答案就是保证是对的。
最大流跑出最小割就是答案。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<climits>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define mod 1000000007
#define LL long long
const int max_n = 20010;
struct no{int to,cap,rev;}; //arc
vector<no>g[max_n]; //图
int level[max_n]; //到起点的距离
int iter[max_n]; //当前弧,在其之前的边已经没用了
void addarc(int s,int e,int c){
g[s].push_back((no){e,c,g[e].size()});
g[e].push_back((no){s,0,g[s].size()-1});
}
//更新层次,即level
void bfs(int s){
memset(level,-1,sizeof(level));
level[s]=0;
queue<int>q;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
int now=q.front();q.pop();
for(int i=0;i<(int)g[now].size();i++){
no &arc=g[now][i];
if(level[arc.to]!=-1||arc.cap<=0) continue;
level[arc.to]=level[now]+1;
q.push(arc.to);
}
}
}
//寻找增广路
int dfs(int v,int t,int f){
if(v==t) return f;
for(iter[v];iter[v]<(int)g[v].size();iter[v]++){
no &arc=g[v][iter[v]];
if(arc.cap<=0||level[arc.to]!=level[v]+1) continue;
int d=dfs(arc.to,t,min(f,arc.cap));
if(d>0) {
arc.cap=arc.cap-d;
g[arc.to][arc.rev].cap+=d;
return d;
}
}
return 0;
}
int Dinic(int s,int t){
int re=0;
while(1){
bfs(s);
memset(iter,0,sizeof(iter));
if(level[t]==-1) return re;
int f;
while((f=dfs(s,t,INT_MAX))>0)
re=re+f;
}
return re;
}
int main(){
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false);
int m,n;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int a,b;cin>>a>>b;
addarc(0,i,a);
addarc(i,n+1,b);
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int a,b,w;cin>>a>>b>>w;
addarc(b,a,w);
addarc(a,b,w);
}
cout<<Dinic(0,n+1);
return 0;
}








 探讨了在双核CPU环境下如何通过最小割算法优化模块调度成本,实现数据交换代价最小化。
探讨了在双核CPU环境下如何通过最小割算法优化模块调度成本,实现数据交换代价最小化。
















 705
705

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








