ESP32多线程
代码:
void setup()
{
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000);
xTaskCreate(
taskOne, /* Task function. */
"TaskOne", /* String with name of task. */
10000, /* Stack size in bytes. */
NULL, /* Parameter passed as input of the task */
1, /* Priority of the task. */
NULL); /* Task handle. */
xTaskCreate(
taskTwo, /* Task function. */
"TaskTwo", /* String with name of task. */
10000, /* Stack size in bytes. */
NULL, /* Parameter passed as input of the task */
1, /* Priority of the task. */
NULL); /* Task handle. */
}
void loop()
{
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
delay(1000);
}
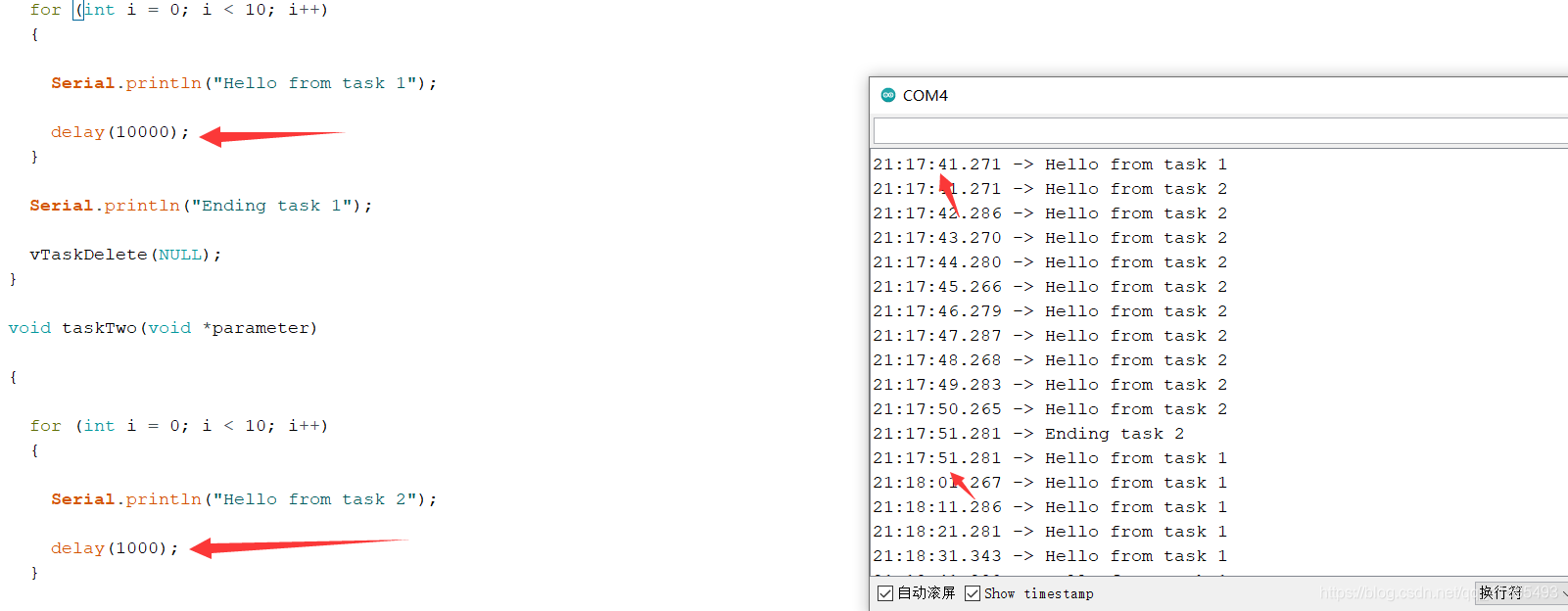
void taskOne(void *parameter)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Serial.println("Hello from task 1");
delay(10000);
}
Serial.println("Ending task 1");
vTaskDelete(NULL);
}
void taskTwo(void *parameter)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Serial.println("Hello from task 2");
delay(1000);
}
Serial.println("Ending task 2");
vTaskDelete(NULL);
}







 本文探讨了ESP32微控制器如何利用其内置的多线程能力进行并发处理。通过示例代码,展示了如何创建并管理线程,以实现更高效的资源利用和任务并行。
本文探讨了ESP32微控制器如何利用其内置的多线程能力进行并发处理。通过示例代码,展示了如何创建并管理线程,以实现更高效的资源利用和任务并行。
















 1884
1884

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








