首先创建一个dog的接口包含bark()和run(),然后去实现这个接口重写对应方法加以输出方便观察。
public interface Dog {
String bark();//叫
void run();//跑
}
public class DogVO implements Dog {
@Override
public String bark() {
System.out.println("狗在叫");
return "汪~汪~汪";
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("狗在跑");
}
}
2.实现动态代理Proxy中有一个静态方法newProxyInstance需要三个参数,先看方法然后再一一介绍
@CallerSensitive
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
/*
* Look up or generate the designated proxy class.
*/
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
/*
* Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler.
*/
try {
if (sm != null) {
checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl);
}
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
final InvocationHandler ih = h;
if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
cons.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
} catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
} else {
throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
}
}
一:ClassLoader loader 类加载。对需要代理对象进行加载
二:Class<?>[] interfaces 接口对象数组。代理对象的接口数组
三:InvocationHandler h 动态代理对象必须实现InvocationHandler接口,每个代理类的实例都关联到了一个handler,当我们通过代理对象调用一个方法的时候,这个方法的调用就会被转发为由InvocationHandler这个接口的 invoke 方法来进行调用。
InvocationHandler h=new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
System.out.println("代理 - 执行"+method.getName()+"方法前");
Object invoke = method.invoke(obj,args);
System.out.println("代理 - 执行"+method.getName()+"方法后 invoke:"+invoke);
return null;
}
};
上图是被 Lambda 简化的部分
invoke方法中 三个参数分别指 对象、方法和参数
一般我们可以从中获取到方法信息和参数信息做特殊处理 ,下图为动态代理的整个过程。
/**
* 动态代理
*/
public class ProxyUtil {
private Object obj;
public ProxyUtil(Object obj){
this.obj = obj;
}
public Object proxyMethod(){
Assert.notNull(obj,"代理对象不能为null");
ClassLoader classLoader = obj.getClass().getClassLoader();//类加载
Class<?>[] interfaces = obj.getClass().getInterfaces();//接口
Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces,
(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) -> {//Lambda
System.out.println("代理 - 执行"+method.getName()+"方法前");
Object invoke = method.invoke(obj,args);
System.out.println("代理 - 执行"+method.getName()+"方法后 invoke:"+invoke);
return invoke;
});
return o;
}
}
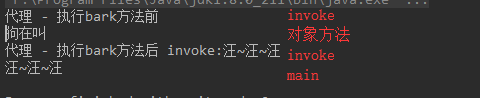
测试=================
Dog dog = new DogVO();
dog = (Dog) new ProxyUtil(dog).proxyMethod();
System.out.println(dog.bark());
观察输出顺序
























 4243
4243

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








