这是一个空的字符驱动程序,供测试
步骤一:申请或指定一个特定没有被其他设备使用的编号
步骤二:生成一个描述字符信息的结构体变量,并将这个变量纳入到系统变量中
步骤三:定义这个设备对应的操作函数
mychr.c文件如下:
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
//设备的名称
#define DEVICE_NAME "emptyChr"
//主设备号
int major=0;
//描述设备结构体指针
struct cdev *empty_cdev;
//打开关闭设备操作函数
int empty_chr_open(struct inode *node,struct file *filep);
int empty_chr_release(struct inode *node,struct file *filep);
//描述设备操作时对应的函数入口的结构体
struct file_operations empty_chr_fops={
.owner=THIS_MODULE,
.open=empty_chr_open,
.release=empty_chr_release,
};
//open
int empty_chr_open(struct inode *node,struct file *filep)
{
printk("empty chr open\n");
return 0;
}
//close
int empty_chr_release(struct inode *node,struct file *filep)
{
printk("empty chr close\n");
return 0;
}
static int __init my_chr_init(void)
{
dev_t dev;
int err=0;
//指定动态分配设备号
if(!major){//动态分配
alloc_chrdev_region(&dev,0,1,DEVICE_NAME);
major=MAJOR(dev);
}else{//静态指定设备号
dev=MKDEV(major,0);
register_chrdev_region(dev,1,DEVICE_NAME);
}
//生成设备号信息描述的结构体对象,并将该结构体变量纳入到系统管理中
empty_cdev=cdev_alloc();
empty_cdev->owner=THIS_MODULE;
empty_cdev->ops=&empty_chr_fops;
err=cdev_add(empty_cdev,dev,1);
if(err){
printk("add device to kernet error\n");
}
printk("my first chr has been loaded\n");
return err;
}
static void __exit my_chr_exit(void)
{
printk("my first chr has been removed\n");
cdev_del(empty_cdev);
//释放分配或指定的设备号
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,0),1);
return ;
}
module_init(my_chr_init);
module_exit(my_chr_exit);
Makefile文件如下:
obj-m =mychr.o
all:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(shell pwd) modules
clean:
-rm *.o *.order *.symvers *.mod.c
命令操作步骤:
make //编译文件
insmod myche.ko //加入内核模块
dmesg |tail //可以查看加入模块成功的输出信息
cat /proc/devices //查看我们加入的设备被分配的设备号
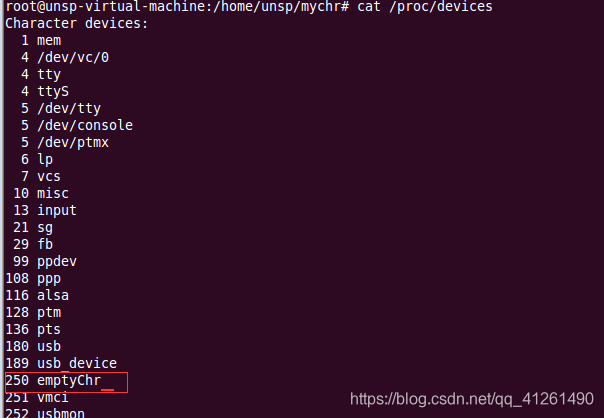
mknod /dev/emptychr c 250 0 //用mknod命令来申请设备文件
ls /dev/emptychr -l 
然后可以写一个简单的程序试一下,我写的是打开文件,读取文件的程序,成功。

























 940
940

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










