制作这个素材是因为无意间发现一个非常炫酷的网站GLSL Sandbox(由于在外网,有时候可能进不去),这个网站提供很多图形,这些图形都是通过一个片段着色器代码进行实现的,刚好spec能提供相关的接口,因此实现了这个素材。
如果你不会写这样的代码,不用担心,我也不会写,但是接下来,我会教你怎么对GLSL Sandbox上的代码进行修改,使得这些素材能够“更好”的在spec中显示。
需要注意的是,这个素材占有相对会较高,具体占有跟代码复杂度和渲染区域相关
首先,你必须了解GLSL的一些东西
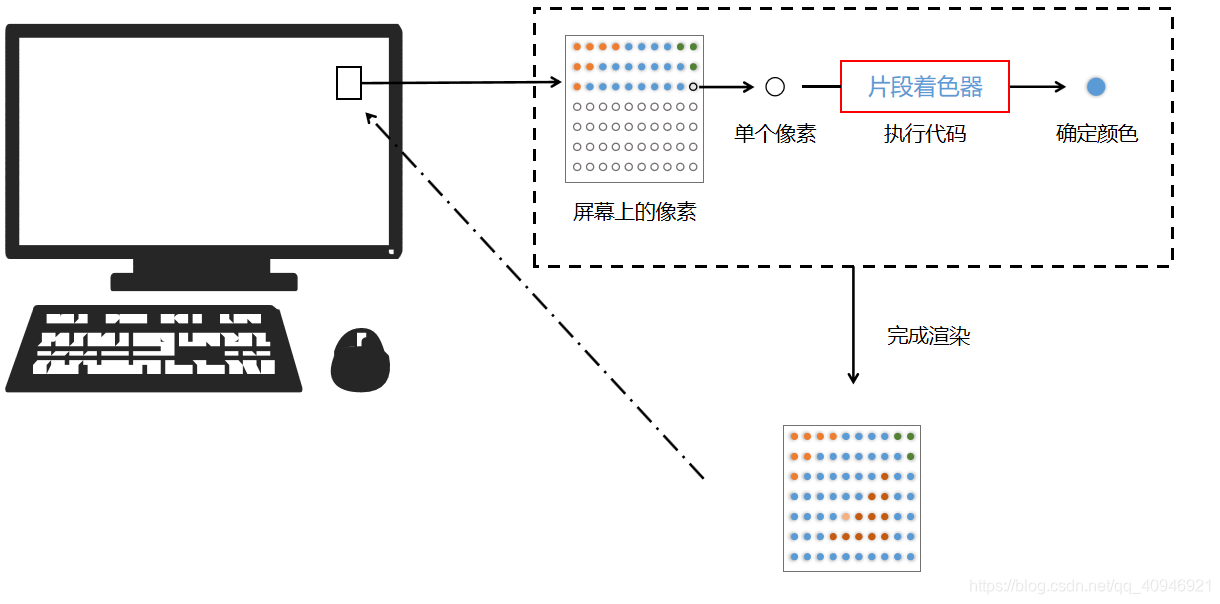
片段着色器代码的作用就是确定一个片段坐标对应像素的颜色,过程看起来就像是这样,我们要完成的,就是片段着色器的部分
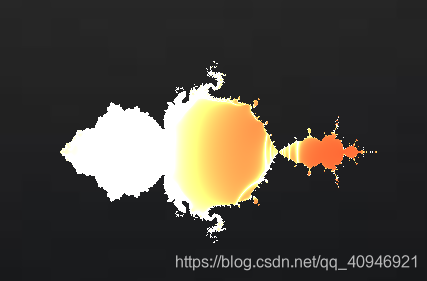
然后我们以一个简单的图形代码为例进行说明
#ifdef GL_ES
precision mediump float;
#endif
#extension GL_OES_standard_derivatives : enable
uniform float time;
uniform vec2 mouse;
uniform vec2 resolution;
varying vec2 surfacePosition;
uniform float peak;
#define PI 3.141592653
#define TWO_PI 2.0*PI
#define t time*0.3
#define MAX 30.
void main( void ) {
vec2 uv = (gl_FragCoord.xy - resolution * 0.5) / max(resolution.x, resolution.y) * 4.0;
uv *= 1.0;
vec2 z = uv;
float e = 0.0;
for (float i=0.0;i<=MAX;i+=1.0) {
z = vec2(z.x * z.x - z.y * z.y, 2.0 * z.x * z.y) - z*cos(t)+uv*sin(t);
e += 0.01*peak/abs(sin(t+z.y) * sin(z.x));
}
gl_FragColor = vec4(vec3(e,e*0.4,e*0.2),1.0);
}
可以看出这个代码是类似于C语言的,如果你会C/C++的话,这样的代码其实并不陌生。
最终目的:确定输出颜色
跟C语言一样,main是主函数入口,主函数运行结束之后,gl_FragColor的值就是该像素的颜色,也有一些着色器代码不是使用gl_FragColor,而是定义了一个out vec4类型的输出变量(可能会叫fragColor)作为输出颜色。
gl_FragColor是一个vec4类型的变量,vec4是一个存储着四个浮点值的变量,你可以使用.xyzw(或者.rgba)获取对应分量的值
vec4可以理解成四维向量(x,y,z,w),也可以理解为颜色(r,g,b,a),需要注意的是,片段着色器中的r,g,b,a的范围需要保证在[0,1]之间,比如(0,0,0,1)表示黑色,(1,1,1,1)表示白色,第4个分量alpha可以理解为透明度。
例如你可以这样对color进行操作:
vec4 color;
float alpha=color.a; //获取第四个分量,跟.w作用一样
vec2 v2=color.rg; //获取红,绿,组成的vec2
vec3 v3=color.rgb; //获取红,绿,蓝通道变量
uniform float time; //获取当前以毫秒为基准的时间
uniform vec2 mouse; //获取鼠标的坐标
uniform vec2 resolution; //当前图形的分辨率(大小)
uniform float peak; //频谱引擎的峰值
uniform float rms; //频谱引擎的均值uniform表示这些变量是外部输入的,目前来说spec片段图形支持的外部变量只有这些
宏定义
#define PI 3.141592653
#define TWO_PI 2.0*PI
#define t time*0.3
#define MAX 30.有一些#define a b 这样格式的代码,#define就是一个简单的宏替换,说白了就是把下面的代码中的 a 用 b 替换。比如第一个,就是把代码中出现的PI替换成3.141592653
#define PI 3.1415926535
float pi=PI*5;
/*等价于*/
float pi=3.1415926535*5;这样做就是方便为了给一些变量取别名,在不修改代码的情况下方便理解,如果理解了上述的内容,那么可以开始进行实际操作了。
核心步骤一——剔除背景
当你复制一个GLSL Sandbox中的代码到spec中,然后编译,你可能就会发现大多数图形都有一个背景,产生这个背景主要原因是因为sandbox中的代码没有做透明度(alpha)计算(也就是的gl_FragColor的第四分量),去除这个背景就是接下来要做的事情。
如果图形有彩色背景(也就是渐变色,非纯色的),那么需要做如下处理
你需要找到代码中绘制背景部分的代码,有些代码可能会把背景的绘制放到一个函数里面,你需要做的就是去除这个函数以及它的调用,对于关联的vec3变量可以使用(0.0,0.0,0.0)进行替换,经过这个处理之后,图形的背景应该以及变成黑色了,如果你是高手的话,完全可以现在就把图形改成背景透明的,并且效果会非常好。如果并不熟悉代码,那么可以按下面的操作进行。
此刻你拥有的应该是一个具有纯色背景(一般是黑色)的图形
如果你拥有的图形背景不是黑色的,你可能需要找一下代码中的一些vec3变量,一般背景颜色的变量命名(或者宏)会有back,background之类的字样,修改为(0.0,0.0,0.0),这样就变成黑色的了
计算Alpha(透明度)
gl_FragColor = vec4(vec3(e,e*0.4,e*0.2),1.0);回到一开始的代码,你会发现代码中gl_FragColor的第四分量(alpha)直接被设置为1.0,也就是不透明。正是因为这样,才产生了黑色的背景。我们要做的就是要修改代码,在当前像素如果是黑色的时候,透明度设置为0;
所以就有以下的一些方法
1.使用某个颜色分量(r,g,b)作为alpha值,就像下面这样。
gl_FragColor = vec4(vec3(e,e*0.4,e*0.2),1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = gl_FragColor.r; //使用红色通道作为透明度
2.同时考虑三个通道的影响
gl_FragColor = vec4(vec3(e,e*0.4,e*0.2),1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = (gl_FragColor.r+gl_FragColor.g+gl_FragColor.b)/3.0; //取均值
gl_FragColor = vec4(vec3(e,e*0.4,e*0.2),1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = max(gl_FragColor.r,max(gl_FragColor.g,gl_FragColor.b)); //取最大值
3.以某个阈值对alpha进行划分
gl_FragColor = vec4(vec3(e,e*0.4,e*0.2),1.0);
if(gl_FragColor.r+gl_FragColor.g+gl_FragColor.b>0.1)
gl_FragColor.a=1.0;
else
gl_FragColor.a=0.0;上面的方法是绘制好图形之后,将图形中的某些颜色设置为透明色,当然不止上面的这些方法,这样做能达到一些较好的效果,但是对于一些特殊的图形,比如说背景是黑色的,而图形中也有一部分东西也是黑色的,通过这个方法,会将所有黑色变透明,这并不是我们想要的,想要解决这个问题,就需要你更多的去了解这个代码,通过代码来确定alpha值,而不是通过rgb分量来确定alpha值,spec中的自带素材【GLSL_立方体】就是通过这样的方法解决的。感兴趣可以看一下。
自定义修改
GLSL Sandbox中大多数代码写的非常好,有些代码会通过宏定义或者变量来定义一些属性,比如颜色,大小之类的一些信息。比如这个字母素材代码:

// N041020N
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
vec2 uv;
uniform float time;
uniform vec2 resolution;;
const vec2 ch_size = vec2(1.0, 2.0) * 0.8; // character size (X,Y)
const vec2 ch_space = ch_size + vec2(1.0, 1.0); // character distance Vector(X,Y)
const vec2 ch_start = vec2 (ch_space.x * -5., 1.); // start position
vec2 ch_pos = vec2 (0.0, 0.0); // character position(X,Y)
#define REPEAT_SIGN false // True/False; True=Multiple, False=Single
#define n0 ddigit(0x22FF);
#define n1 ddigit(0x0281);
#define n2 ddigit(0x1177);
#define n3 ddigit(0x11E7);
#define n4 ddigit(0x5508);
#define n5 ddigit(0x11EE);
#define n6 ddigit(0x11FE);
#define n7 ddigit(0x2206);
#define n8 ddigit(0x11FF);
#define n9 ddigit(0x11EF);
#define A ddigit(0x119F);
#define B ddigit(0x927E);
#define C ddigit(0x007E);
#define D ddigit(0x44E7);
#define E ddigit(0x107E);
#define F ddigit(0x101E);
#define G ddigit(0x807E);
#define H ddigit(0x1199);
#define I ddigit(0x4466);
#define J ddigit(0x4436);
#define K ddigit(0x9218);
#define L ddigit(0x0078);
#define M ddigit(0x0A99);
#define N ddigit(0x8899);
#define O ddigit(0x00FF);
#define P ddigit(0x111F);
#define Q ddigit(0x80FF);
#define R ddigit(0x911F);
#define S ddigit(0x8866);
#define T ddigit(0x4406);
#define U ddigit(0x00F9);
#define V ddigit(0x2218);
#define W ddigit(0xA099);
#define X ddigit(0xAA00);
#define Y ddigit(0x4A00);
#define Z ddigit(0x2266);
#define _ ch_pos.x += ch_space.x;
#define s_dot ddigit(0);
#define s_minus ddigit(0x1100);
#define s_plus ddigit(0x5500);
#define s_greater ddigit(0x2800);
#define s_less ddigit(0x8200);
#define s_sqrt ddigit(0x0C02);
#define nl1 ch_pos = ch_start; ch_pos.y -= 3.0;
#define nl2 ch_pos = ch_start; ch_pos.y -= 6.0;
#define nl3 ch_pos = ch_start; ch_pos.y -= 9.0;
float dseg(vec2 p0, vec2 p1)
{
vec2 dir = normalize(p1 - p0);
vec2 cp = (uv - ch_pos - p0) * mat2(dir.x, dir.y,-dir.y, dir.x);
return distance(cp, clamp(cp, vec2(0), vec2(distance(p0, p1), 0)));
}
bool bit(int n, int b)
{
return mod(floor(float(n) / exp2(floor(float(b)))), 2.0) != 0.0;
}
float d = 1e6;
void ddigit(int n)
{
float v = 1e6;
vec2 cp = uv - ch_pos;
if (n == 0) v = min(v, dseg(vec2(-0.405, -1.000), vec2(-0.500, -1.000)));
if (bit(n, 0)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2( 0.500, 0.063), vec2( 0.500, 0.937)));
if (bit(n, 1)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2( 0.438, 1.000), vec2( 0.063, 1.000)));
if (bit(n, 2)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2(-0.063, 1.000), vec2(-0.438, 1.000)));
if (bit(n, 3)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2(-0.500, 0.937), vec2(-0.500, 0.062)));
if (bit(n, 4)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2(-0.500, -0.063), vec2(-0.500, -0.938)));
if (bit(n, 5)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2(-0.438, -1.000), vec2(-0.063, -1.000)));
if (bit(n, 6)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2( 0.063, -1.000), vec2( 0.438, -1.000)));
if (bit(n, 7)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2( 0.500, -0.938), vec2( 0.500, -0.063)));
if (bit(n, 8)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2( 0.063, 0.000), vec2( 0.438, -0.000)));
if (bit(n, 9)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2( 0.063, 0.063), vec2( 0.438, 0.938)));
if (bit(n, 10)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2( 0.000, 0.063), vec2( 0.000, 0.937)));
if (bit(n, 11)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2(-0.063, 0.063), vec2(-0.438, 0.938)));
if (bit(n, 12)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2(-0.438, 0.000), vec2(-0.063, -0.000)));
if (bit(n, 13)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2(-0.063, -0.063), vec2(-0.438, -0.938)));
if (bit(n, 14)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2( 0.000, -0.938), vec2( 0.000, -0.063)));
if (bit(n, 15)) v = min(v, dseg(vec2( 0.063, -0.063), vec2( 0.438, -0.938)));
ch_pos.x += ch_space.x;
d = min(d, v);
}
mat2 rotate(float a)
{
float c = cos(a);
float s = sin(a);
return mat2(c, s, -s, c);
}
vec3 hsv2rgb_smooth( in vec3 c )
{
vec3 rgb = clamp( abs(mod(c.x*6.0+vec3(0.0,4.0,2.0),6.0)-3.0)-1.0, 0.0, 1.0 );
rgb = rgb*rgb*(3.0-2.0*rgb); // cubic smoothing
return c.z * mix( vec3(1.0), rgb, c.y);
}
void main( void )
{
vec2 aspect = resolution.xy / resolution.y;
uv = ( gl_FragCoord.xy / resolution.y ) - aspect / 2.0;
float _d = 1.0-length(uv);
uv *= 10;
uv -= vec2(-3., 1.);
//uv *= rotate(time+uv.x*0.05);
vec3 ch_color = hsv2rgb_smooth(vec3(time*0.4+uv.y*0.1,0.5,1.0));
uv.x += 0.5+sin(time+uv.y*0.7)*0.5;
ch_pos = ch_start;
uv.y -= 0.5;
_ _ _ _ _ S P E C _ nl1; _ _ _ _ I T A L I N K nl2;
vec3 color = mix(ch_color, vec3(0), 1.0- (0.08 / d*2.0)); // shading
gl_FragColor = vec4(color, color.x);
}这些代码调整了字体的格式:
const vec2 ch_size = vec2(1.0, 2.0) * 0.8; // character size (X,Y)
const vec2 ch_space = ch_size + vec2(1.0, 1.0); // character distance Vector(X,Y)
const vec2 ch_start = vec2 (ch_space.x * -5., 1.); // start position
vec2 ch_pos = vec2 (0.0, 0.0); // character position(X,Y)
uv确定了图形的缩放
uv *= 10;这个确定了输出的字母 (其实是通过宏定义调用函数):
_ _ _ _ _ S P E C _ nl1; _ _ _ _ I T A L I N K nl2; 如果属性并没有明确定义,你可以尝试修改代码中的常量(数字)
或许你并不知道这串数字的作用,你完全可以改动一下,然后点编译,说不定会有些什么意想不到的效果哦
说这么多差点忘了spec是一个频谱软件?
spec对片段代码提供了单频谱数据的输入,输入的值是一个float类型的数据,并且值的大小位于[0,1.0]之间, 你可以在着色器代码上声明两个变量,然后就能在代码中使用了
uniform float peak; //频谱引擎的峰值
uniform float rms; //频谱引擎的均值怎么用呢?在上面的代码中你可能已经找到某些常量数字代表的属性,你只需要把这个float跟这个数据关联起来就好了。
比如我们已经知道上面字母素材uv*=10确定了缩放,我们可以这么改:
首先声明peak变量
uniform float peak;然后peak跟uv参数关联
uv *= 10/peak;如果此时你的电脑没有发出声音,你会发现图形不见了,因为peak为0,除数为0,其实是出错了。
因此可以改成这样:
uv *= 10/(0.1+peak);你会发现字母会随着节奏进行伸缩,就像下面这样:

好了,这个素材基本就是这样了,遇到问题可以评论,作者看到第一时间回复=.=





 本文介绍如何利用GLSLSandbox网站上的片段着色器代码在spec中创建炫酷图形,包括去除背景、调整透明度及利用频谱数据动态改变图形等技巧。
本文介绍如何利用GLSLSandbox网站上的片段着色器代码在spec中创建炫酷图形,包括去除背景、调整透明度及利用频谱数据动态改变图形等技巧。
















 5459
5459

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








