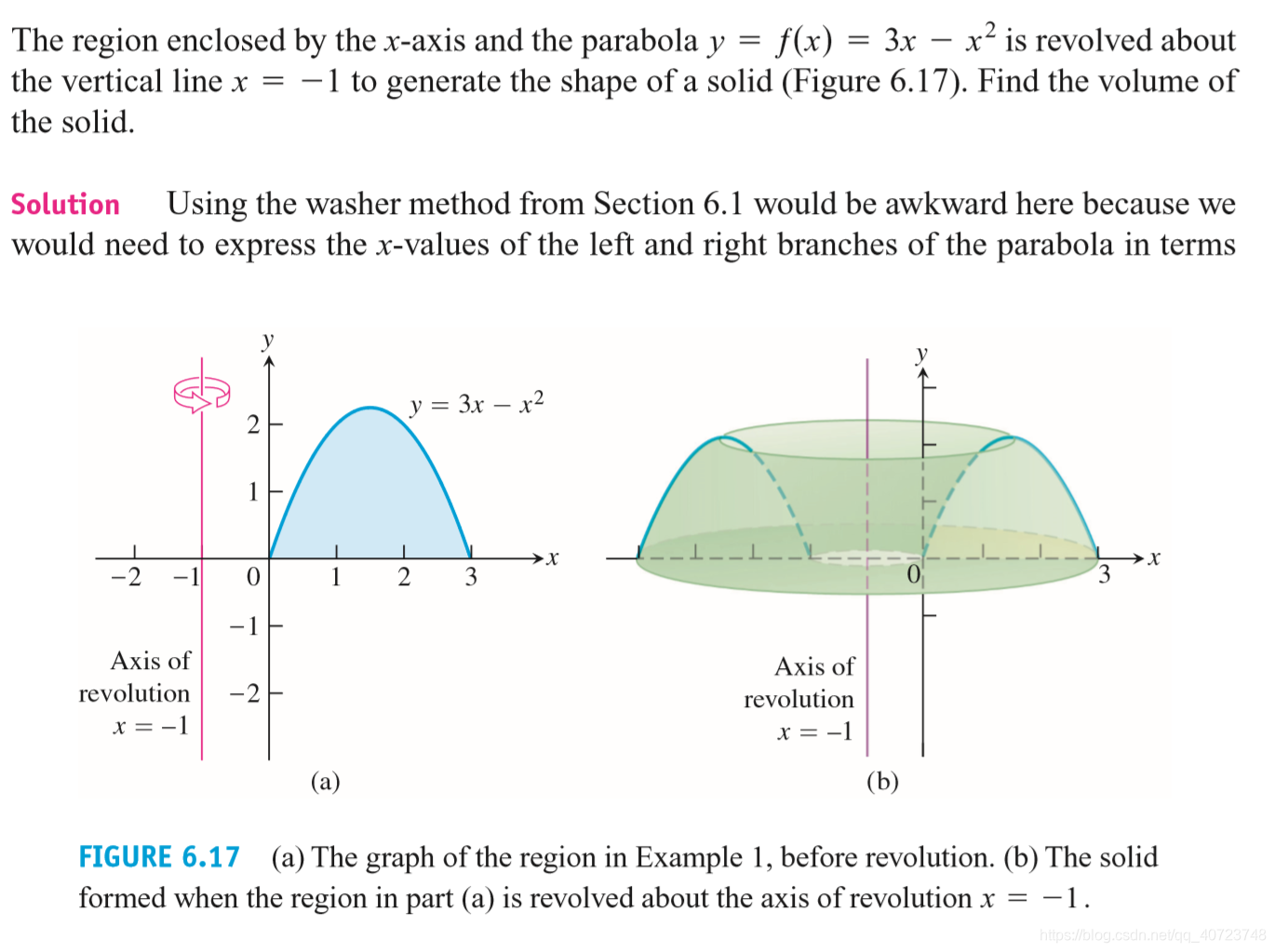
6.1 Volumes by Slicing and Rotation About an Axis
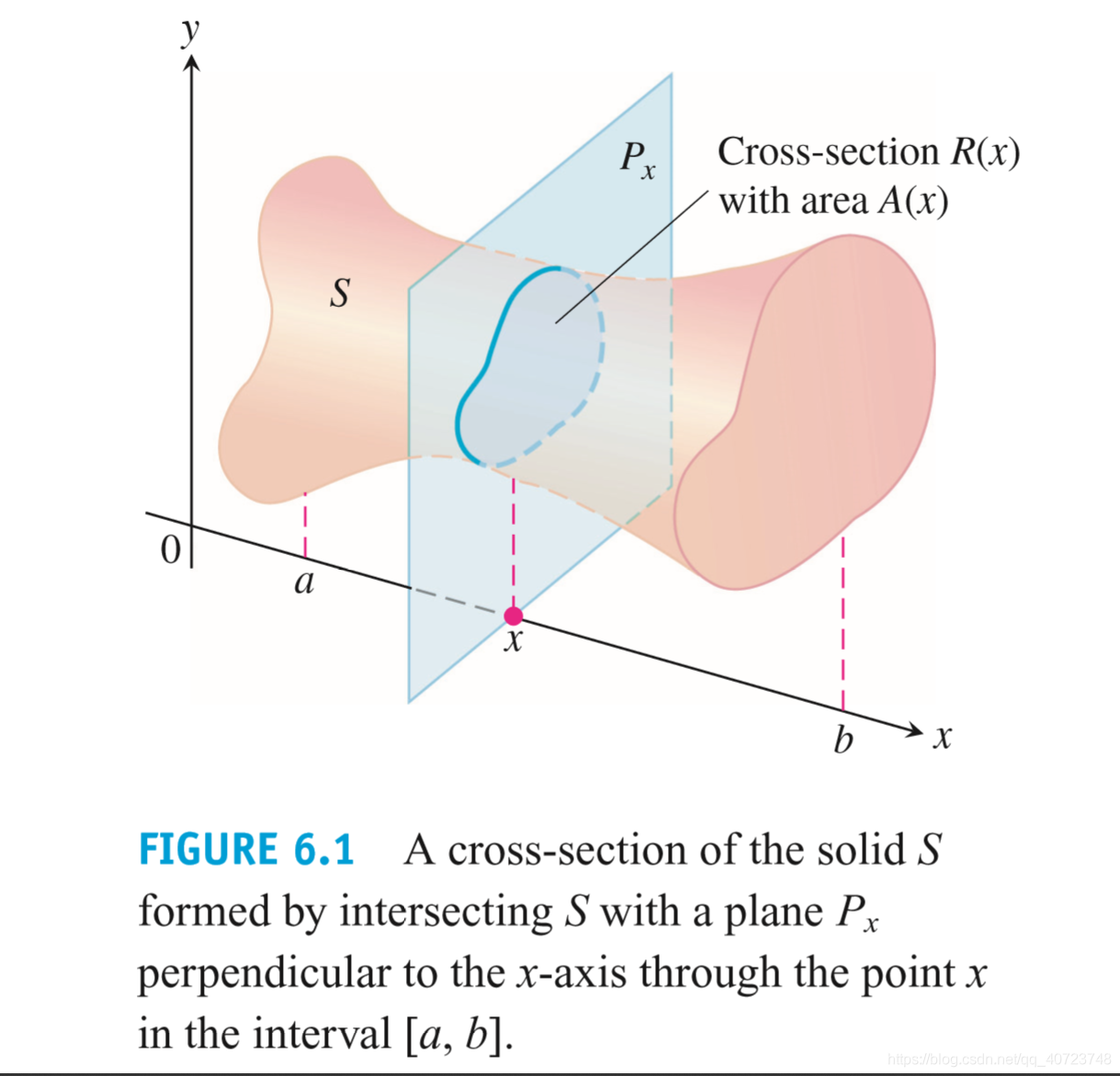
In this section we define volumes of solids whose cross-sections are plane regions. A cross-section of a solid S is the plane region formed by intersecting S with a plane (Figure 6.1).
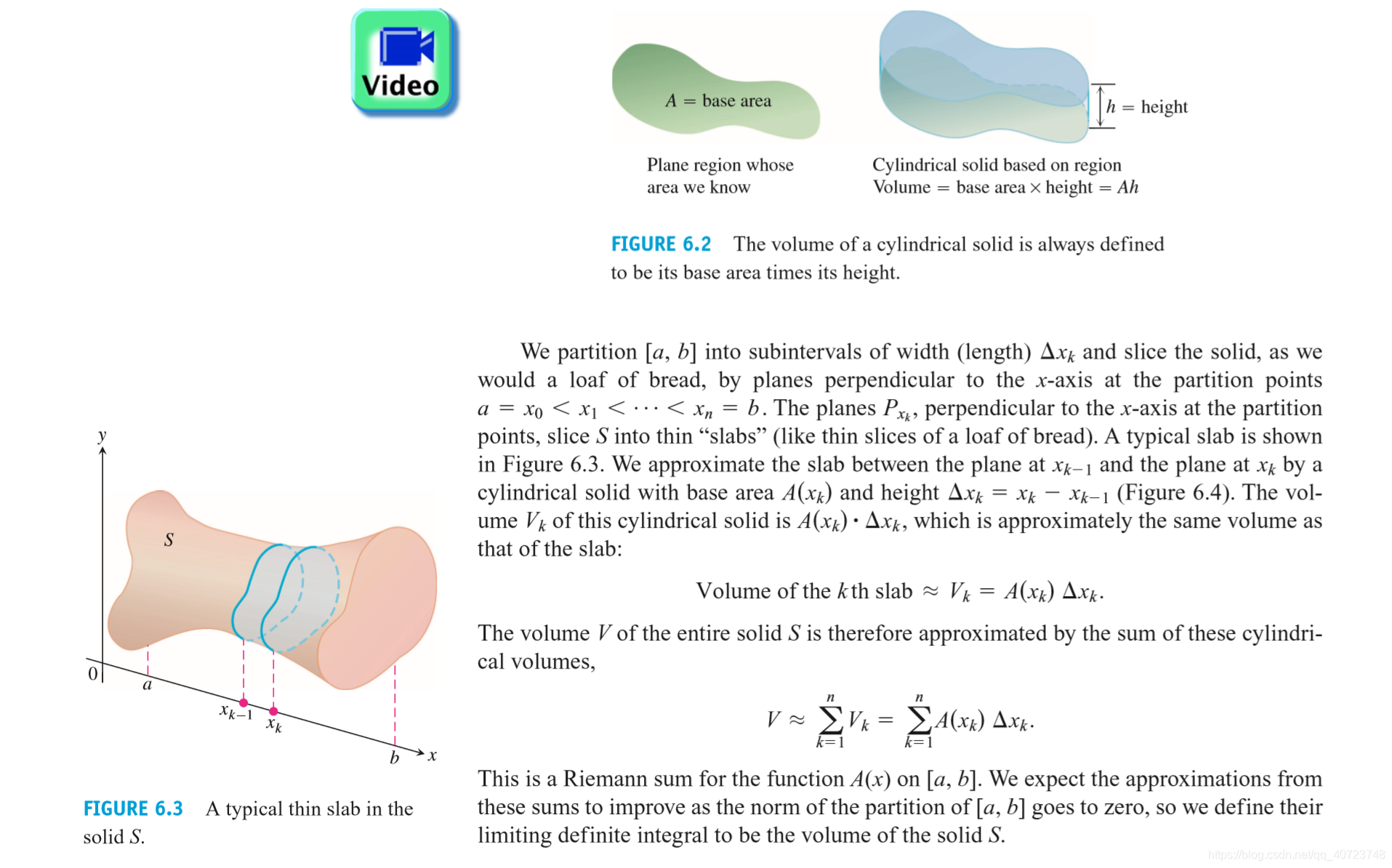
Suppose we want to find the volume of a solid S like the one in Figure 6.1. We begin by extending the definition of a cylinder from classical geometry to cylindrical solids with arbitrary bases (Figure 6.2). If the cylindrical solid has a known base area A and height h, then the volume of the cylindrical solid is
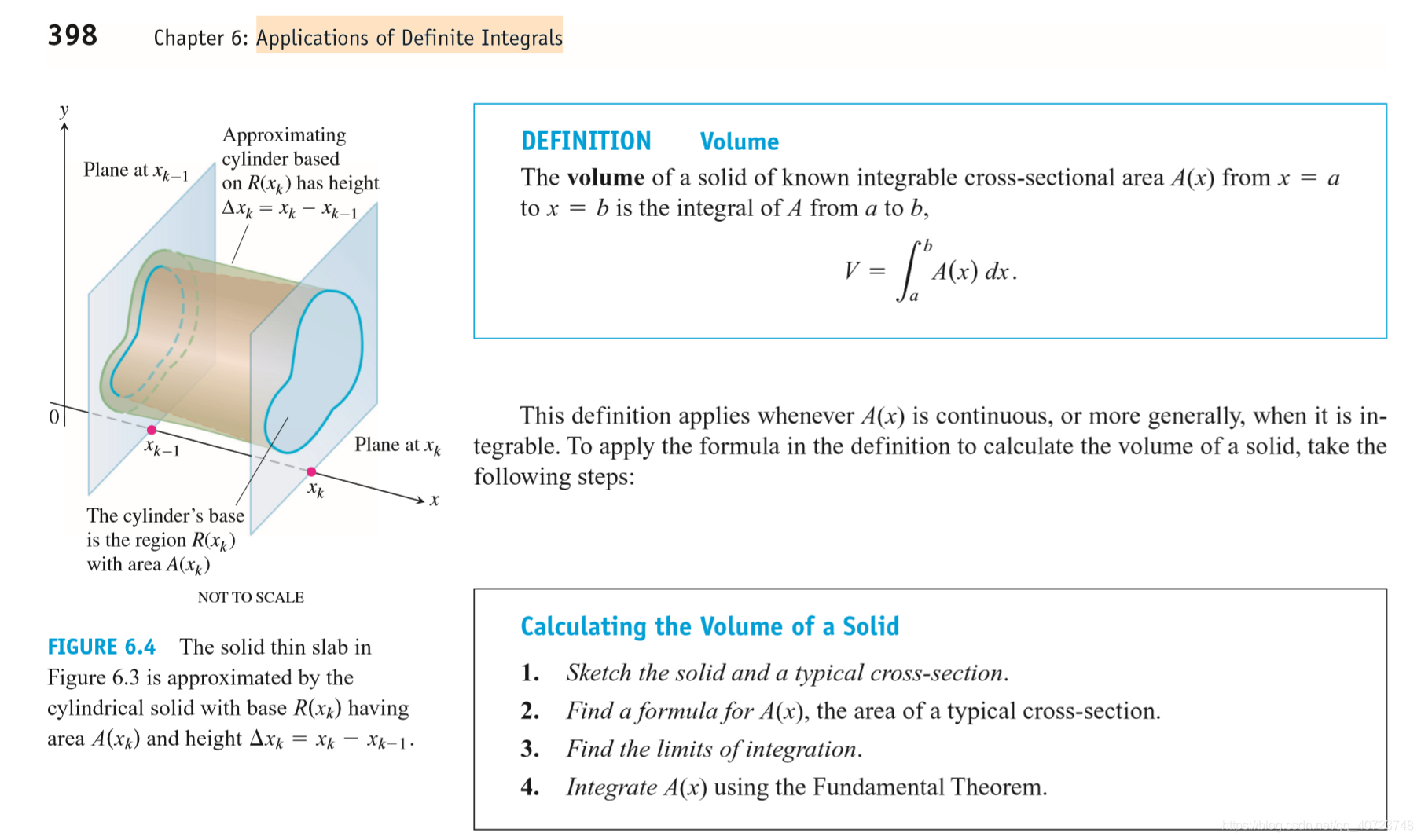
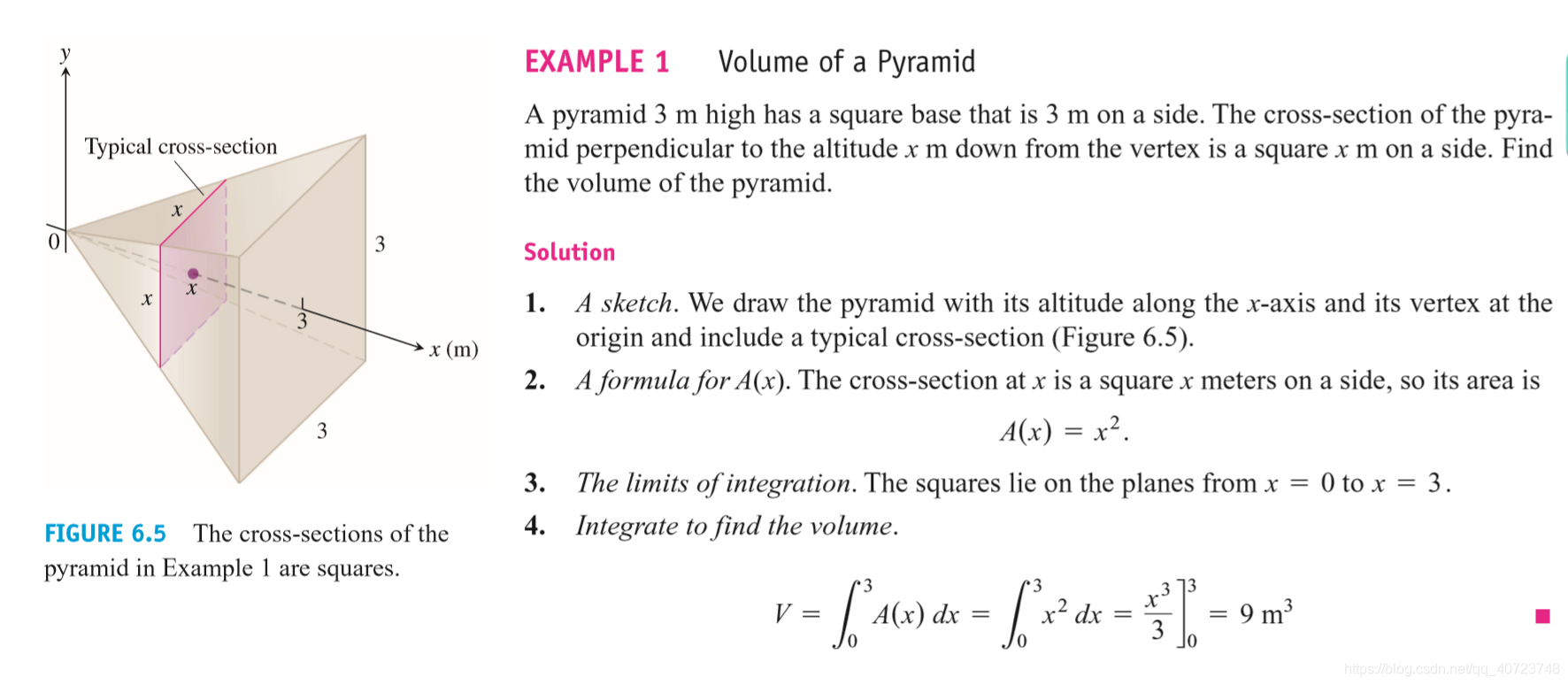
This equation forms the basis for defining the volumes of many solids that are not cylindrical by the method of slicing. If the cross-section of the solid S at each point in the interval [a, b] is a region R(x) of area A(x), and A is a continuous function of x, we can define and calculate the volume of the solid S as a definite integral in the following way.

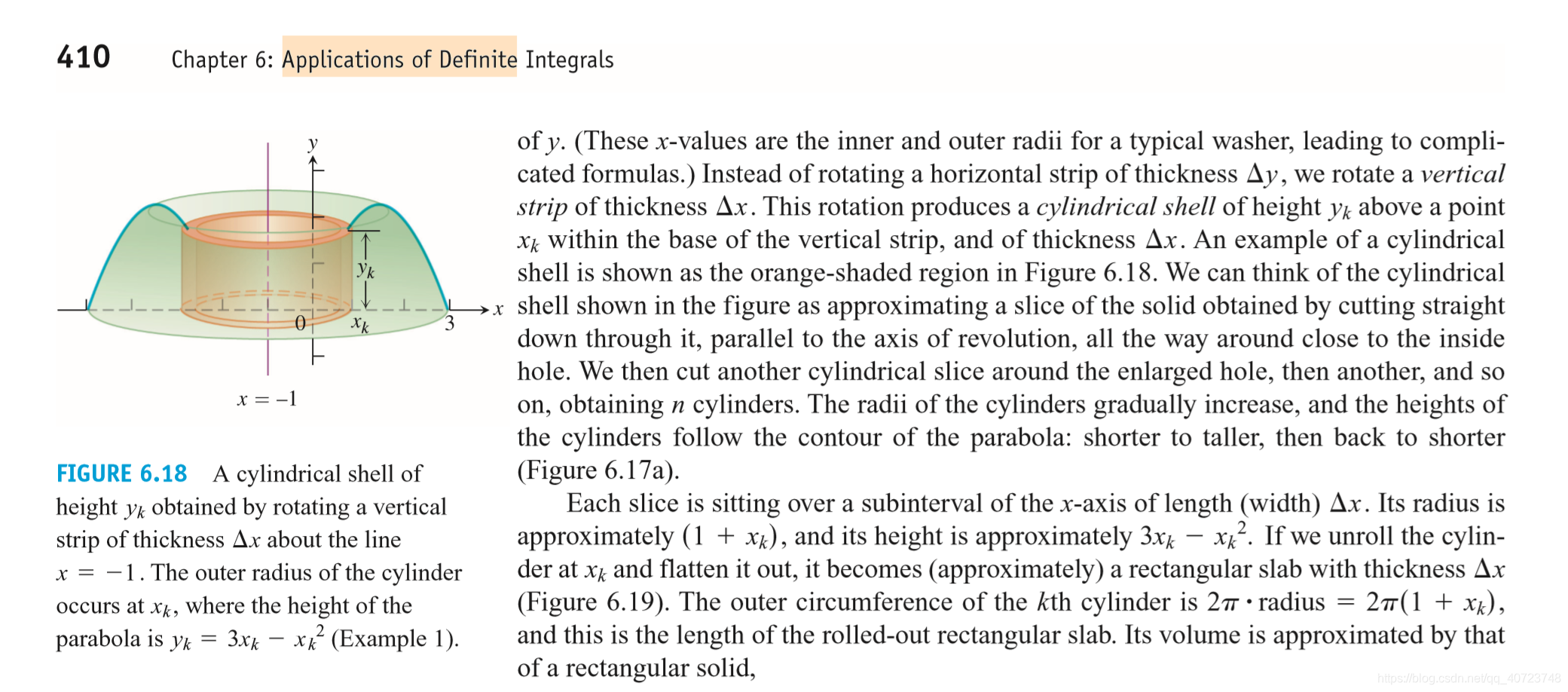
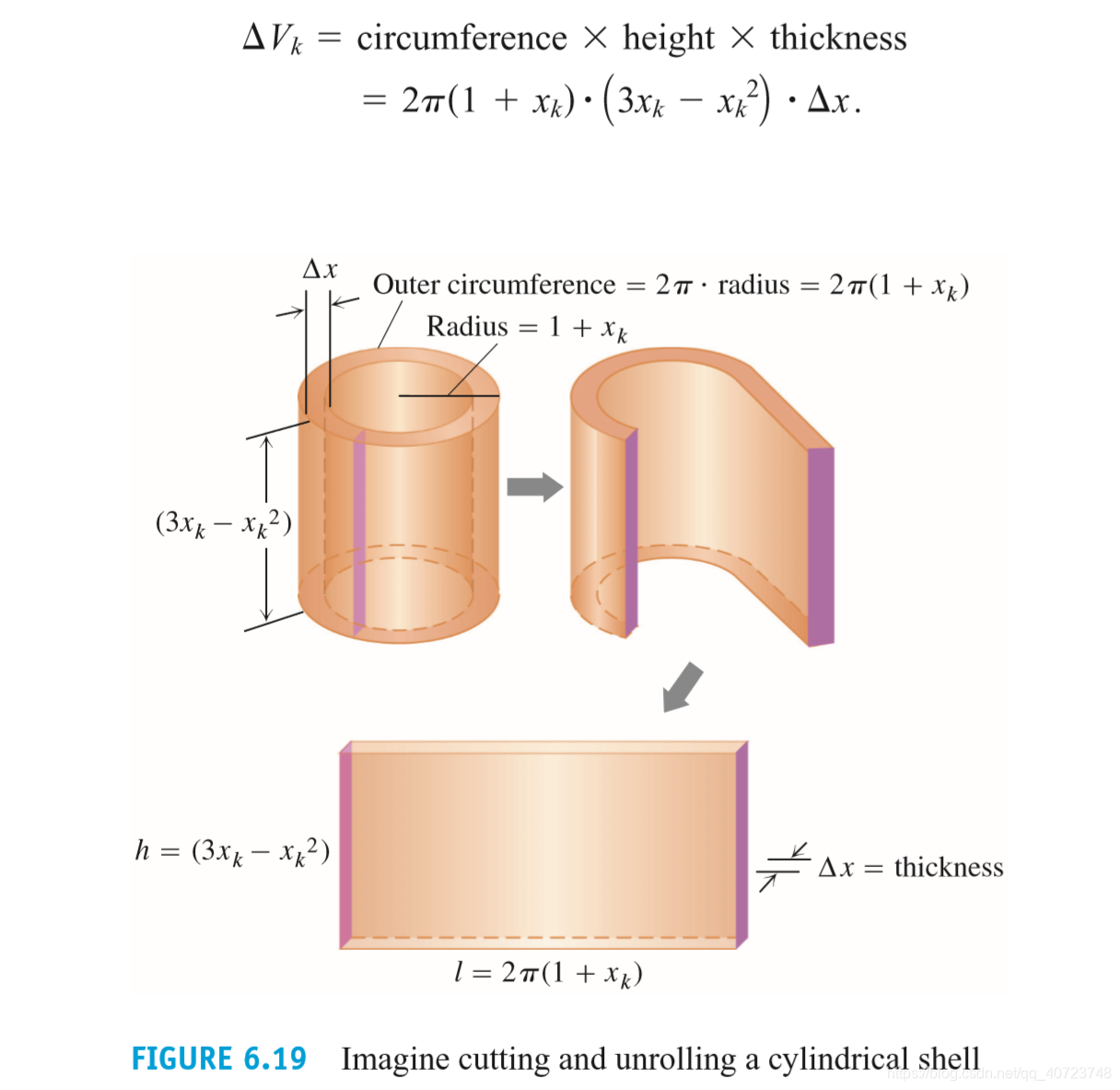
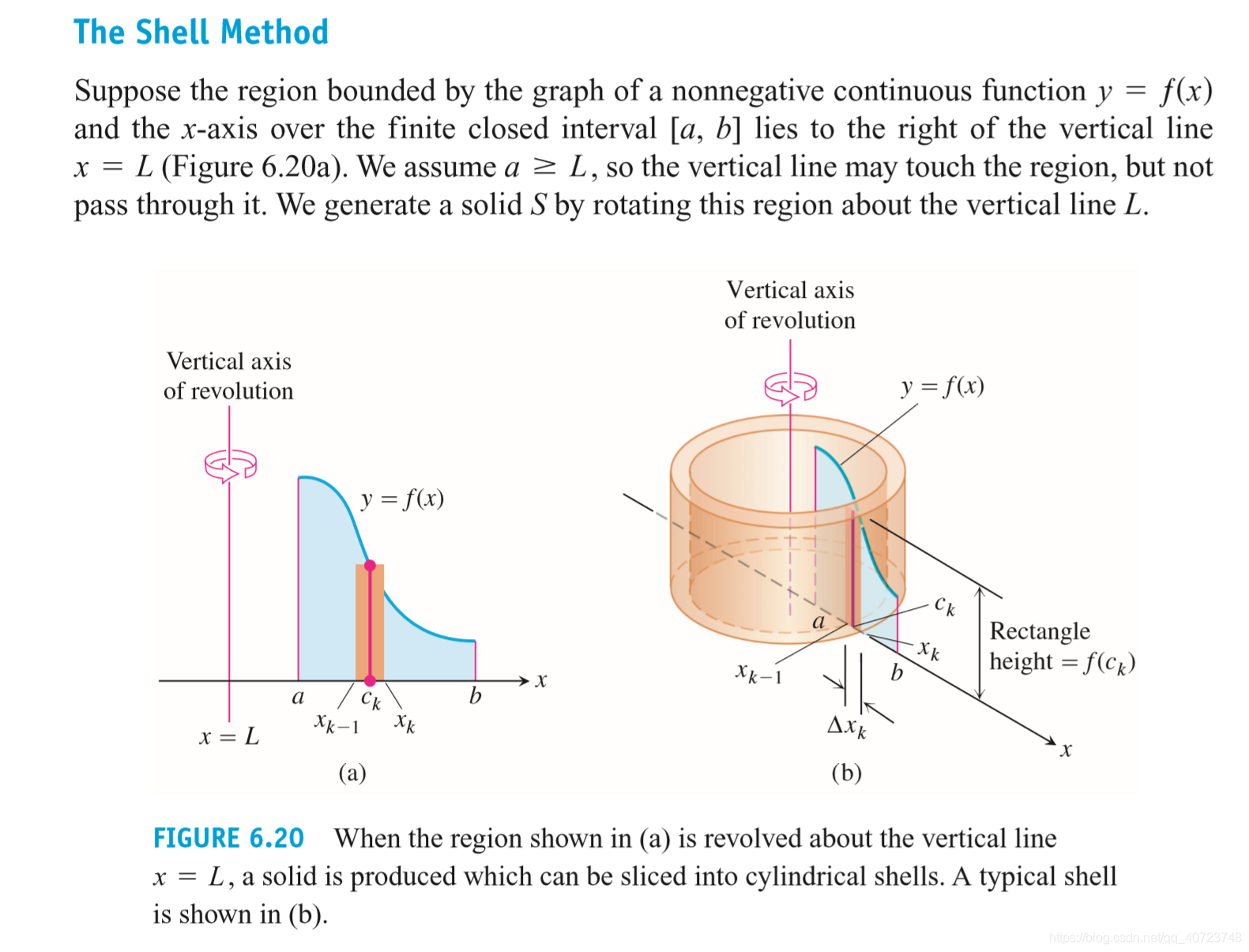
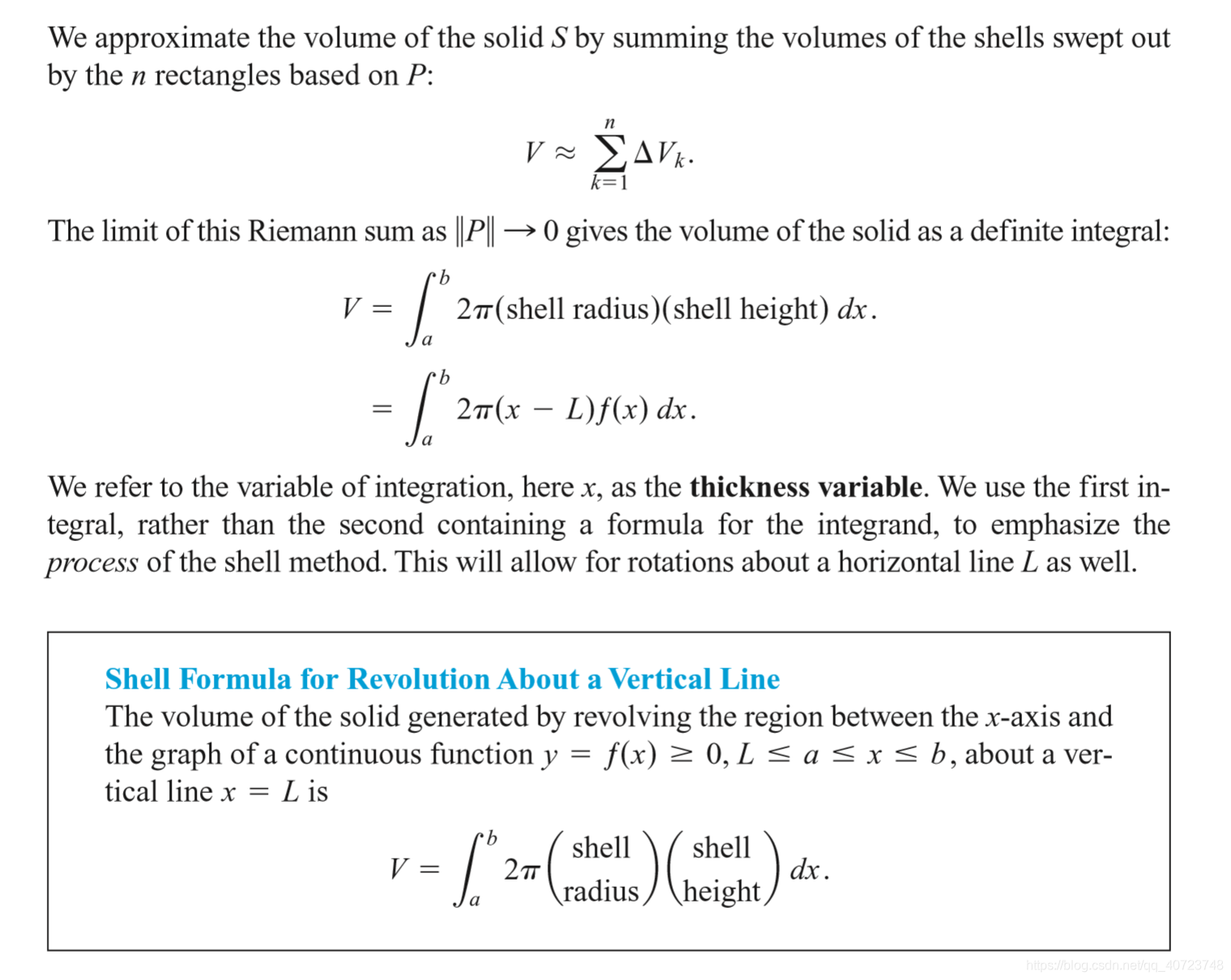
6.2 Volumes by Cylindrical Shells
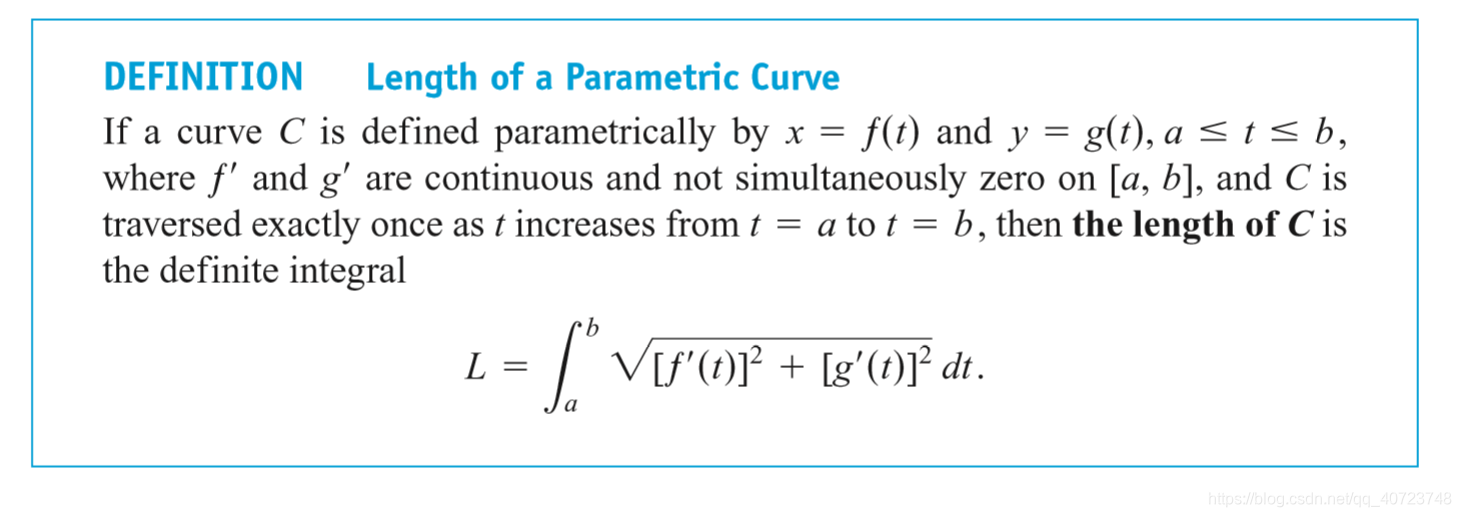
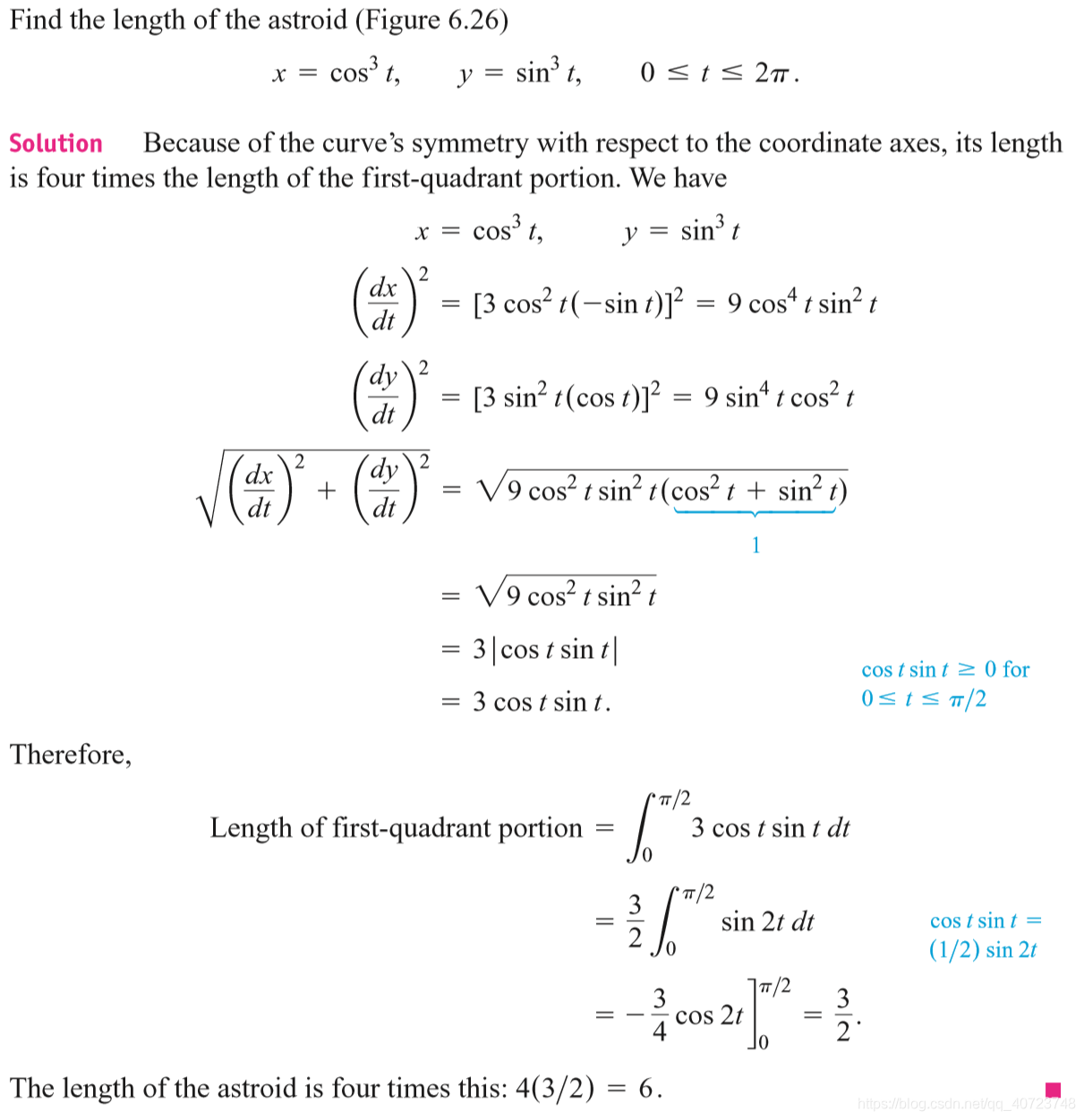
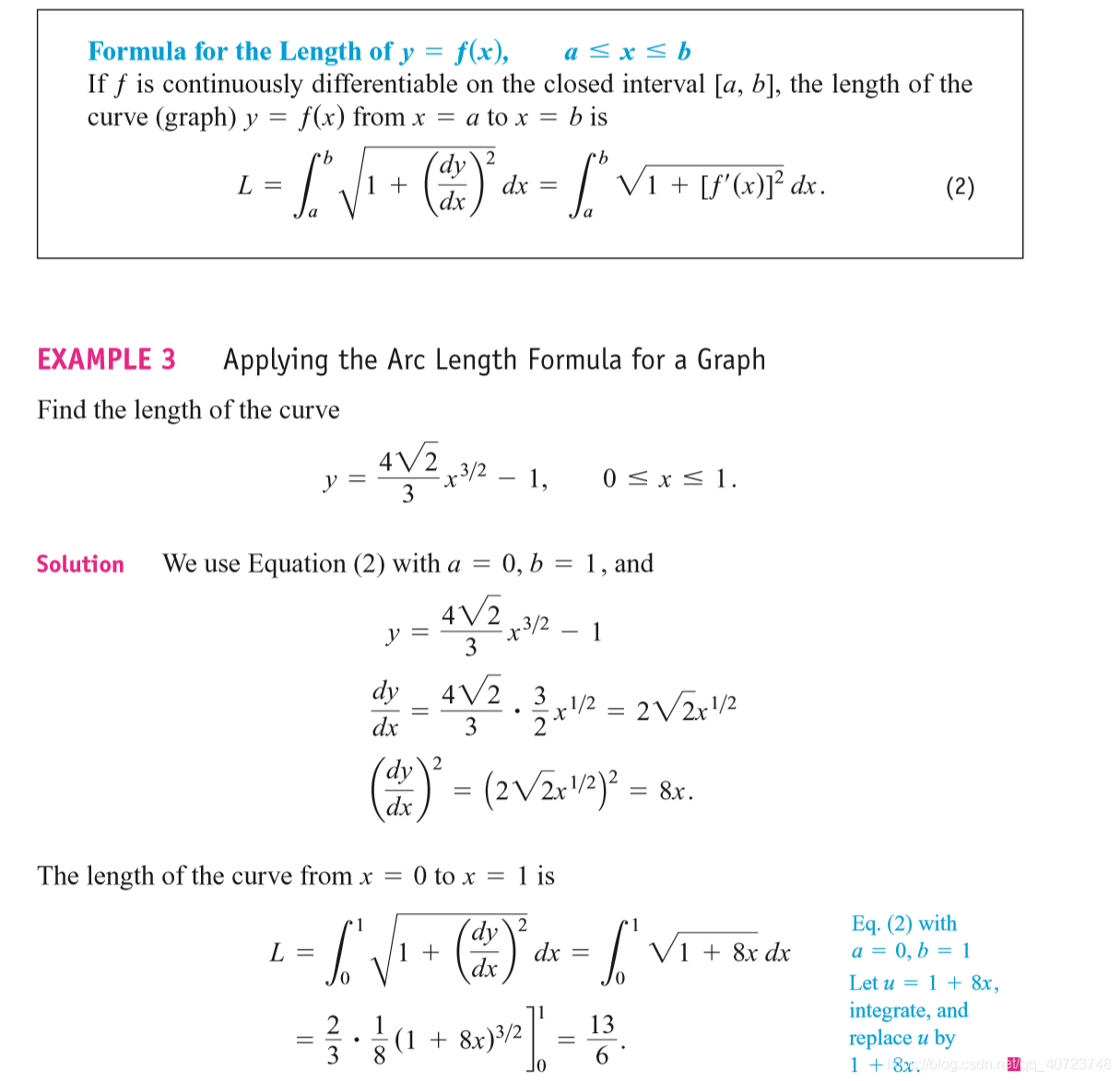
6.3 Lengths of Plane Curves
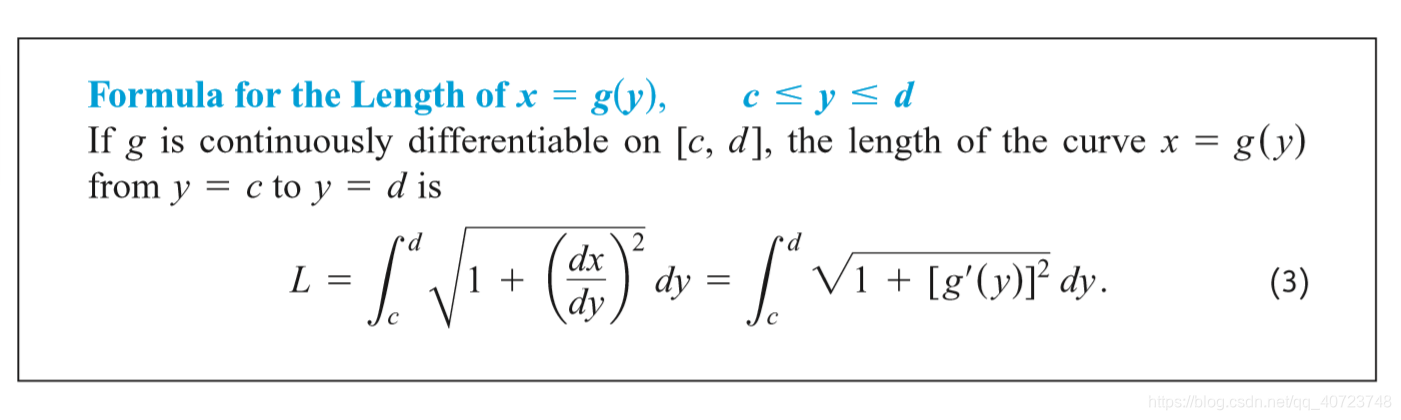
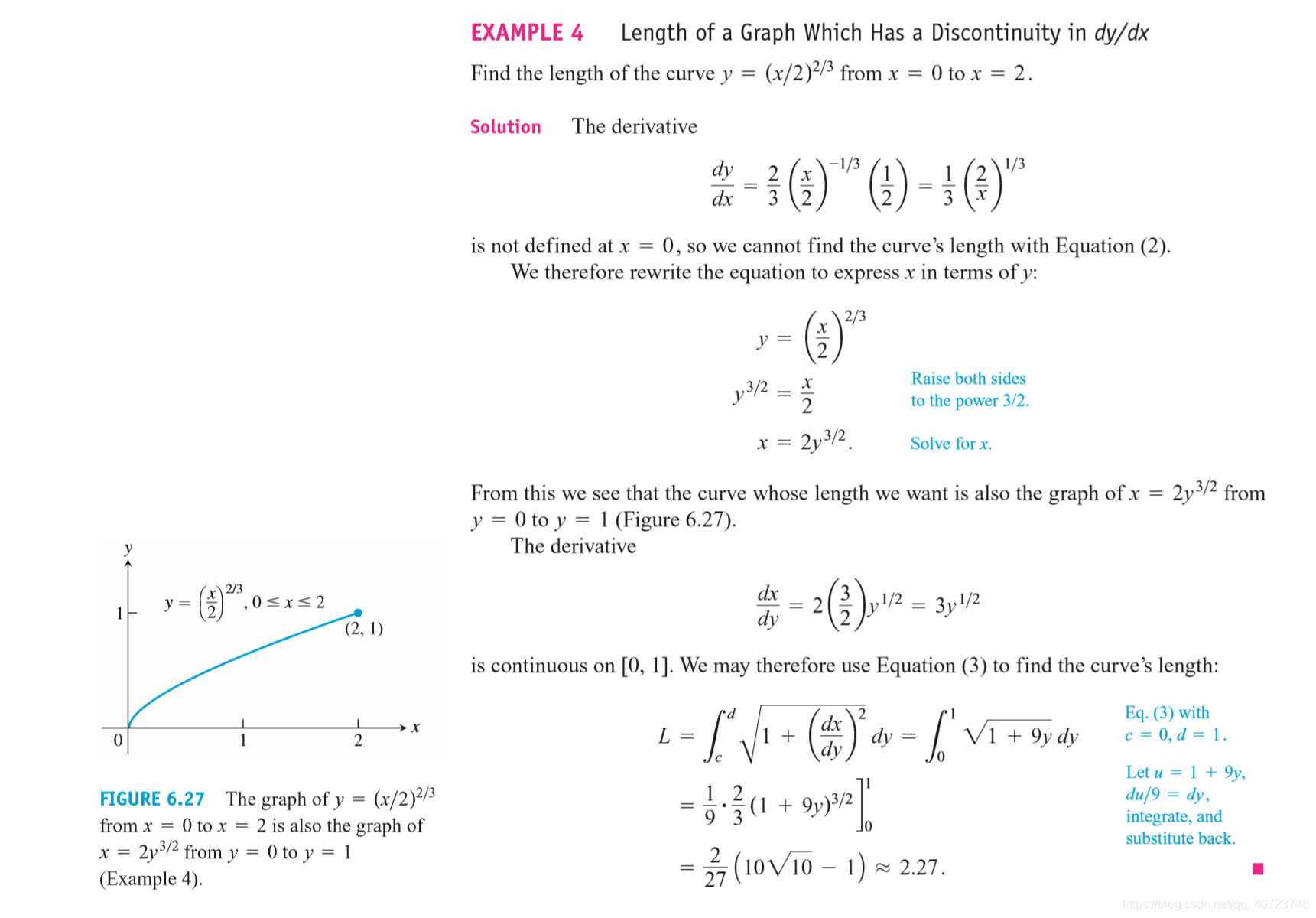
6.4 Moments and Centers of Mass
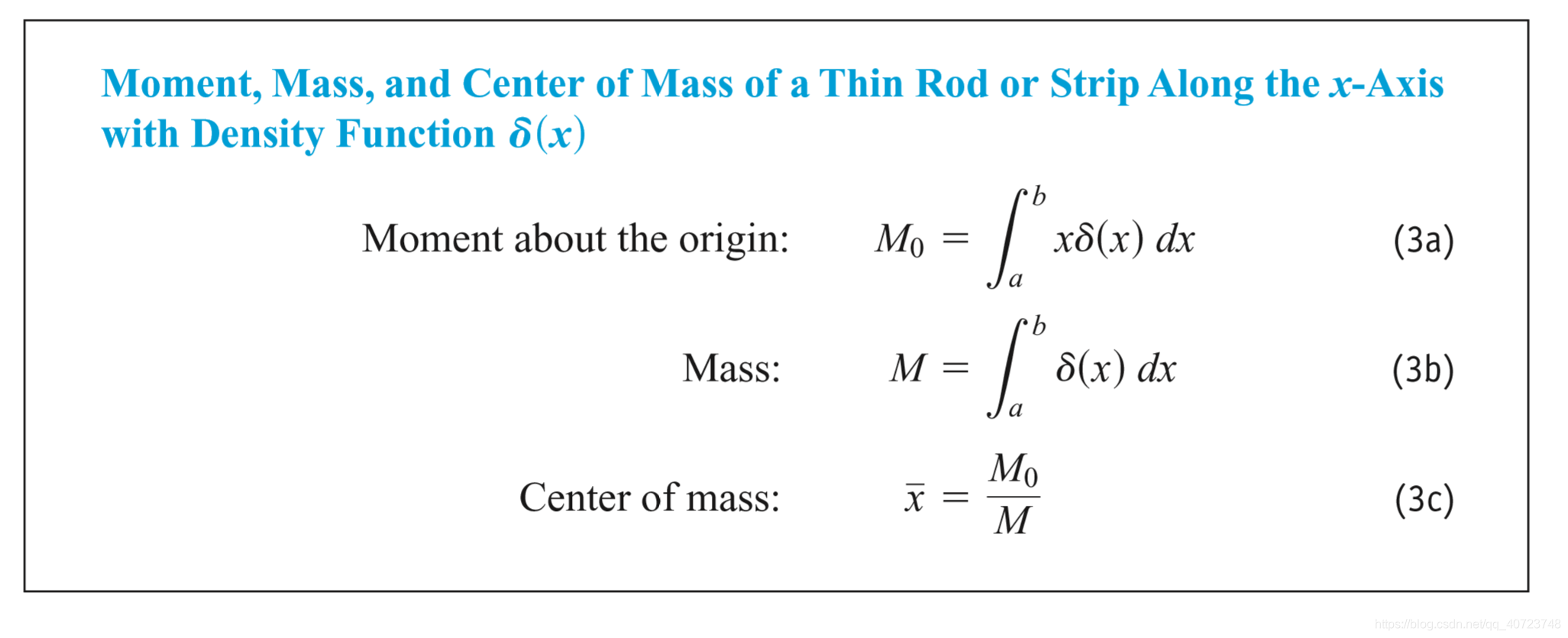
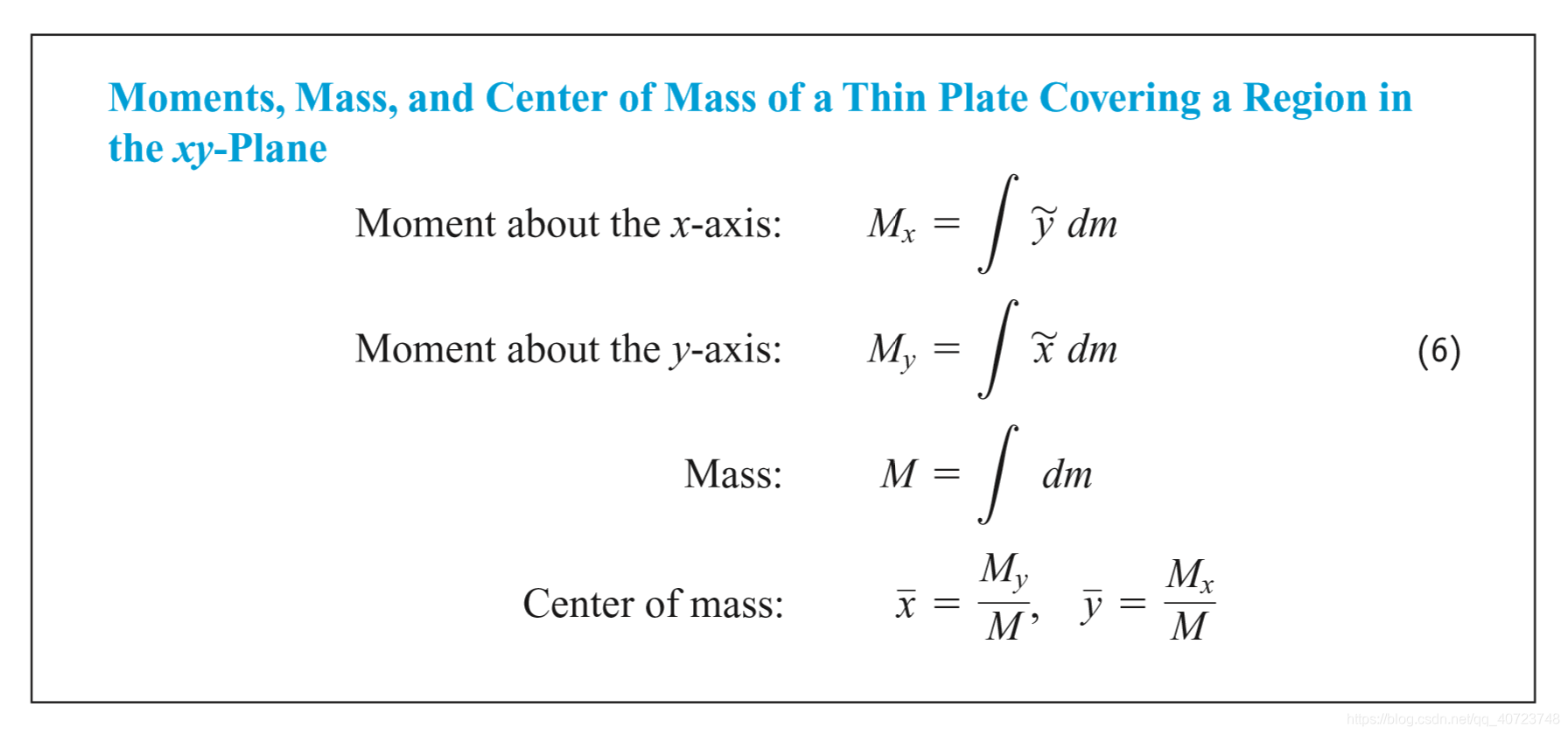
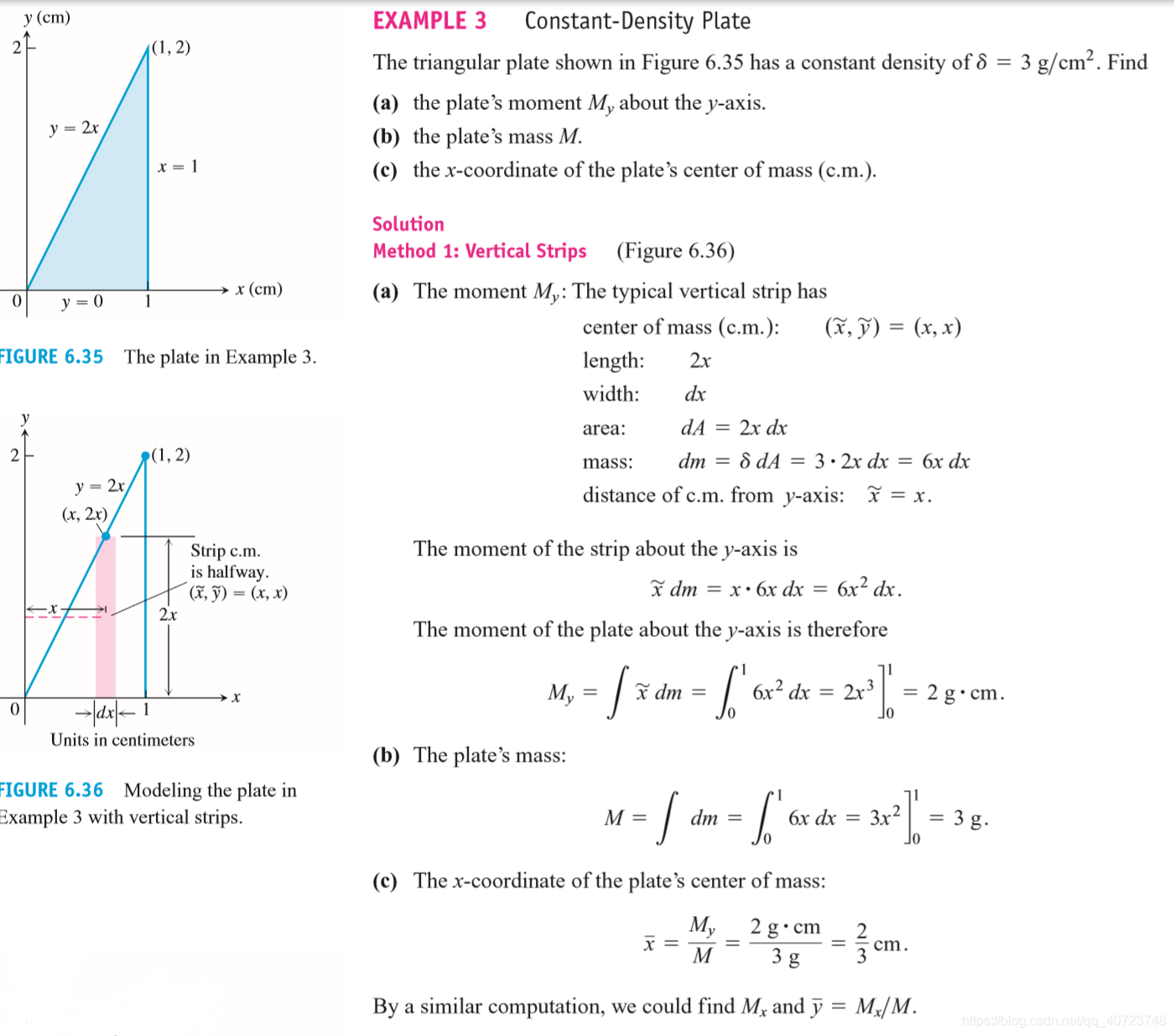
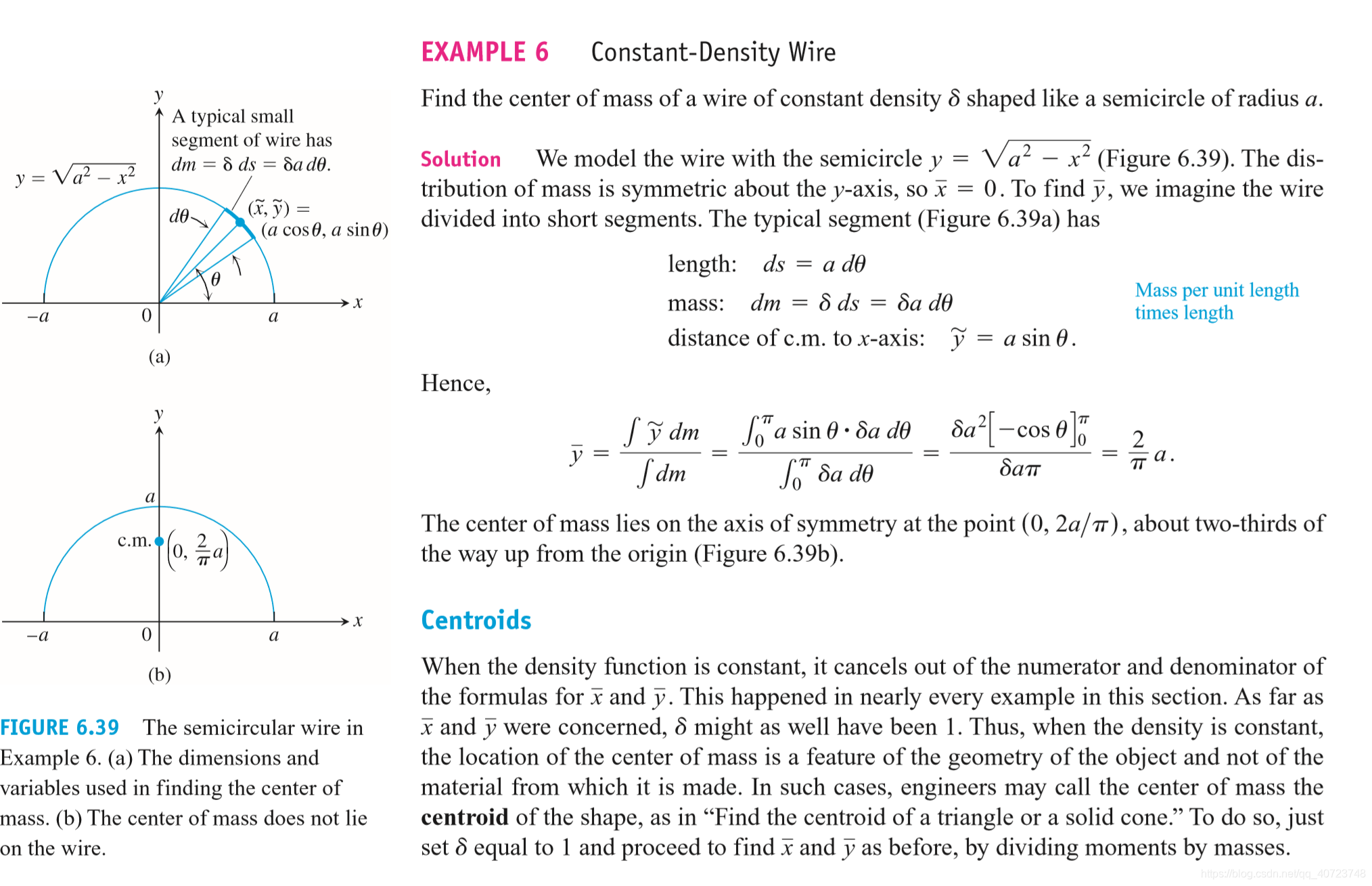
The coordinates of the centroid of a differentiable plane curve are
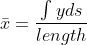
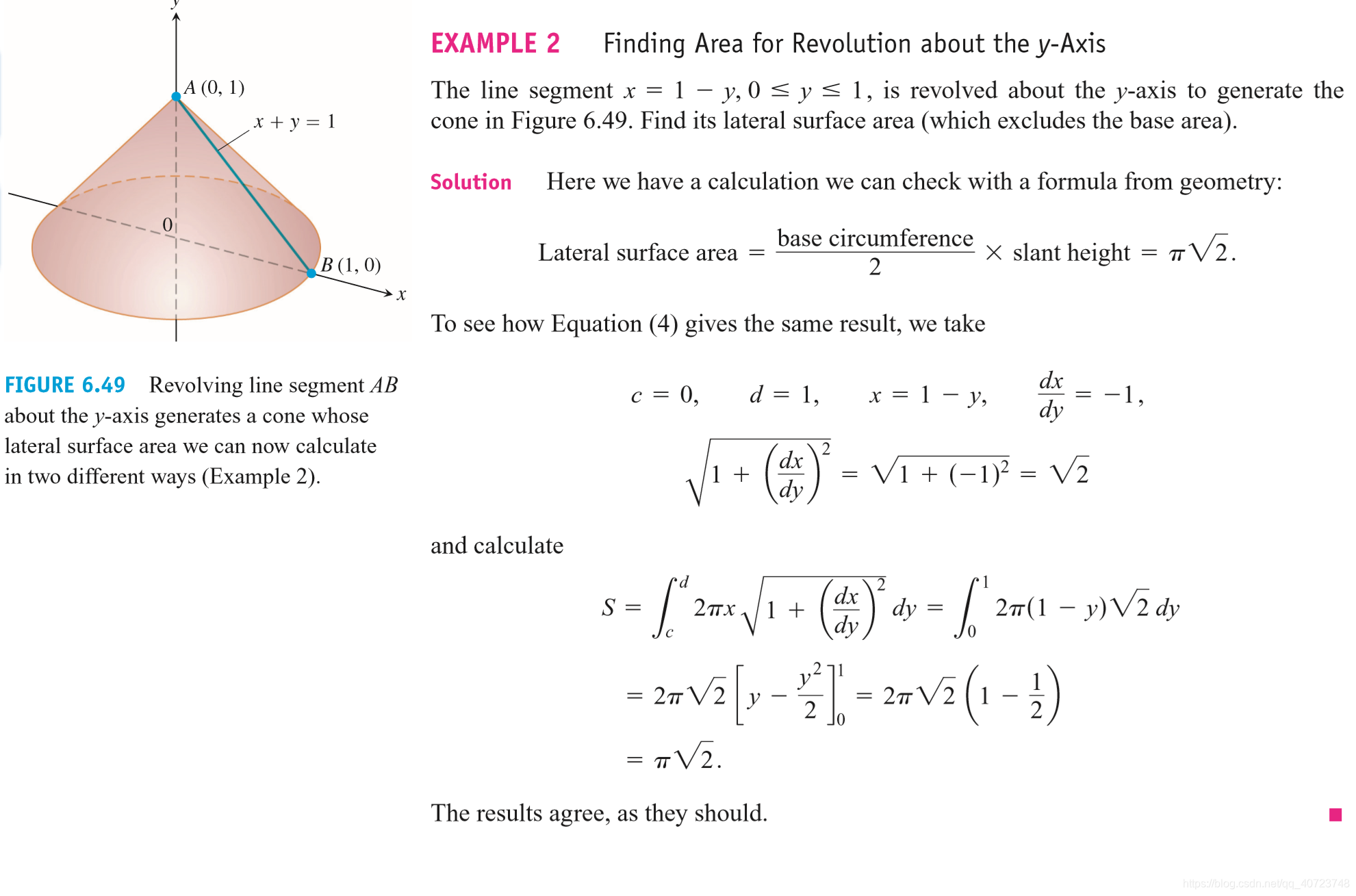
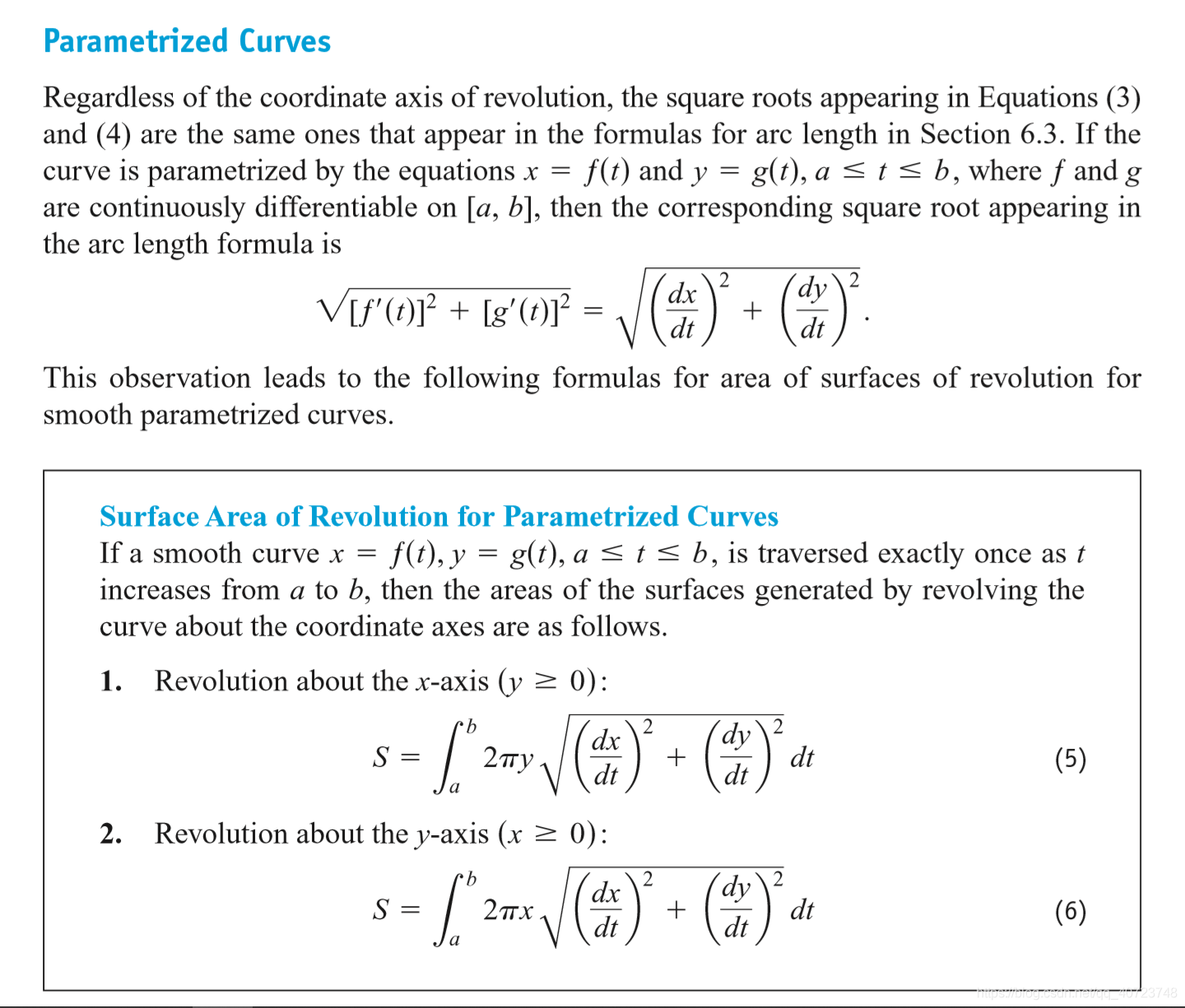
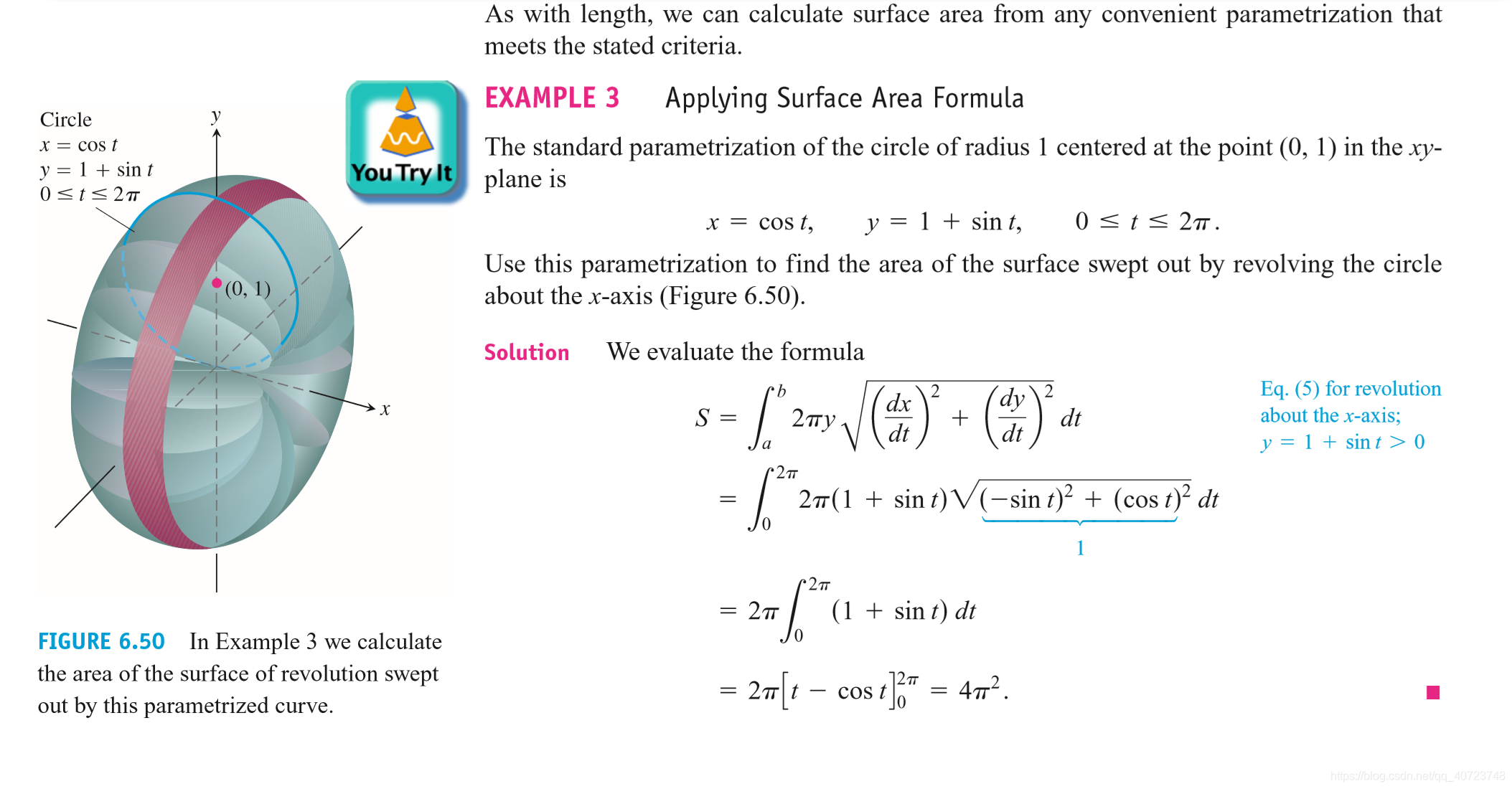
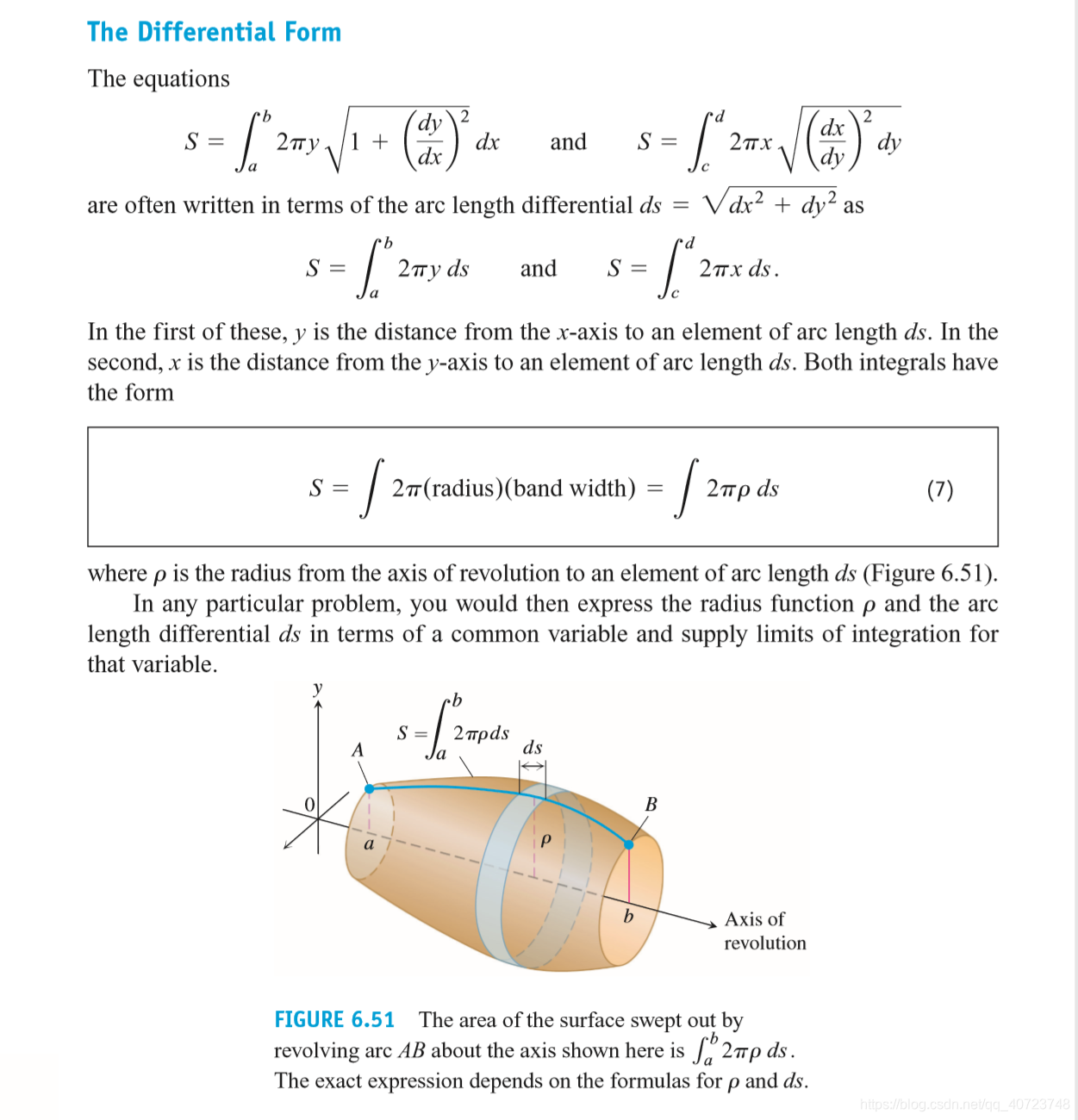
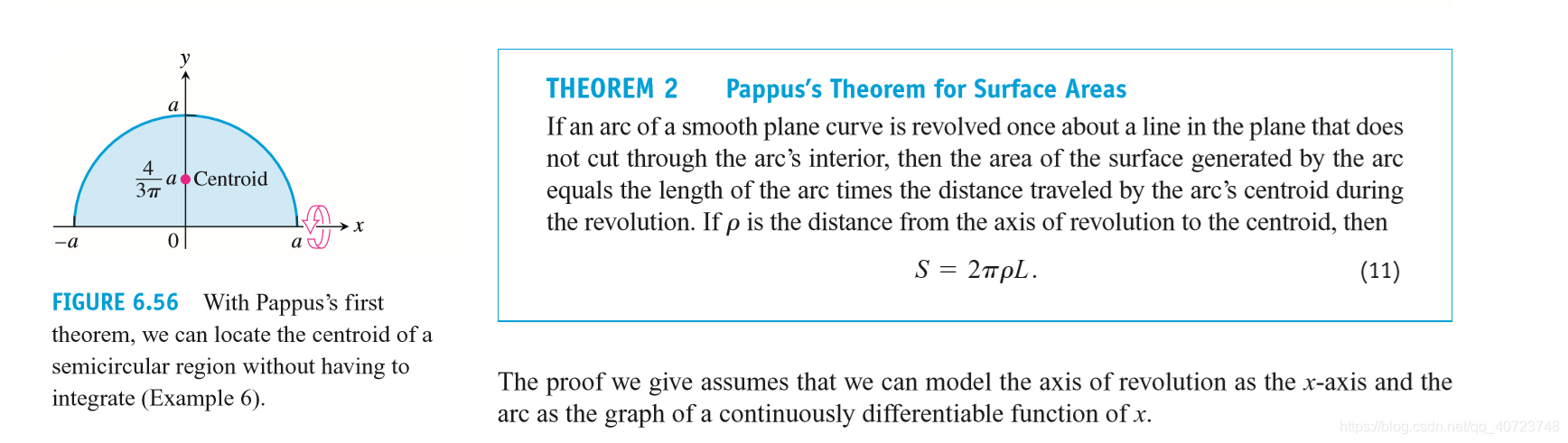
6.5 Areas of Surfaces of Revolution and the Theorems of Pappus











 本文探讨了通过切片和绕轴旋转来计算几何固体体积的方法,介绍了如何利用圆柱壳法求体积,以及平面曲线长度、质心坐标、旋转曲面面积等概念。通过定义任意基底的圆柱固体体积,引出了切片法计算非圆柱形固体体积的积分公式。
本文探讨了通过切片和绕轴旋转来计算几何固体体积的方法,介绍了如何利用圆柱壳法求体积,以及平面曲线长度、质心坐标、旋转曲面面积等概念。通过定义任意基底的圆柱固体体积,引出了切片法计算非圆柱形固体体积的积分公式。
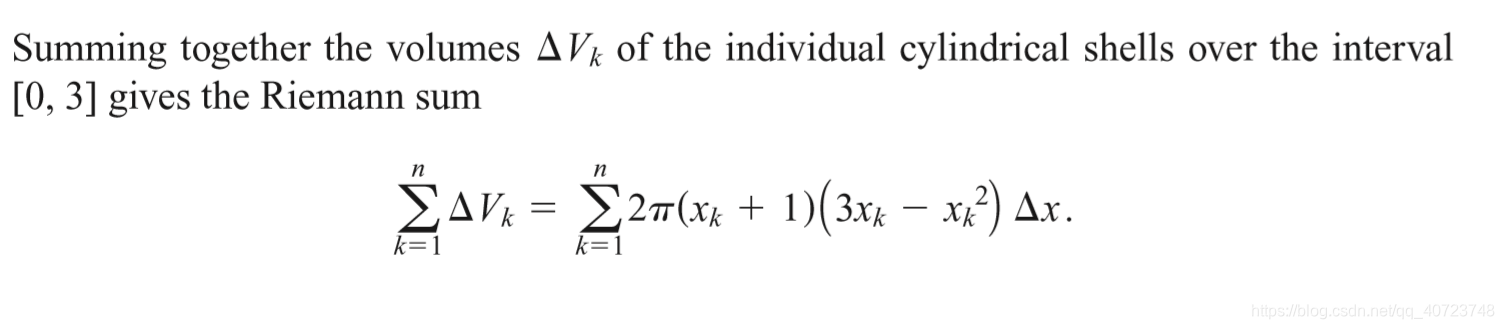


















 8541
8541

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










