84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Given an array of integers heights representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, return the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram.
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
if (heights.size()==0) return 0;
heights.push_back(0); //Note: add another element 0 at the end of the vector;
//to pop all elemnts from stack as 0<all other heights
stack<int> stk;
stk.push(-1);
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++){
while(stk.top() != -1 && heights[stk.top()] > heights[i]){
int idx = stk.top(); stk.pop();
ans = max(ans, heights[idx] * (i - stk.top() - 1));
// cout << "iterate" << " " << ans << endl;
}
stk.push(i);
// cout << "i " << i << endl;
}
heights.pop_back();
return ans;
}
};
这个是我做的单调栈的第一道题;看别人的解析也是看了很久;
在这个方法中点睛之笔有三处:
第一处:在最开始的时候在stack的开头push一个(-1)元素,注意这个栈存放的是vector的索引。
第二处:在我们题目中给定的vector height的最后push_back一个元素0;(我一开始没有留意到这个细节,导致我后来始终想不通对于那种本身就是一直单调增加的那种vector怎么办)
第三处:就是这个stack的使用,因为除了stack要递增,他里面存放的元素也要递增,例如对于一个heights vector 2 1 5 3 4 6;
我随便举一个例子:
stack 一开始存放的是 -1 然后0 进来;0 对应的value 是2 ;此时的栈是(-1, 0)
接下里index = 1;然后发现 index 1 对应的value是1;但是这个时候1 < 2;
所以这个时候 栈顶的元素 0 要pop出来;之后的栈是(-1)
0对应位置的value是 2; 这个长方形的宽度是:此时要进来的是index 1;
留在栈中的栈顶元素是 -1 (其实就是 -1 和 1 中间就是那个pop出来的0; 所以此时pop出来的那个元素的宽度就是 [ i - new_stack. top() - 1])
此时更新一下那个方框的面积;
以此类推一直更新;
如果最后遇到的都是单调递增的元素;直到最后遍历完了heights中的元素;但是注意⚠️ 在最开始的时候,在heights后面增加了一个元素0; 所以这个0 使得我们那个while 循环可以继续。
类似(1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2)就可以完美解决~
85. Maximal Rectangle
Given a rows x cols binary matrix filled with 0's and 1's, find the largest rectangle containing only 1's and return its area.
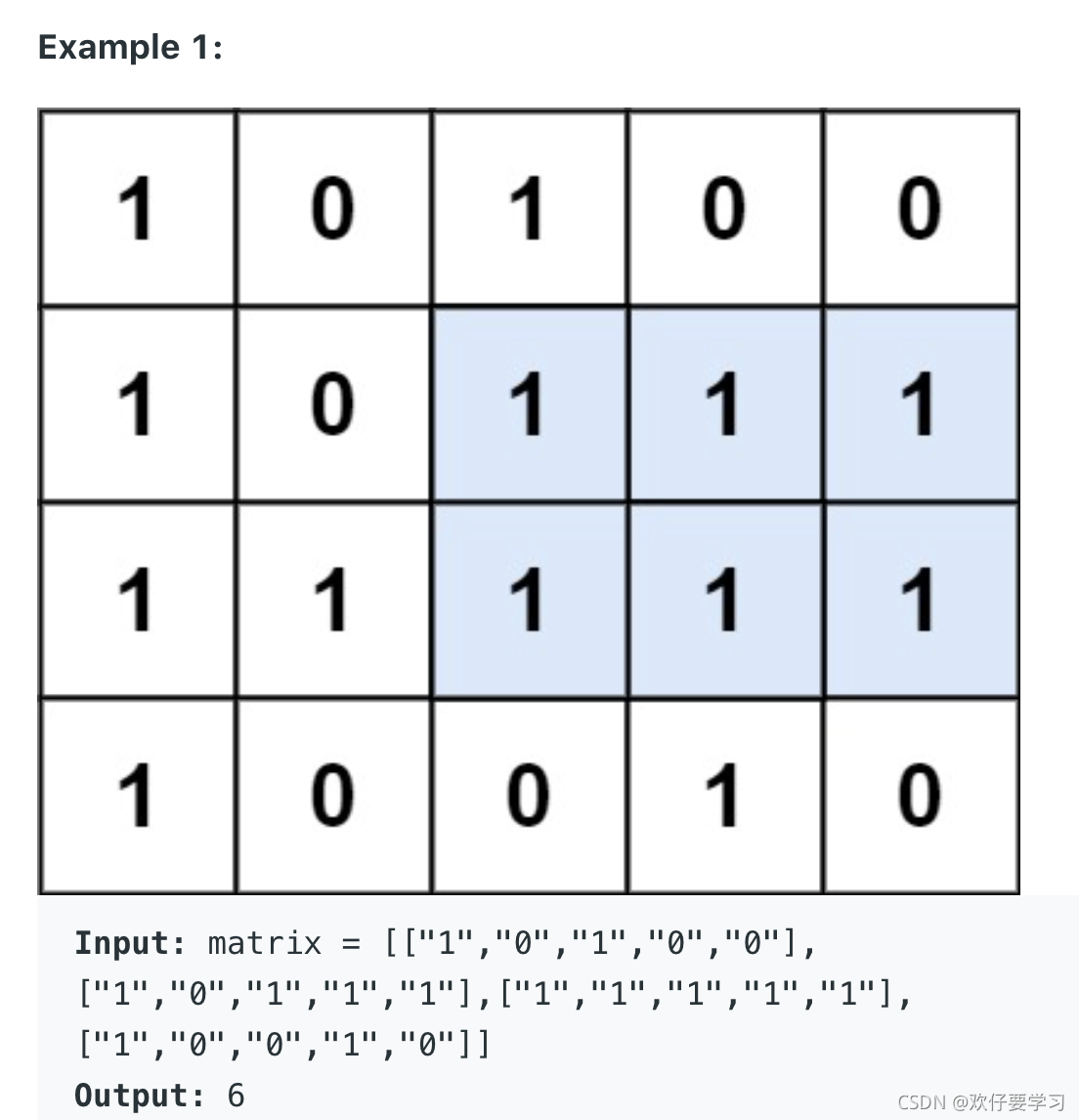
这一题其实和上一题非常类似;
上一题是找直方图中最大的长方形;
其实这个就可以看作找直方图中最大的长方形;只不过是2维的。
对于这个matric;我们先只看第一行;那么就是第一行,那一行作为直方图。
看前两行;那么这个直方图就是[ 2 0 2 1 1] 然后要找这个直方图的最大长方形;
看前三行:这个直方图就是[3 1 3 2 2] 然后找这个直方图的最大长方形。
看前四行:这个直方图是[ 4 0 0 3 0]
所以解决这个问题可以看作先遍历每一行;确定那一行的高度值。之后找所有厘米的最大值。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix)
{
if(matrix.empty())
{
return 0;
}
int maxRec = 0;
vector<int> height(matrix[0].size(), 0);
for(int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < matrix[0].size(); j++)
{
if(matrix[i][j] == '0'){
height[j] = 0;
}
else{
height[j]++;
}
}
maxRec = max(maxRec, largestRectangleArea(height));
}
return maxRec;
}
//后面这部分与84题方法一样,就是复制粘贴过来的这个函数
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
if (heights.size()==0) return 0;
heights.push_back(0); //Note: add another element 0 at the end of the vector;
//to pop all elemnts from stack as 0<all other heights
stack<int> stk;
stk.push(-1);
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++){
while(stk.top() != -1 && heights[stk.top()] > heights[i]){
int idx = stk.top(); stk.pop();
ans = max(ans, heights[idx] * (i - stk.top() - 1));
// cout << "iterate" << " " << ans << endl;
}
stk.push(i);
// cout << "i " << i << endl;
}
heights.pop_back();
return ans;
}
};






 该博客介绍了如何使用单调栈解决两个计算机科学问题:找到直方图中最大的矩形面积以及二维二进制矩阵中最大的全1矩形的面积。通过分析代码,解释了单调栈在处理这两个问题时的关键步骤和技巧,包括在栈首添加特殊元素、处理栈中元素以及不断更新最大矩形面积。
该博客介绍了如何使用单调栈解决两个计算机科学问题:找到直方图中最大的矩形面积以及二维二进制矩阵中最大的全1矩形的面积。通过分析代码,解释了单调栈在处理这两个问题时的关键步骤和技巧,包括在栈首添加特殊元素、处理栈中元素以及不断更新最大矩形面积。
















 1374
1374

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








