栈
栈只允许访问一个数据项,即最后插入的数据项。移除这个数据项才能访问倒数第二个插入的数据项。(后进先出)
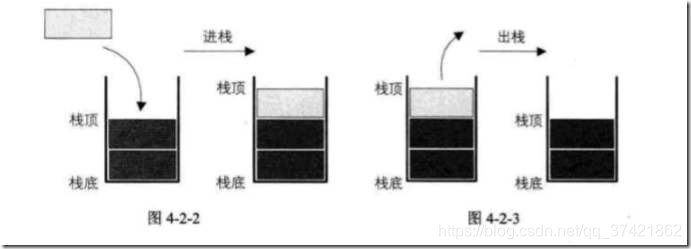
数组实现栈
// 通过数组实现栈
public class StackX {
private int maxSize;
private long[] stackArray;
private int top;
public StackX(int size) {
maxSize = size;
stackArray = new long[maxSize];
top = -1;
}
public void push(long value) {
stackArray[++top] = value;
}
public long pop() {
return stackArray[top--];
}
public long peek() {
return stackArray[top];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
}
入栈和出栈操作时间复杂度均为 O(1)。
栈操作所耗时间不依赖栈中数据项的个数,操作时间短,因为不需要进行比较和移动操作。
队列
在队列中第一个插入的数据项会被最先移除(先进先出),相比于栈是相反的。
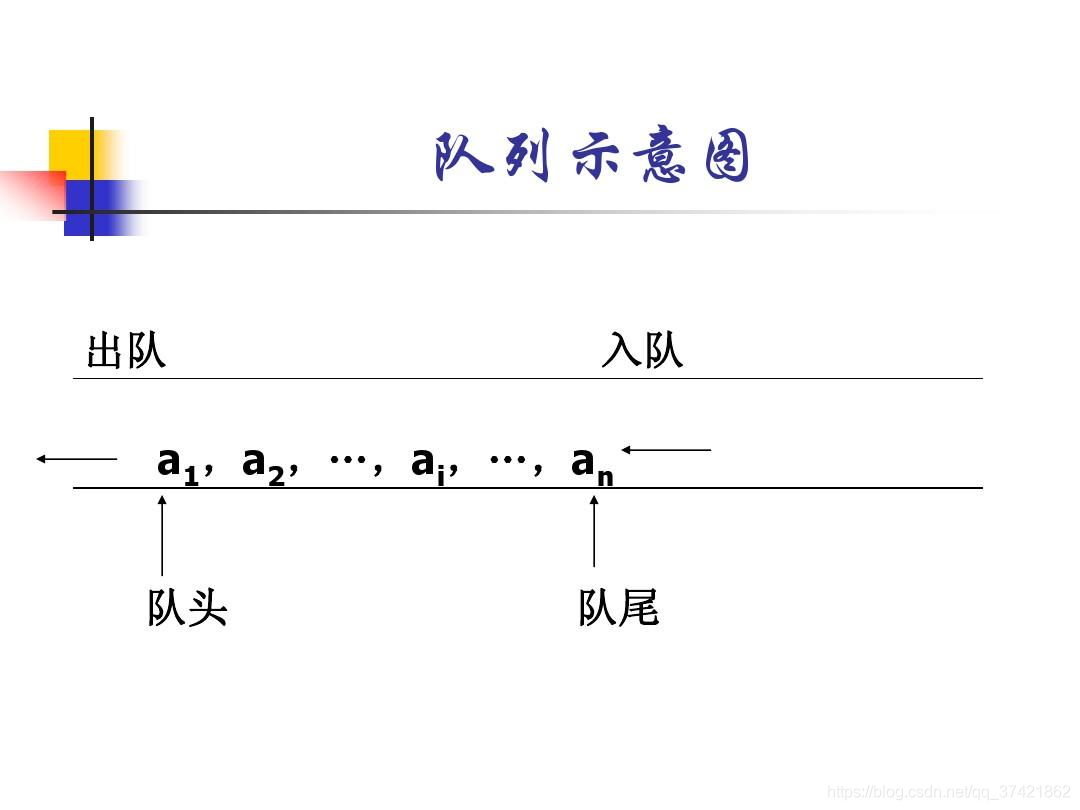
数组实现队列
public class Queue {
private int maxSize;
private long[] queArray;
private int front; // 队头
private int rear; // 队尾
private int nItems;
public Queue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.queArray = new long[this.maxSize];
this.front = 0;
this.rear = -1;
this.nItems = 0;
}
public void insert(long value) {
if (rear == maxSize - 1)
rear = -1;
queArray[++rear] = value;
nItems++;
}
public long remove() {
long temp = queArray[front];
queArray[front++] = 0;
if (front == maxSize)
front = 0;
nItems--;
return temp;
}
public long peekFront() {
return queArray[front];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return nItems == 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return nItems == maxSize;
}
public int size() {
return nItems;
}
}
和栈一样,队列中插入数据项和移除数据项的时间复杂度均为 O(1) 。
优先级队列
优先级队列是比栈和队列更专用的数据结构,像普通队列一样,优先级队列有一个队头和队尾,并且也是在队头移除数据项。在优先级队列中,数据项按关键字的值有序,这样关键字最小(或者最大)的数据项总在队头,数据项在插入时按照顺序插入到合适的位置以确保队列的顺序。
public class PriorityQueue {
private int maxSize;
private long[] queArray;
private int nItems;
public PriorityQueue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.queArray = new long[this.maxSize];
this.nItems = 0;
}
public void insert(long value) {
int j;
if (nItems == 0) {
this.queArray[nItems++] = value;
} else {
for (j = nItems - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (value > this.queArray[j]) {
this.queArray[j + 1] = this.queArray[j];
} else {
break;
}
}
this.queArray[j + 1] = value;
this.nItems++;
}
}
public long remove() {
long temp = this.queArray[--nItems];
this.queArray[nItems] = 0;
return temp;
}
public long peekMin() {
return this.queArray[nItems - 1];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.nItems == 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.nItems == this.maxSize;
}
public void print() {
for (long temp : this.queArray) {
System.out.print(temp + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(5);
priorityQueue.insert(20);
priorityQueue.insert(10);
priorityQueue.insert(50);
priorityQueue.insert(30);
priorityQueue.insert(40);
priorityQueue.print();
priorityQueue.remove();
priorityQueue.remove();
priorityQueue.remove();
priorityQueue.insert(30);
priorityQueue.insert(60);
priorityQueue.insert(70);
priorityQueue.print();
}
}
数组实现的优先级队列,插入操作需要 O(N) 的时间,删除操作需要 O(1) 的时间。
扩展
算法题-用两个栈实现队列
用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作。 队列中的元素为int类型。
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() {
if (!stack2.isEmpty()) {
return stack2.pop();
} else {
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack2.pop();
}
}
算法题-包含min函数的栈
定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的min函数(时间复杂度应为O(1))
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
private Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
private int[] minArray = new int[9999];// 用于存放递增的元素
private int effectiveLength = 0;// 数组中有效元素所占有的长度
public void push(int node) {
// 第一个元素直接放到minArray的最左边
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
minArray[0] = node;
} else {
// 如果新加入的元素比数组中最小的小,
// 将node放到下标0位置,数组中其他元素后移
if (node < minArray[0]) {
for (int i = effectiveLength - 1; i > -1; i--) {
minArray[i + 1] = minArray[i];
}
minArray[0] = node;
} else {
// 找到node的位置,将之后的元素后移
for (int i = 0, len = effectiveLength; i < len; i++) {
int temp = minArray[i];
if (node < temp) {
for (int j = len - 1; j >= i; j--) {
minArray[j + 1] = minArray[j];
}
minArray[i] = node;
break;
}
// node为最大的元素,放到数组最后面
if (i + 1 == len) {
minArray[i + 1] = node;
}
}
}
}
// 有效长度+1
effectiveLength++;
stack.push(node);
}
public void pop() {
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Integer popTemp = stack.pop();
for (int i = 0, len = effectiveLength; i < len; i++) {
int minTemp = minArray[i];
// 找到相同值元素,将其从数组中移出
if (minTemp == popTemp) {
for (int j = i; j < effectiveLength; j++) {
minArray[j] = minArray[j + 1];
}
}
}
// 有效长度-1
effectiveLength--;
}
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int min() {
// 直接返回数组中最左边的元素,即栈中最小元素
return minArray[0];
}
}





 本文深入解析了栈、队列及优先级队列的数据结构原理,阐述了它们的特性、应用场景及实现方式。特别讨论了栈与队列的O(1)时间复杂度操作,以及优先级队列的O(N)插入时间复杂度。并通过实例展示了如何使用两个栈实现队列,以及包含min函数的栈设计。
本文深入解析了栈、队列及优先级队列的数据结构原理,阐述了它们的特性、应用场景及实现方式。特别讨论了栈与队列的O(1)时间复杂度操作,以及优先级队列的O(N)插入时间复杂度。并通过实例展示了如何使用两个栈实现队列,以及包含min函数的栈设计。
















 25万+
25万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








