学习笔记,参考有风险
无监督域自适应(test-time adaptation)方法:
(1)特征匹配(特征提取时):熵最小化,原型调整,信息最大化,批归一化统计对齐。
(2)预测调整(分类时)
(3)test-time training:训练数据可得
(4)test-time adaptation:训练数据不可得

2021-NIPS-Test-Time Classifier Adjustment Module for Model-Agnostic Domain Generalization(T3A)
通过构建支持集来调整类原型,使其具有更统一的表示:把在不同域上训练好的模型当作一个特征提取器,然后在测试数据上采用一个最近邻分类。因为采用了最近邻,所以需要给每个类维持一个类别原型,这个类别原型会随着测试数据的变化而动态变化。只调整顶部的线性分类器,将在源域上训练的线性分类器的输出层替换为一个伪原型分类器:


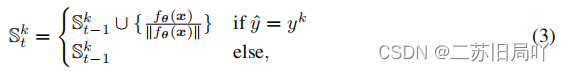
2021-ICLR-TENT: fully test-time adaption by entropy minimization
提出fully test-time adaptation,通过修改特征来最小化预测熵,以调节BN参数。
![]()
在测试阶段,目标函数从CE变为Entropy,并且更新参数时,只更新BN层中的β\betaβ和γ\gammaγ。
2022-CVPR-Parameter-free Online Test-time Adaptation
使用拉普拉斯最大似然估计鼓励相邻样本在特征空间中具有相似预测(分类结果)。 test-time adaptation methods只在有限的实验设置下表现良好,错误的超参数选择会导致性能下降。受测试时条件的不确定性启发,提出:
(1)用拉普拉斯调整最大似然估计(LAME)解决域自适应问题,调整模型的输出(而不是它的参数)
![]()
(2)使用concave-convex procedure优化整体损失:在每次迭代中,将当前解Z~(n){\tilde Z^{(n)}}Z~(n)作为目标的紧上界的最小值。
![]()

2022-CVPR-Contrastive Test-Time Adaptation
(1)伪标签增强:使用弱增强数据,利用记忆队列得到软近邻,实现软近邻投票,得到精细伪标签
(2)自监督对比学习:使用强增强数据进行自监督对比学习,优化特征。
(3)正则化:通过强弱一致性,使聚类得到的标签、模型的预测值一致。
2022-CVPR-Self-Taught Metric Learning without Labels
(1)基于教师网络,预测数据间的class-equivalence relation,并将预测的关系作为伪标签,优化学生网络。
(2)基于学生网络,计算其基于动量的移动平均,用于优化教师网络。
(3)将近邻的重叠程度作为衡量语义相似的指标。语境化的语义相似度精确地近似于类等价性。
2023-CVPR-Feature Alignment and Uniformity for Test Time Adaptation
将Test Time Adaptation作为特征修订问题,通过实现对齐和一致性来完成特征修正。其中,对齐指相似的图像应该具有相似的表示,一致性指不同类别的图像在空间中尽可能均匀地分布:
(1)特征一致性:
提出了自蒸馏策略,在不同层间传递信息,保证当前batch和以往batch内表征的一致性。
![]()
(2)特征对齐:
提出记忆化的空间局部聚类,对齐未来batch内的邻域样本之间的表示。

(3)解决噪声标签
为了解决常见的噪声标签问题,提出熵和一致性滤波器来选择和删除可能的噪声标签。在计算原型时,过滤具有高熵的噪声特征,因为不可靠的样本通常较高的熵。

2022-ICLR-CONTRASTIVE LABEL DISAMBIGUATION FOR PARTIAL LABEL LEARNING(PICO)
部分标签学习:使每个样本具有一个粗糙的标签候选集
解决问题:
(1)表示学习
(2)标签歧义消除:在标签集中识别真实标签,依赖良好的特征表示,且假设距离较近的样本具有相同标签。但是标签不确定使得特征学习困难。
PICO:通过对比标签歧义消除,实现部分标签学习。为来自相同类别的样本产生紧密对齐的表示,并促进标签歧义消除。
(1)构造伪正对完成对比学习,实现部分标签学习。
(2)基于类原型的标签歧义消除算法




 文章探讨了无监督域自适应方法,如特征匹配和预测调整在模型泛化中的应用。介绍了Test-TimeAdaptation(T3A)通过调整类原型来提升模型表现,以及TENT通过最小化预测熵来适应新域。此外,还提到了使用拉普拉斯最大似然估计的在线测试时间适应方法,以及ContrastiveTest-TimeAdaptation结合伪标签和对比学习优化特征表示。最后,文章讨论了部分标签学习中的对比学习和标签歧义消除策略。
文章探讨了无监督域自适应方法,如特征匹配和预测调整在模型泛化中的应用。介绍了Test-TimeAdaptation(T3A)通过调整类原型来提升模型表现,以及TENT通过最小化预测熵来适应新域。此外,还提到了使用拉普拉斯最大似然估计的在线测试时间适应方法,以及ContrastiveTest-TimeAdaptation结合伪标签和对比学习优化特征表示。最后,文章讨论了部分标签学习中的对比学习和标签歧义消除策略。


















 644
644

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










