测试文本
{"name":"Michael","age": 29}
{"name":"Andy", "age":30}
{"name":"Justin", "age":19}
读取文件:
val df: DataFrame = session.read.json("src/file/sql/people.json")
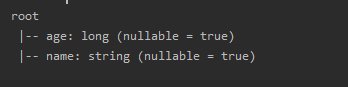
1.printSchema()
官方解释:Prints the plans (logical and physical) to the console for debugging purposes.
就是以树的形式打印显示到控制台
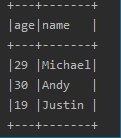
2. show()
df. show( numRows = 10, truncate = false)
默认显示20行,可以通过更改参数显示
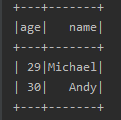
3.select()
可以通过select选择所需要的列
有2种写法:
1.df.select(“age”)
2. df.select($“age”)
$是语法糖需要导入:import spark.implicts._来使用
支持在DataFrame中使用$”列名” 这个语法糖,表示的是Column对象
如果不加$,那么就会当一个String来处理
等价于df.select(col(“age”))
可以直接将年龄+10
df.select($“age”+10)
或者df.select($“age”.plus(10).alias(“age+10”))
as() 或者alias()可以为列取新的名字
4.filter()
filter()和where()等价,都是根据某一列的值进行过滤
df.filter($"age">20).show()
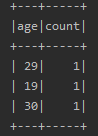
5.groupBy()
根据某一列进行分组,然后再进行聚合操作
df.groupBy($"age").count().show()
6.wIndow()函数
使用DF来实现sql中的开窗函数
import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.{Window, WindowSpec}
val win: WindowSpec =window.partitionBy(\$"列名").orderBt(\$"列名")#也可以加上.rowBetween(-3,3)开始和结束的行....我还没弄懂有什么用,先放在这
df.select($"age".over(win)).show()
7.when().otherwise()
类似于case when
when(boolean,结果).otherwise(不满足条件的结果)




 本文详细介绍了Apache Spark中DataFrame的基本操作,包括读取JSON文件、打印数据结构、展示数据、列选择、过滤、分组聚合及窗口函数应用,是Spark SQL初学者的实用教程。
本文详细介绍了Apache Spark中DataFrame的基本操作,包括读取JSON文件、打印数据结构、展示数据、列选择、过滤、分组聚合及窗口函数应用,是Spark SQL初学者的实用教程。
















 1057
1057

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








