面向对象–OOP,针对业务处理过程的实体及其属性和行为进行抽象封装,以获得更加清晰高效的逻辑单元划分
面向切面–AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming):针对业务处理过程中的切面进行提取,它所面对的是处理过程中的某个步骤或阶段,以获得逻辑过程中各部分之间低耦合性的隔离效果。这两种设计思想在目标上有着本质的差异
AOP使用场景:日志记录,权限,跟踪,优化和监控,事物的处理,资源池(如数据库连接池),系统的异常捕获和处理
aop是一种思想,一种思路,一种模式
而aspectJ则是实现了这AOP思想的框架,
为了理解AOP
以下以实现打印输出各类执行方法的时间以及内容输出到控制台为例,
例子:
问题:
有一个Person类,具有一个方法是eat(String food),我想要在执行eat方法的时候,将执行时的时间和方法名输出到控制台
Person.java
package models;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
//@Getter: 生成get方法,是类、成员变量注解。
//@Setter: 生成set方法,是类、成员变量注解。
//@Data: 生成get、set方法、空构造器、toString方法、equals方法、hashCode方法,是类注解。AppLombokDto 类的注解换成@Data试试。
//@ToString: 生成toString方法,是类注解。
//@EqualsAndHashCode:生成equals方法、hashCode方法,是类注解。
@Data
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(){
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void eat(String food){
System.out.println(this.name+" is having "+food);
}
}
有什么思路呢?
思路一:直接改方法代码(最笨最直接的方法)
在该类的方法执行时,添加输出语句,打印当前时间和方法名
即eat方法变为如下:
public void eat(String food){
System.out.println(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis())+
" "+this.getClass().getName()+" ,method eat");
System.out.println(this.name+" is having "+food);
}
效果:
但是,如果有很多个类都需要打印输出这个时间呢?就需要在每一个类的方法中添加代码打印输出时间
思路二:继承
继承,在子类中重写父类方法,加上时间输出(子类是父类功能的增强,多了日志功能)
新建类PersonLog,继承自类Person
PsersonLog.java
public class PersonLog extends Person {
public PersonLog(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat(String food){
// 这里只输出时间
System.out.println(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis())+
" "+this.getClass().getName()+" ,method eat");
super.eat(food);
}
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis())+
" "+this.getClass().getName()+" ,method run");
super.run();
}
效果:

思考:思路二似乎还是需要在很多的地方去添加时间输出语句,灵活性很低,也没有复用代码的可能,如果能够对所有类的所有方法都实用,只需要一个专门用来输出任意方法的方法名和执行的时间的呢?
思路三:使用aop的思想,(动态代理机制)
代码实现时,不知道要代理的对象具体是什么,在代码运行时,通过反射,获取对象的方法和属性,加以一些处理
新建动态代理类:TimeLog,专门用来输出被代理对象的方法执行前后得到时间
TimeLog.java 需要实现 InvocationHandler接口
代码如下“
public class TimeLog implements InvocationHandler {
Object realObject;//被代理对象
public TimeLog(Object realObject){
this.realObject=realObject;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
before(method);
// 执行被代理对象realObject里的方法
// 传入参数是:被代理对象和方法参数数组args
method.invoke(realObject,args);
// 方法执行之后
end(method);
return null;
}
public void before(Method method){
System.out.println(method.getName()+" start at "+new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));
}
public void end(Method method){
System.out.println(method.getName()+" end at "+new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));
}
}
测试代码:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person =new Person("小强",12);
// person.eat("烤地瓜");
// person.run();
TimeLog timeLog=new TimeLog(person);//person是被代理对象
Person personLog= (Person) Proxy.newProxyInstance(person.getClass().getClassLoader(),person.getClass().getInterfaces(),timeLog);
personLog.run();
personLog.eat("芒果");
}
}
报错解决:Proxy.newProxyInstance() 执行出错
新建接口 PersonInterface,包含eat(String food),run()方法,由Person类实现该接口
代码如下:
PersonInterface.java
package models;
public interface PersonInterface {
void eat(String food);
void run();
}
Person类:
@Data
//实现PersonInterface接口
public class Person implements PersonInterface {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(){
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public void eat(String food){
System.out.println(this.name+" is having "+food);
}
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println(this.name +"run");
}
}
测试代码:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person =new Person("小强",12);
// person.eat("烤地瓜");
// person.run();
TimeLog timeLog=new TimeLog(person);//person是被代理对象
//注意这里是强转为接口类型,如果强转为Person类型转换错误
// 注意第二个参数是Person类的接口数组,newProxyInstance的返回值可以强转为接口类型
PersonInterface personLog= (PersonInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance(person.getClass().getClassLoader(),person.getClass().getInterfaces(),timeLog); personLog.run(); personLog.eat("芒果"); }}
测试效果:
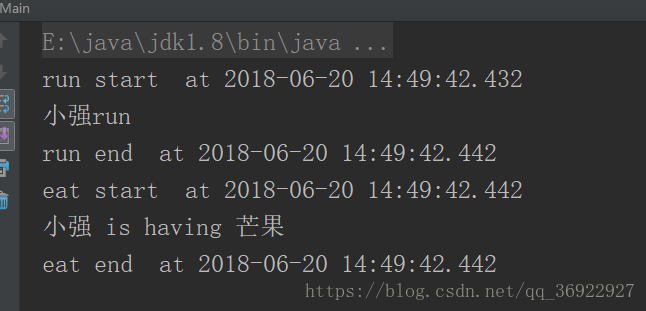
总结:动态代理的好处:
为什么动态代理会比较好呢?
- 首先,不局限于具体的类
- 可以自由组合新的功能
- 不需要改变已有代码,就可以添加新的功能
- 代码可以复用
比如:我除了想输出时间外,还想输出一下参数内容
新建动态代理类 MethodArgsLog(当然可以修改之前的TimeLog类)
public class MethodArgsLog implements InvocationHandler{
Object realObject;//被代理对象
public MethodArgsLog(Object realObject){
this.realObject=realObject;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
before(args);
// 执行被代理对象realObject里的方法
// 传入参数是:被代理对象和方法参数数组args
method.invoke(realObject,args);
return null;
}
public void before(Object []args){
System.out.println("args:"+ args);
}
}
测试类代码:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person =new Person("小强",12);
// person.eat("烤地瓜");
// person.run();
TimeLog timeLog=new TimeLog(person);//person是被代理对象
PersonInterface personLog= (PersonInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance(person.getClass().getClassLoader(),
person.getClass().getInterfaces(),timeLog);
personLog.run();
personLog.eat("芒果");
System.out.println("加上参数输出之后 测试 ");
MethodArgsLog argsLog=new MethodArgsLog(person);
personLog= (PersonInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance(person.getClass().getClassLoader(),
person.getClass().getInterfaces(),argsLog);
personLog.run();
personLog.eat("火锅");
}
}
timeLog);
personLog.run();
personLog.eat("芒果");
System.out.println("加上参数输出之后 测试 ");
MethodArgsLog argsLog=new MethodArgsLog(person);
personLog= (PersonInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance(person.getClass().getClassLoader(),
person.getClass().getInterfaces(),argsLog);
personLog.run();
personLog.eat("火锅");
}
}
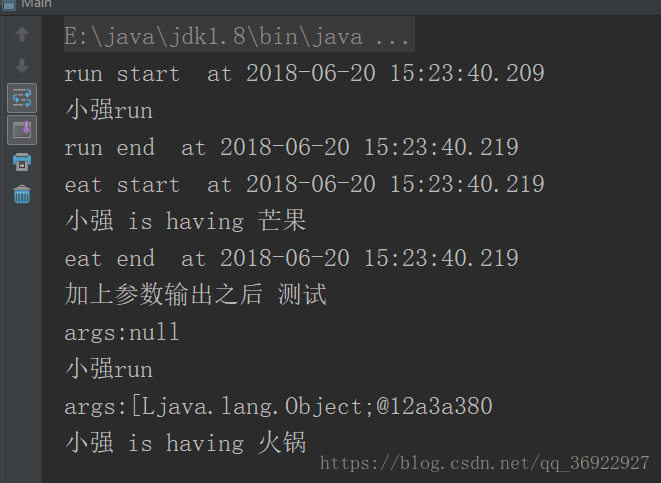
红色部分代码( argsLog 与personLog 的实例化顺序)交换,输出顺序会不一样
输出效果:
aop在spring中的使用:是非常多的,一般debug,会看到spring很多层的invoke的类似的方法
aop在Spring中使用(HandlerInterceptor)是比较方便的,常常用来做登录拦截,权限控制,在aop中判断是否在线,角色身份
附上一个比较优雅的aop示例:(前面看着比较乱,可以直接看以下代码)
package top.forethought.designpattern;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @author wangwei
* @date 2019/1/24 12:18
* @classDescription
*
*/
/**
* 设计模式:代理模式,此代理类来给目标类的方法增加执行时间
*/
public class TimeLog implements InvocationHandler {
private Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(this.getClass().getSimpleName());
private Object target; // 代理目标
private Object proxy; // 代理对象
private static HashMap<Class<?>, InvocationHandler> invokHandlers = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 代理方法
* @param proxy 代理对象
* @param method 方法
* @param args 参数
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = method.invoke(target, args); //执行代理对象的方法
logger.info("execute time MillionsSeconds:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start));
return result;
}
/**
* 获取动态代理对象:原对象上添加时间输出功能后的增强对象
*
*/
/**
* 通过Class来生成动态代理对象Proxy
*
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
public synchronized static <T> T getProxyInstance(Class<T> clazz) {
TimeLog invoHandler = (TimeLog) invokHandlers.get(clazz);
if (null == invoHandler) {
invoHandler = new TimeLog();
try {
T tar = clazz.newInstance();
invoHandler.setTarget(tar);
invoHandler.setProxy(Proxy.newProxyInstance(tar.getClass().getClassLoader(),
tar.getClass().getInterfaces(), invoHandler));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
invokHandlers.put(clazz, invoHandler);
}
return (T) invoHandler.getProxy();
}
public Object getTarget() {
return target;
}
public void setTarget(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
public Object getProxy() {
return proxy;
}
public void setProxy(Object proxy) {
this.proxy = proxy;
}
}
一个选择排序类:
package top.forethought.sorts.selective;
import top.forethought.common.utils.ArrayUtil;
import top.forethought.sorts.interfaces.Sortable;
/**
* @author wangwei
* @date 2019/1/24 10:47
* @classDescription 简单选择排序
* 排序思想:从无序子序列中"选择"关键字最小或最大的记录,并将其加入到有序子序列中,以此扩充有序子序列长度
*
*/
public class SimpleSelectSort implements Sortable{
@Override
public void sort(int[] array) {
for(int lastSortedIndex=0;lastSortedIndex<array.length;lastSortedIndex++){
int maxIndex=lastSortedIndex;
for(int lookIndex=lastSortedIndex;lookIndex<array.length;lookIndex++){
if(array[lookIndex]>array[maxIndex]){
maxIndex=lookIndex;
}
}
if(maxIndex!=lastSortedIndex){
ArrayUtil.swap(array,lastSortedIndex,maxIndex);
}
}
}
}
测试类:
@Test
public void testSimpleSelectSort2(){
int []data= Arrays.copyOf(finalArray,finalArray.length);
RandomUtil.printArray(data);
Sortable simpleSelectSort=TimeLog.getProxyInstance(SimpleSelectSort.class);
simpleSelectSort.sort(data);
RandomUtil.printArray(data);
}
与未使用代理时的测试类:
@Test
public void testSimpleSelectSort(){
int []data= Arrays.copyOf(finalArray,finalArray.length);
RandomUtil.printArray(data);
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
new SimpleSelectSort().sort(data);
long spent=System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
RandomUtil.printArray(data);
System.out.println("SimpleSelectSort sort 耗时 :"+spent);
}
代理测试输出效果:
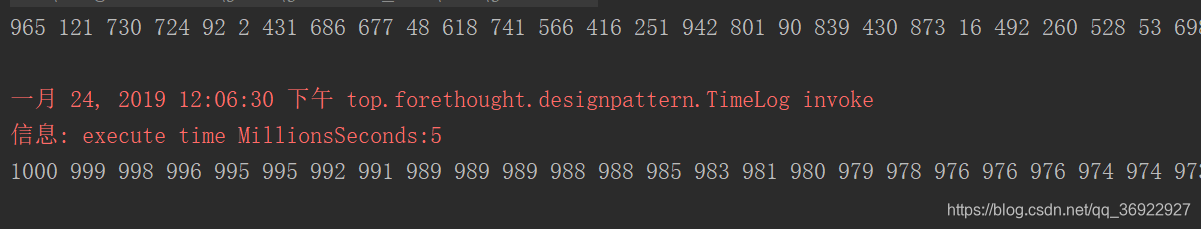








 本文介绍了AOP(面向切面编程)的基本概念和使用场景,通过一个具体的例子展示了如何使用代理模式实现方法执行时间及内容的日志记录。通过动态代理,可以在不修改原有代码的情况下,为多个类的方法添加时间戳和参数内容的输出功能,提高了代码的复用性和灵活性。此外,还探讨了AOP在Spring框架中的应用,如登录拦截和权限控制。
本文介绍了AOP(面向切面编程)的基本概念和使用场景,通过一个具体的例子展示了如何使用代理模式实现方法执行时间及内容的日志记录。通过动态代理,可以在不修改原有代码的情况下,为多个类的方法添加时间戳和参数内容的输出功能,提高了代码的复用性和灵活性。此外,还探讨了AOP在Spring框架中的应用,如登录拦截和权限控制。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








