链接:
https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/106/L
来源:牛客网
来源:牛客网
It’s universally acknowledged that there’re innumerable trees in the campus of HUST.
And you know that, trees have the special ability to refresh the air. If an area, which is surrounded by trees, is separated from the outer atmosphere, you can call it “the supercalifragilisticexpialidocious area”. Students can enjoy the healthiest air there. Then, you happened to know that HUST will plant N trees in a bare plain, so you want to calculate the total size of “the supercalifragilisticexpialidocious area” after each operation.
We describe the position of trees with a coordinate.(X
i,Y
i).

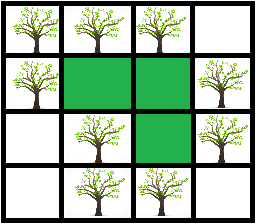
For example, after 9 trees were planted, the green area is a supercalifragilisticexpialidocious area, its size is 3.

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mp make_pair
const int maxn = 2000;
int e[maxn+32][maxn+32], cnt;
const int dirx[] = {0,0,1,-1};
const int diry[] = {1,-1,0,0};
bool inside(int i,int j)
{
return i>=0&&i<=maxn&&j>=0&&j<=maxn;
}
pair<int,int> p[100007];
int res[100007];
void bfs(int x, int y)
{
queue<pair<int,int> > que;
que.push(mp(x, y));
e[x][y] = 2;
while(!que.empty()) {
cnt --;
auto it = que.front(); que.pop();
int x, y;
tie(x, y) = it;
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i ++) {
int dx = x + dirx[i];
int dy = y + diry[i];
if(inside(dx, dy) && e[dx][dy] == 0) {
e[dx][dy] = 2;
que.push(mp(dx, dy));
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++) {
int x, y;
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
x += 1000, y += 1000;
e[x][y] = 1; // tree is 1
p[i] = mp(x, y);
}
cnt = 2001 * 2001 - n;
bfs(0, 0);
auto check = [&](int x, int y) ->bool{
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i ++) {
int dx = x + dirx[i];
int dy = y + diry[i];
if(inside(dx, dy) && e[dx][dy] == 2) return 1;
}
return 0;
};
for(int i = n;i >= 1;i --) {
res[i] = cnt ++;
int x, y;
tie(x,y) = p[i];
e[x][y] = 0;
if( check(x ,y) ) bfs(x, y);
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++) printf("%d\n",res[i]);
return 0;
}
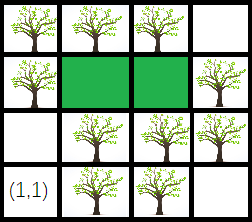
After planting a new tree in (3,2), its size is 2.
输入描述:
The first line is an integer N
 as described above.
as described above.
 as described above.
as described above.
Then following N lines, each line contains two integer X
i and Y
i, indicating a new tree is planted at (X
i,Y
i)
 .
.
 .
.
输出描述:
Output N lines, each line a integer indicating the total size of supercalifragilisticexpialidocious areas after each operation.
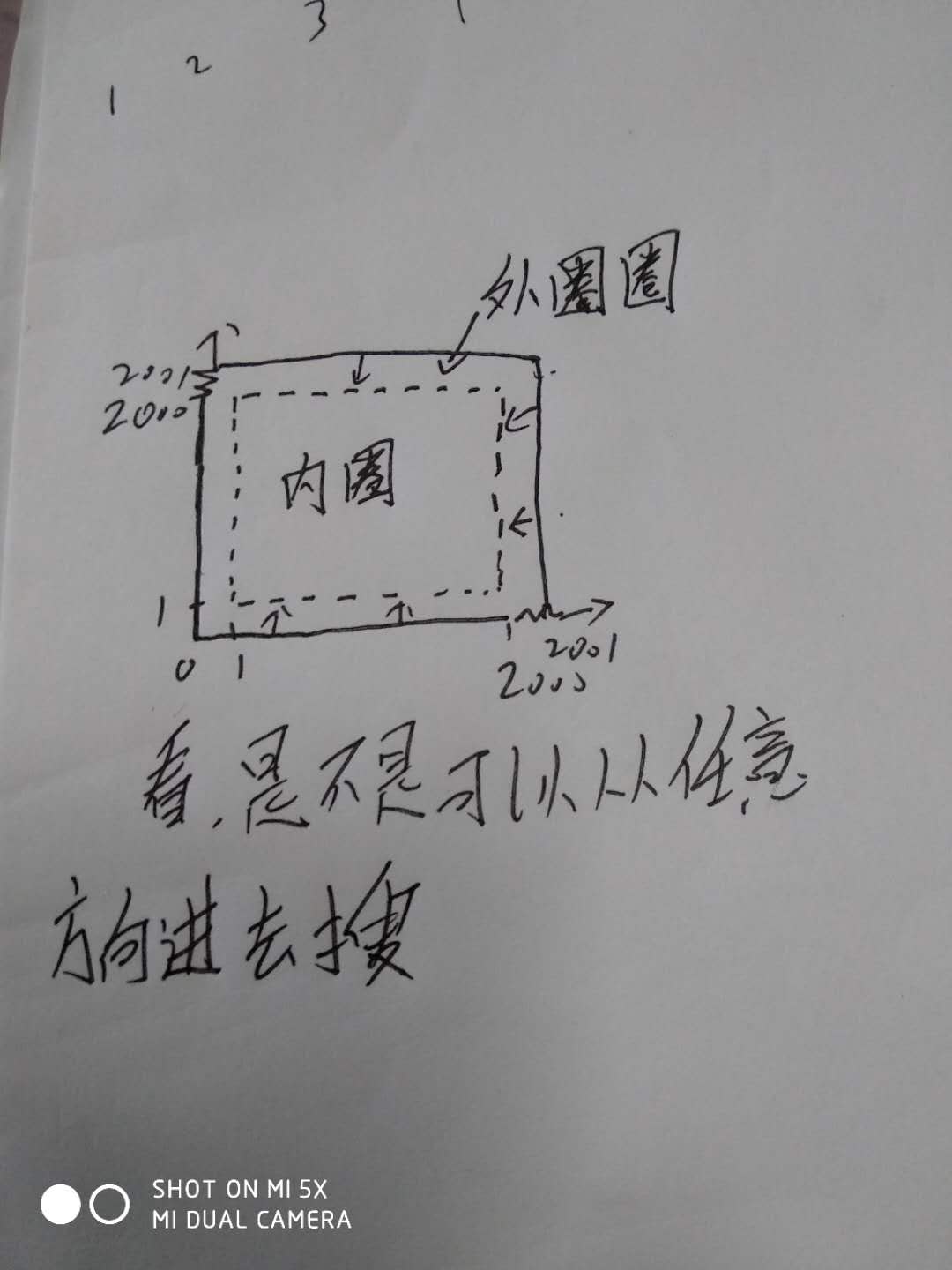
这里解释一下为什么从(0,0)开始,我们知道坐标范围是,坐标在输入时处理了一下,都加了1000,
那么处理后的坐标范围就是(1<Xi,Yi<2000),我们要想在图中都把没被围这空地0走一遍,不能在坐标范围(1<Xi,Yi<2000)中随便找一个坐标就走,不实际,为什么?因为你选的坐标可能走着走着就不能继续走了,但还有空地0(没被围的)没去走并赋值为空地2。这时那我们该怎么解决这个问题呢?很简单,将坐标范围(1<Xi,Yi<2000)的圈外多加单位为1的圈,围住坐标范围(1<Xi,Yi<2000),这时我们可以在多加的一圈内随便找一个点去搜(哪个坐标顺眼就选哪个),这样就能保证能从范围(1<Xi,Yi<2000)圈外的任意个位置进去搜,嗯呢,搞定。啊,我这么热心肠,还是画个图吧!





 本文介绍了一个算法问题,即计算在种植树木后形成的特殊封闭区域(thesupercalifragilisticexpialidociousarea)的总面积。通过使用广度优先搜索(BFS)算法来遍历未被树木包围的所有空白区域,并详细解释了如何实现这一过程。
本文介绍了一个算法问题,即计算在种植树木后形成的特殊封闭区域(thesupercalifragilisticexpialidociousarea)的总面积。通过使用广度优先搜索(BFS)算法来遍历未被树木包围的所有空白区域,并详细解释了如何实现这一过程。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








