Mancala II
时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 128 MB
题目描述
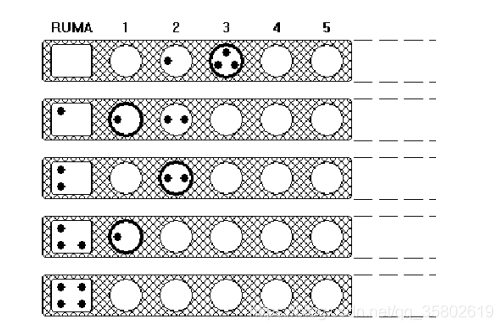
Mancala is a family of board games played around the world, sometimes called sowing games, or count-and-capture games, which describes the game play. One simple variant is a solitaire game called Tchoukaillon which was described by Véronique Gautheron. Tchoukaillon is played on a board with an arbitrary number of bins numbered 1, 2, …, containing b[1], b[2], …, counters respectively and an extra empty bin called the Roumba on the left.
A single play consists on choosing a bin, n, for which b[n] = n (indicated by the darker circles in the diagram) and distributing the counters one per bin to the bins to the left including the Roumba (getting the next diagram below in the fi gure above). If there is no bin where b[n] = n, then the board
is a losing board.
If there is a sequence of plays which takes the initial board distribution to one in which every counter is in the Roumba, the initial distribution is called a winnable board. In the example above, 0, 1, 3, …is a winnable board (the “…” indicates all the bins to the right of bin 3 contain 0). For each total number of counters, there is a unique distribution of the counters to bins to make a winnable board for that total count (so 0, 1, 3, …is the only winnable board with 4 counters).
Write a program which fi nds the winnable board for a total count input.
输入
The first line of input contains a single integer P, (1 ≤ P ≤ 1000), which is the number of data sets that follow. Each data set should be processed identically and independently.
Each data set consists of a single line of input. It contains the data set number, K, followed by a single space, followed by the total count N (1 ≤ N ≤ 2000) of the winnable board to be found.
输出
For each data set there will be multiple lines of output. The first line of output contains the data set number, K, followed by a single space, followed by the index of the last bin, B, with a non-zero count.
Input will be chosen so that B will be no more than 80. The first line of output for each dataset is followed by the bin counts b[1], b[2], …, b[B], 10 per line separated by single spaces.
样例输入
3
1 4
2 57
3 500
样例输出
1 3
0 1 3
2 12
1 2 2 2 2 6 2 4 6 8
10 12
3 39
0 2 2 1 3 2 2 2 6 7
5 0 6 12 2 6 10 14 18 1
3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21
23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39
对于这个题我们写出前几项找规律:
1 0 0 0 0 0 0…
0 2 0 0 0 0 0…
1 2 0 0 0 0 0…
0 1 3 0 0 0 0…
1 1 3 0 0 0 0 …
0 0 2 4 0 0 0…
1 0 2 4 0 0 0…
0 2 2 4 0 0 0…
1 2 2 4 0 0 0…
0 1 1 3 5 0 0…
结果发现递推关系:对于每一项,我们找到这一项的第一个0,让这个箱子装满,它前面的数全部减一就是下一项。数据很小,直接打表(注意格式控制)。
下面是ac代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int p[2024][85];
void init()
{
p[1][1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= 2005; i++)
{
int p0 = 1;
while(p[i-1][p0])
{
p0++;
}
for (int j = 1; j < p0; j++)
{
p[i][j] = p[i-1][j]-1;
}
p[i][p0] = p0;
for (int j = p0+1; j <= 80; j++)
p[i][j] = p[i-1][j];
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
int t0 = 1;
cin >> t;
init();
// for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 1; j <= 20; j++)
// cout << p[i][j] <<" ";
// cout <<endl;
// }
while(t--)
{
int k, n;
scanf("%d%d", &k, &n);
int i;
for (i = 80; i >= 1; i--)
{
if (p[n][i]) break;
}
printf("%d %d\n", k, i);
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
printf("%d", p[n][j]);
if (j % 10) printf(" ");
else printf("\n");
}
if (i%10) printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}





















 452
452

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








