抽象类与接口的区别
1:两者的区别
在实际的开发之中可以发现抽象类和接口的定义是非常相似,这一点从JDK1.8开始实际上就特别明显了,因为在JDK1.8里面接口ue可以定义default方法和static方法,但是这两者依然是有着明显的定义区别于使用区别的。
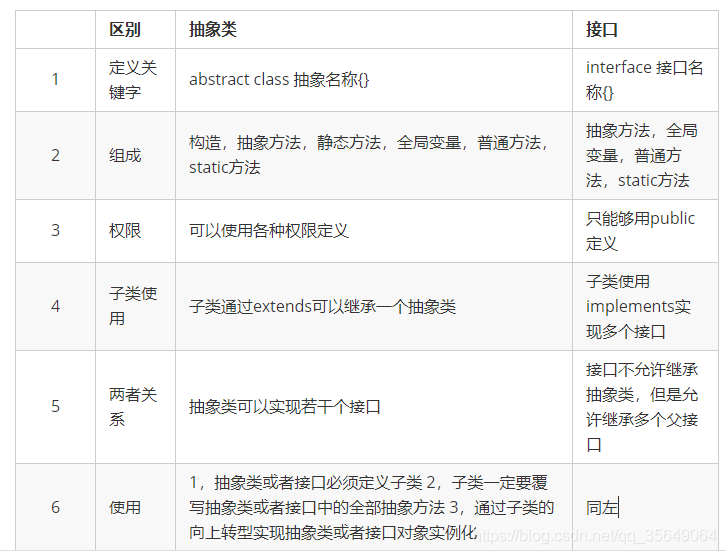
当抽象类和接口都可以使用的情况下优先考虑接口,因为接口可以避免子类的单继承局限。
另外从一个正常的设计角度而言,也需要先从接口来进行项目的整体设计。(如下图)
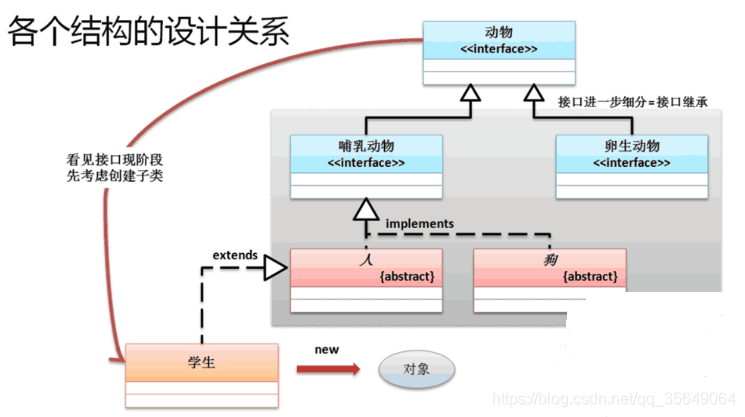
2:抽象类于接口开发案例
背景:抽象类和接口是Java里面最核心的概念,也是所有设计模式的综合体现,包括在日后学习的过程中也会接触许多的系统提供的接口和抽象类; 接口和抽象类都可以使用的情况下一定要优先使用接口,因为接口可以避免单继承的局限。
1:案例分析一:定义一个ClassName接口,接口中只有一个抽象方法getClassName();设计一个类Company,该类实现接口ClassName中的方法getClassName(),功能是获取该类的类名称;编写应用程序使用Company类。
interface IClassName { // 按照要求定义接口
public String getClassName() ; // 数据一定要返回
}
class Company implements IClassName {
public String getClassName() {
return "Company" ;
}
}
public class JavaDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
IClassName ica = new Company() ;
System.out.println(ica.getClassName()) ;
}
}
案例分析二:考虑一个表示绘图的标准,并且可以根据不同的图形来进行绘制;
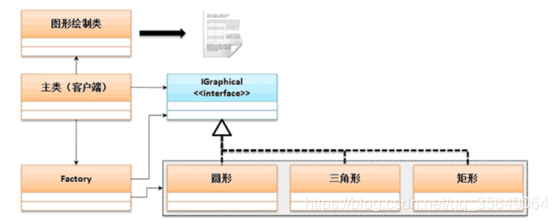
interface IGraphical { // 定义绘图标准
public void paint() ; // 绘图
}
class Point {
private double x ;
private double y ;
public Point(double x,double y) {
this.x = x ;
this.y = y ;
}
public double getX() {
return this.x ;
}
public double getY() {
return this.y ;
}
}
class Triangle implements IGraphical { // 绘制三角形
private Point [] x ; // 保存第一条边的坐标
private Point [] y ; // 保存第二条边的坐标
private Point [] z ; // 保存第三条边的坐标
public Triangle(Point [] x,Point [] y , Point [] z) {
this.x = x ;
this.y = y ;
this.z = z ;
}
public void paint() {
System.out.println("绘制第一条边,开始坐标:[" + this.x[0].getX() + "," + this.x[0].getY() +"],结束坐标:[" + this.x[1].getX() + "," + this.x[1].getY() +"]" ) ;
System.out.println("绘制第二条边,开始坐标:[" + this.y[0].getX() + "," + this.y[0].getY() +"],结束坐标:[" + this.y[1].getX() + "," + this.y[1].getY() +"]" ) ;
System.out.println("绘制第三条边,开始坐标:[" + this.z[0].getX() + "," + this.z[0].getY() +"],结束坐标:[" + this.z[1].getX() + "," + this.z[1].getY() +"]" ) ;
}
}
class Circular implements IGraphical {
private double radius ;
public Circular(double radius) {
this.radius = radius ;
}
public void paint() {
System.out.println("以半径为“"+this.radius+"”绘制圆形。") ;
}
}
class Factory {
public static IGraphical getInstance(String className,double ... args) {
if("triangle".equalsIgnoreCase(className)) {
return new Triangle(
new Point[] {
new Point(args[0],args[1]) , new Point(args[2],args[3])} ,
new Point[] {
new Point(args[4],args[5]),new Point(args[6],args[7])} ,
new Point[] {
new Point(args[8],args[9]),new Point(args[10],args[11])}
) ;
} else if("circular".equalsIgnoreCase(className)) {
return new Circular(args[0]) ;
} else {
return null ;
}
}
}
public class JavaDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
IGraphical iga = Factory.getInstance("triangle",1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,11.11,22.22,33.33,44.44,111.111,222.222,333.333,444.444) ;
iga.paint() ;
IGraphical igb = Factory.getInstance("circular",88.11) ;
igb.paint() ;
}
}
3:案例分析三:定义类Shape,用来表示一般二维图形。Shape具有抽象方法area和perimeter,分别用来计算形状的面积和周长。试定义一些二维形状类(如矩形、三角形、圆形、椭圆形等),这些类均为Shape类的子类。
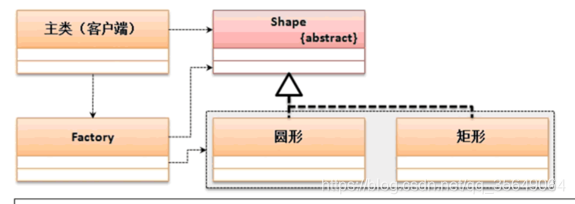
abstract class AbstractShape {
public abstract double area() ;
public abstract double perimeter() ;
}
class Circular extends AbstractShape {
private double radius ;
public Circular(double radius) {
this.radius = radius ;
}
public double area() {
return 3.1415926 * this.radius * this.radius ;
}
public double perimeter() {
return 2 * 3.1415926 * this.radius ;
}
}
class Rectangle extends AbstractShape {
private double length ;
private double width ;
public Rectangle(double length,double width) {
this.length = length ;
this.width = width ;
}
public double area() {
return this.length * this.width ;
}
public double perimeter() {
return 2 * (this.length + this.width) ;
}
}
class Factory {
public static AbstractShape getInstance(String className,double ... args) {
if ("Circular".equalsIgnoreCase(className)) {
return new Circular(args[0]) ;
} else if ("Rectangle".equalsIgnoreCase(className)) {
return new Rectangle(args[0],args[1]) ;
} else {
return null ;
}
}
}
public class JavaDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
AbstractShape asa = Factory.getInstance("Circular",1.1) ;
AbstractShape asb = Factory.getInstance("Rectangle",1.5,10.2) ;
System.out.println("圆形面积:" + asa.area() + "、圆形周长:" + asa.perimeter()) ;
System.out.println("矩形面积:" + asb.area() + "、矩形周长:" + asb.perimeter()) ;
}
}
使用工厂设计模式完全隐藏了实现的子类。








 本文详细解析了抽象类与接口的区别,包括两者在Java开发中的定义与使用场景,通过具体案例阐述了如何选择使用接口而非抽象类,以及它们在设计模式中的应用。
本文详细解析了抽象类与接口的区别,包括两者在Java开发中的定义与使用场景,通过具体案例阐述了如何选择使用接口而非抽象类,以及它们在设计模式中的应用。
















 16万+
16万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








