5、归并排序(Merge Sort)
归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法。该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为2-路归并。
5.1 算法描述
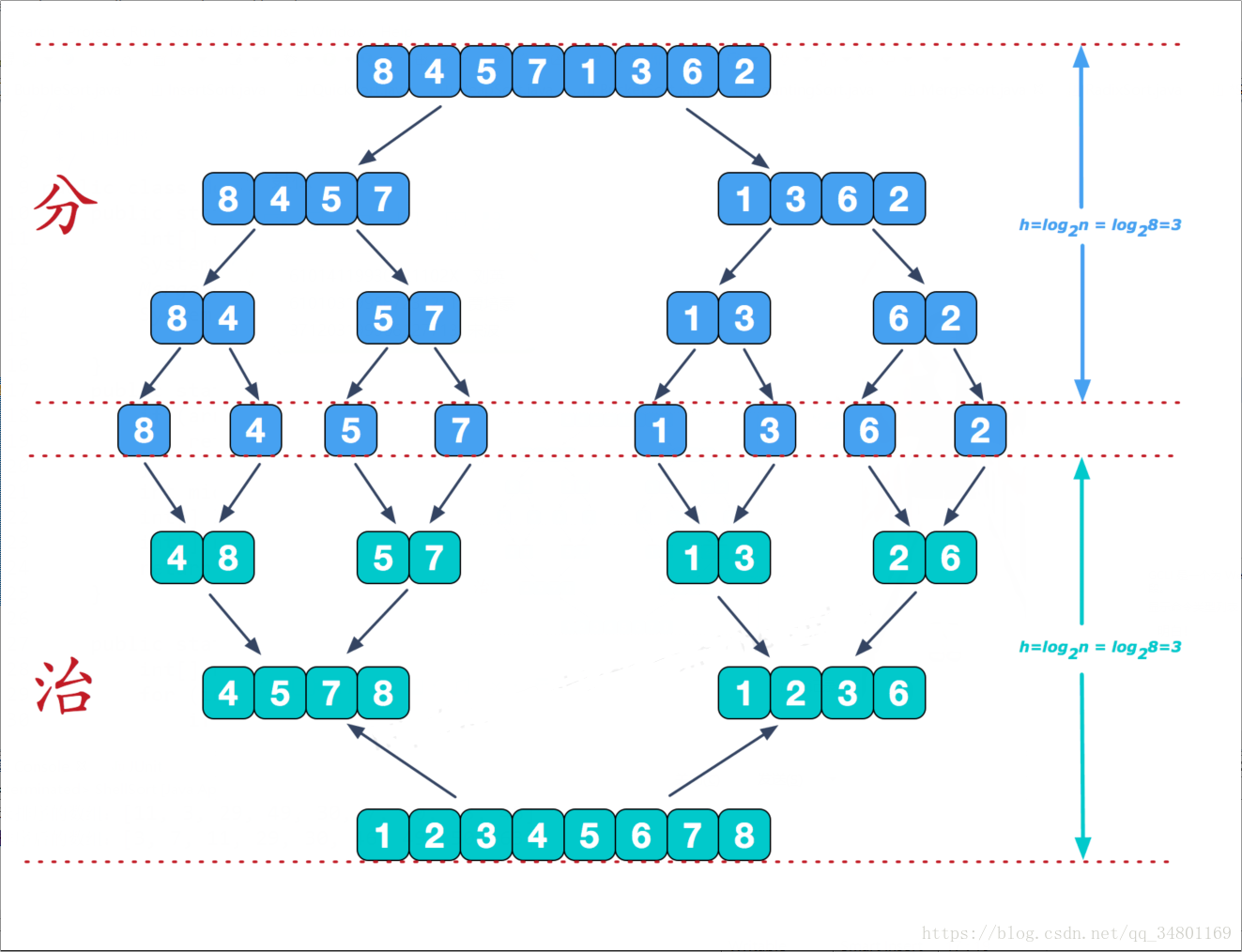
- 把长度为n的输入序列分成两个长度为n/2的子序列;
- 对这两个子序列分别采用归并排序;
- 将两个排序好的子序列合并成一个最终的排序序列。
5.2 动图演示

5.3 代码实现
/**
* 归并排序
*/
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrays = new int[] { 11, 3, 29, 49, 30, 7, 50, 63, 46 };
System.out.println("未排序的数组:" + Arrays.toString(arrays));
mergesort(arrays);
System.out.println("排序后的数组:" + Arrays.toString(arrays));
}
public static void mergesort(int[] arr) {
// 在排序前,先建好一个长度等于原数组长度的临时数组,避免递归中频繁开辟空间
int[] temp = new int[arr.length];
sort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, temp);
}
private static void sort(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
sort(arr, left, mid, temp);// 左边归并排序,使得左子序列有序
sort(arr, mid + 1, right, temp);// 右边归并排序,使得右子序列有序
merge(arr, left, mid, right, temp);// 将两个有序子数组合并操作
}
}
private static void merge(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right,
int[] temp) {
int i = left;// 左序列指针
int j = mid + 1;// 右序列指针
int t = 0;// 临时数组指针
while (i <= mid && j <= right) {
if (arr[i] <= arr[j]) {
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
} else {
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
}
while (i <= mid) {// 将左边剩余元素填充进temp中
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}
while (j <= right) {// 将右序列剩余元素填充进temp中
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
t = 0;
// 将temp中的元素全部拷贝到原数组中
while (left <= right) {
arr[left++] = temp[t++];
}
}
}
5.4 算法分析
归并排序是一种稳定的排序方法。和选择排序一样,归并排序的性能不受输入数据的影响,但表现比选择排序好的多,因为始终都是O(nlogn)的时间复杂度。代价是需要额外的内存空间。
归并排序是稳定排序,它也是一种十分高效的排序,能利用完全二叉树特性的排序一般性能都不会太差。java中Arrays.sort()采用了一种名为TimSort的排序算法,就是归并排序的优化版本。从上文的图中可看出,每次合并操作的平均时间复杂度为O(n),而完全二叉树的深度为|log2n|。总的平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。而且,归并排序的最好,最坏,平均时间复杂度均为O(nlogn)。








 本文详细介绍归并排序算法,包括其工作原理、动图演示、Java代码实现及算法分析。归并排序是一种稳定的排序方法,始终拥有O(nlogn)的时间复杂度。
本文详细介绍归并排序算法,包括其工作原理、动图演示、Java代码实现及算法分析。归并排序是一种稳定的排序方法,始终拥有O(nlogn)的时间复杂度。
















 338
338

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








