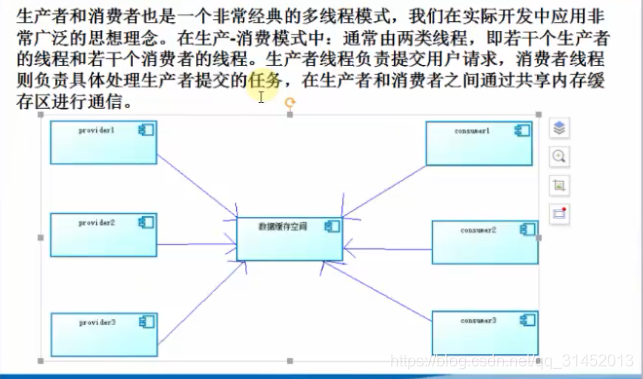
例子:
//主类
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
BlockingQueue<Data> queue=new LinkedBlockingQueue<Data>(10);
//生产者
Provider p1 = new Provider(queue);
Provider p2 = new Provider(queue);
Provider p3 = new Provider(queue);
//消费者
Consumer c1 = new Consumer(queue);
Consumer c2 = new Consumer(queue);
Consumer c3 = new Consumer(queue);
//创建线程池
ExecutorService cachePool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
cachePool.execute(p1);
cachePool.execute(p2);
cachePool.execute(p3);
cachePool.execute(c1);
cachePool.execute(c2);
cachePool.execute(c3);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
p1.stop();
p2.stop();
p3.stop();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//生产者
public class Provider implements Runnable {
//共享缓存区
private BlockingQueue<Data> queue;
private volatile boolean isRunning =true;
private static AtomicInteger count= new AtomicInteger();
private static Random r = new Random();
public Provider(BlockingQueue queue){
this.queue=queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (isRunning){
try {
Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(1000));
//获取的数据进行累计
int id = count.incrementAndGet();
//比如通过一个getData方法获取了
Data data = new Data(Integer.toString(id), "数据" + id);
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",获取了数据Id," +data.getId()+
"装载到queue中去");
//2秒钟没有加进去,返回false
if (!this.queue.offer(data,2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)){
System.out.println("提交到Queue数据失败");
}
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void stop(){
this.isRunning=false;
}
}
//消费者
public class Consumer implements Runnable{
private BlockingQueue<Data> queue;
public Consumer(BlockingQueue queue){
this.queue=queue;
}
//随机对象
private static Random r =new Random();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
try {
Data data = this.queue.take();
//模仿数据处理
Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(1000));
System.out.println("当前消费线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",消费成功" +
"消费数据Id为:"+data.getId());
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//data类
public class Data {
private String id;
private String name;
public Data(String id,String name){
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Data{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
输出结果:
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1,获取了数据Id,1装载到queue中去
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3,获取了数据Id,2装载到queue中去
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5,消费成功消费数据Id为:2
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1,获取了数据Id,3装载到queue中去
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3,获取了数据Id,4装载到queue中去
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5,消费成功消费数据Id为:4
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-6,消费成功消费数据Id为:3
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2,获取了数据Id,5装载到queue中去
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5,消费成功消费数据Id为:5
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4,消费成功消费数据Id为:1
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2,获取了数据Id,6装载到queue中去
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1,获取了数据Id,7装载到queue中去
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3,获取了数据Id,8装载到queue中去
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1,获取了数据Id,9装载到queue中去
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2,获取了数据Id,10装载到queue中去
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-6,消费成功消费数据Id为:6
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3,获取了数据Id,11装载到queue中去
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-6,消费成功消费数据Id为:9
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2,获取了数据Id,12装载到queue中去
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1,获取了数据Id,13装载到queue中去
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2,获取了数据Id,14装载到queue中去
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4,消费成功消费数据Id为:8
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5,消费成功消费数据Id为:7
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2,获取了数据Id,15装载到queue中去
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4,消费成功消费数据Id为:11
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2,获取了数据Id,16装载到queue中去
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3,获取了数据Id,17装载到queue中去
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4,消费成功消费数据Id为:13
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-6,消费成功消费数据Id为:10
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2,获取了数据Id,18装载到queue中去
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3,获取了数据Id,19装载到queue中去
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4,消费成功消费数据Id为:14
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3,获取了数据Id,20装载到queue中去
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1,获取了数据Id,21装载到queue中去
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5,消费成功消费数据Id为:12
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4,消费成功消费数据Id为:16
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2,获取了数据Id,22装载到queue中去
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-6,消费成功消费数据Id为:15
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5,消费成功消费数据Id为:17
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4,消费成功消费数据Id为:18
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5,消费成功消费数据Id为:20
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-6,消费成功消费数据Id为:19
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4,消费成功消费数据Id为:21
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5,消费成功消费数据Id为:22
Executor框架:

发现都是调用底层的同一个方法ThreadPoolExecutor()
实现自定义线程池:

第一个参数corePoolSize:核心线程
表示线程池初始化的线程数量
第二个参数maxinumPoolSize:线程池最大线程数量
第三四个参数:表示线程执行完之后,多长时间回收 0表示线程执行完立刻回收
第五个参数:任务多了会放在该队列中
第七个参数:拒绝策略
newScheduledThreadPool:
class Temp extends Thread {
public void run(){
System.out.println("run");
}
}
public class ScheduleJob{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Temp temp = new Temp();
//初始化线程的数量
ScheduledExecutorService schedule = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
//第二个参数1表示初始化1秒之后去执行的时间,第二个参数表示3秒轮询
schedule.scheduleWithFixedDelay(temp,1,3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
自定义线程池使用详解:

例子:
1.有界队列
public class UseThreadPoolExecutor1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 在使用有界队列时,若有新的任务需要执行,如果线程池实际线程数小于corePoolSize,则优先创建线程,
* 若大于corePoolSize,则会将任务加入队列,
* 若队列已满,则在总线程数不大于maximumPoolSize的前提下,创建新的线程,
* 若线程数大于maximumPoolSize,则执行拒绝策略。或其他自定义方式。
*
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1,//核心线程数量
2,// 最大线程数量
60,//空闲时间
TimeUnit.SECONDS,//空闲时间的单位
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3)//指定一种队列 (有界队列)
);
MyTask mt1 = new MyTask(1, "任务1");
MyTask mt2 = new MyTask(2, "任务2");
MyTask mt3 = new MyTask(3, "任务3");
MyTask mt4 = new MyTask(4, "任务4");
MyTask mt5 = new MyTask(5, "任务5");
MyTask mt6 = new MyTask(6, "任务6");
pool.execute(mt1);
pool.execute(mt2);
/* pool.execute(mt3);
pool.execute(mt4);
pool.execute(mt5);*/
// pool.execute(mt6);
pool.shutdown();
}
}
public class MyTask implements Runnable {
private int taskId;
private String taskName;
public MyTask(int taskId, String taskName){
this.taskId = taskId;
this.taskName = taskName;
}
public int getTaskId() {
return taskId;
}
public void setTaskId(int taskId) {
this.taskId = taskId;
}
public String getTaskName() {
return taskName;
}
public void setTaskName(String taskName) {
this.taskName = taskName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("run taskId =" + this.taskId);
Thread.sleep(5*1000);
//System.out.println("end taskId =" + this.taskId);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String toString(){
return Integer.toString(this.taskId);
}
}
说明:
pool.execute(mt1);
pool.execute(mt2);
pool.shutdown();
运行结果:
run taskId =1
run taskId =2
当放2个任务的时候,因为核心线程为1,第二个任务会放在队列里面。第一个结果出来之后5秒钟才会输出 run taskId =2 。
pool.execute(mt1);
pool.execute(mt2);
pool.execute(mt3);
pool.execute(mt4);
pool.execute(mt5);
pool.shutdown();
运行结果:
run taskId =1
run taskId =5
run taskId =2
run taskId =3
run taskId =4
放了5个任务已经,初始化一个线程执行一个,队列里面放3个 一共4个,超出的一个会另起一个线程。
所以先同时输出run taskId =1 run taskId =5,5秒后在同时输出run taskId =2 run taskId =3最后输出run taskId =4
pool.execute(mt1);
pool.execute(mt2);
pool.execute(mt3);
pool.execute(mt4);
pool.execute(mt5);
pool.execute(mt6);
pool.shutdown();
放了6个任务,队列满了,而且超出线程池最大线程数量。会执行拒绝策略。第6个任务会抛出异常。
2.无界队列
package com.bjsxt.height.concurrent018;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class UseThreadPoolExecutor2 implements Runnable{
private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public void run() {
try {
int temp = count.incrementAndGet();
System.out.println("任务" + temp);
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue =
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>();
//new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(10);
ExecutorService executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
5, //core
10, //max
120L, //2fenzhong
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
queue);
for(int i = 0 ; i < 20; i++){
executor.execute(new UseThreadPoolExecutor2());
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("queue size:" + queue.size()); //10
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
}
输出结果:
任务2
任务1
任务3
任务4
任务5
queue size:15
任务6
任务7
任务8
任务10
任务9
任务11
任务12
任务13
任务15
任务14
任务16
任务17
任务18
任务20
任务19
说明:会5个5个的执行
策略:
public class UseThreadPoolExecutor1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 在使用有界队列时,若有新的任务需要执行,如果线程池实际线程数小于corePoolSize,则优先创建线程,
* 若大于corePoolSize,则会将任务加入队列,
* 若队列已满,则在总线程数不大于maximumPoolSize的前提下,创建新的线程,
* 若线程数大于maximumPoolSize,则执行拒绝策略。或其他自定义方式。
*
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, //coreSize
2, //MaxSize
60, //60
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3) //指定一种队列 (有界队列)
//new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()
// , new MyRejected()
, new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy()
);
MyTask mt1 = new MyTask(1, "任务1");
MyTask mt2 = new MyTask(2, "任务2");
MyTask mt3 = new MyTask(3, "任务3");
MyTask mt4 = new MyTask(4, "任务4");
MyTask mt5 = new MyTask(5, "任务5");
MyTask mt6 = new MyTask(6, "任务6");
pool.execute(mt1);
pool.execute(mt2);
pool.execute(mt3);
pool.execute(mt4);
pool.execute(mt5);
pool.execute(mt6);
pool.shutdown();
}
}
DiscardOldestPolicy丢弃最老的任务
输出结果:
run taskId =1
run taskId =5
run taskId =3
run taskId =4
run taskId =6
丢弃了任务2.。。
可以自定义策略:
例子:
public class UseThreadPoolExecutor1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 在使用有界队列时,若有新的任务需要执行,如果线程池实际线程数小于corePoolSize,则优先创建线程,
* 若大于corePoolSize,则会将任务加入队列,
* 若队列已满,则在总线程数不大于maximumPoolSize的前提下,创建新的线程,
* 若线程数大于maximumPoolSize,则执行拒绝策略。或其他自定义方式。
*
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, //coreSize
2, //MaxSize
60, //60
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3) //指定一种队列 (有界队列)
//new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()
, new MyRejected()
// , new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy()
);
MyTask mt1 = new MyTask(1, "任务1");
MyTask mt2 = new MyTask(2, "任务2");
MyTask mt3 = new MyTask(3, "任务3");
MyTask mt4 = new MyTask(4, "任务4");
MyTask mt5 = new MyTask(5, "任务5");
MyTask mt6 = new MyTask(6, "任务6");
pool.execute(mt1);
pool.execute(mt2);
pool.execute(mt3);
pool.execute(mt4);
pool.execute(mt5);
pool.execute(mt6);
pool.shutdown();
}
}
//拒绝的类
public class MyRejected implements RejectedExecutionHandler{
public MyRejected(){
}
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
System.out.println("自定义处理..");
System.out.println("当前被拒绝任务为:" + r.toString());
}
}
实现了RejectedExecutionHandler接口
运行结果:
自定义处理…
run taskId =1
run taskId =5
当前被拒绝任务为:6
run taskId =2
run taskId =3
run taskId =4
可以在自定义策略里http请求返回给任务提交者,或者保存到日志,再次在后台统一处理比如跑批处理








 本文详细解析了Java线程池的工作原理,包括有界队列与无界队列的区别,以及不同拒绝策略的实现方式。通过具体示例,展示了线程池如何处理任务,如何在任务过多时进行队列管理和线程调度。
本文详细解析了Java线程池的工作原理,包括有界队列与无界队列的区别,以及不同拒绝策略的实现方式。通过具体示例,展示了线程池如何处理任务,如何在任务过多时进行队列管理和线程调度。
















 295
295

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








