题目一
给定一个数组arr,求差值为k的去重数字对。
思路
对于数组中的每个值,使用STL里面的find查找是否有与之差值为k的值存在,如果存在,则在用于标记的数组mark中将该数字的索引位置标为1.最后将每个索引位置被标为1的值存入set容器中进行去重。
实现代码
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
set<int> remove(vector<int>&nums, int k){
vector<int>mark(nums.size());
//找到相应的数字,记录数字的索引位置
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
if((find(nums.begin(), nums.end(),nums[i]-k)!=nums.end())||
(find(nums.begin(), nums.end(),nums[i]+k)!=nums.end())){
mark[i]=1;
}
}
//放到set里面,自动去重
set<int>answer;
for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++){
if(mark[i])
answer.insert(nums[i]);
}
return answer;
}
int main(){
vector<int>nums={3,16,53,72,33,1,6,7,3,73,146,23,64,1,78,52};
int k=13;
set<int>answer=remove(nums, k);
for(auto i : answer)
cout<<i<<endl;
return 0;
}
加题
如果两个只包含小写英文字母的字符串所含字符种类相同,则这两个字符串被称为同源词。比如“ab”和“abbba”就是同源词。“ab”和“abbbbc”就不是同源词。
写一个函数,判断两个词是否为同源词
思路
还是用set。分别村两个字符串的各个字符。如果两个set容器的size相同,则两个词是同源词。(这个太简单,就不实现了)
或者使用26位二进制代表一个词,每一位对应一个字母。如果两个字符串对应的数相同,则说明两个词是同源词。
实现代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void compare(string first, string second){
int num1=0, num2=0;
for(int i=0; i<first.length(); i++){
num1 |= 1<<(first[i]-'a');
}
for(int j=0; j<second.length(); j++){
num2 |=1<<(second[j]-'a');
}
if(num1==num2)
cout<<"两个字符串同源"<<endl;
else
cout<<"两个字符串不同源"<<endl;
}
int main(){
string first, second;
cout<<"请输入一个由小写字母组成的字符串"<<endl;
cin>>first;
cout<<"请再次输入一个由小写字母组成的字符串"<<endl;
cin>>second;
compare(first, second);
return 0;
}
题目二
给一个包含n个整数元素的集合a,一个包含m个整数元素的集合b。定义magic操作为,从一个集合中取出一个元素,放到另一个集合里,且操作过后每个集合的平均值都大大于于操作前。
注意以下两点:
- 1)不可以把一个集合的元素取空,这样就没有平均值了
- 2)值为x的元素从集合b取出放入集合a,但集合a中已经有值为x的元素,则a的平均值不变(因为集合元素不会重复),b的平均值可能会改变(因为x被取出了)
问最多可以进行多少次magic操作?
思路:
集合,因此不会存在重复值。
对于集合a和集合b,如果两个集合的平均值相同,则无法进行此操作
实现magic操作的方法是拿出平均值高的那个集合里,值小于该集合的平均值且高于另一个集合的平均值的值,且该值在平均值小的集合中并没有出现过(因为集合中元素不会发生重复)。则会发生magic操作。
实现代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//要取得[a,b)的随机整数,使用(rand() % (b-a))+ a;
//要取得[a,b]的随机整数,使用(rand() % (b-a+1))+ a;
int CreatRandomNum(){
//随机产生1到100的整数
return (rand() % 100)+1;
}
int magic(vector<int>a, vector<int>b){
int sum_a=0, sum_b=0;
for(auto i : a) sum_a+=i;
for(auto i : b) sum_b+=i;
double ave_a=sum_a/a.size();
double ave_b=sum_b/b.size();
if(ave_a==ave_b) return 0;
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
sort(b.begin(),b.end());
int answer=0;
//从a往b拿
if(ave_a>ave_b){
for(int i=0; i<a.size();i++){
//该值大于b的均值且小于a的均值,且在b中没出现过
if((a[i]>ave_b)&&(a[i]<ave_a)&&(find(b.begin(),b.end(),a[i])==b.end())){
answer++;
}
}
}
//从b往a拿
else{
for(int i=0; i<b.size();i++){
//该值大于a的均值且小于b的均值,且该值在a中没出现过
if((b[i]>ave_a)&&(b[i]<ave_b)&&(find(a.begin(),a.end(),b[i])==a.end())){
answer++;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
int main(){
vector<int>a, b;
int len_a=CreatRandomNum(), len_b=CreatRandomNum();
while(len_a--)
a.push_back(CreatRandomNum());
while(len_b--)
b.push_back(CreatRandomNum());
int answer=magic(a,b);
cout<<answer<<endl;
return 0;
}
题目三
将给定的数转换为字符串,原则如下:1对应 a,2对应b,…..26对应z,
例如12258可以转换为"abbeh", "aveh", "abyh", "lbeh" and "lyh",个数为5,
编写一个函数,给出可以转换的不同字符串的个数。
思路:
暴力递归解思路(配合后面的代码更容易理解):
对于字符串,遍历每个字符:
- 如果当前位置为字符串的结尾位置,则只有一种表达方式——空串。
- 如果当前字符是“0”,则无法转换,因为1111可以转成aaaa,也可以11和11组合。但是字符以0开头,没有对应的字符
- 如果开头不是“0”,且后续有字符。只要该位置不是“0”,则结果sum=1(该位置的字符自己表示一个字母)+余下的组合方式
- 当遍历到字符串的末尾,则结束递归。
动态规划解法——dp只是用来记录每一步的最优解的一个容器
暴击解转动态规划。
由于暴力解中,指针可以指向字符串末尾位置的后一位,因此初始化动态规划数组的长度是字符串长度+1。
vector<int>con(input.length()+1);
动态规划数组的最后一位只有一种情况,那就是空串,因此动态规划数组最后一位的值为1.
con[input.length()]=1;
倒数第二位的判断:如果最后一位字符是“0”,则有零种,如果不是“0”,则有一种(因为只有一个字符)
con[input.length() - 1] = input[input.length() - 1] == '0' ? 0 : 1;
从n-2一直算到0状态。递归怎么写,动态规划就怎么填。
实现代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//产生一个10000-100000的随机数
int CreatRandomNum(){
/*
要取得[a,b)的随机整数,使用(rand() % (b-a))+ a;
要取得[a,b]的随机整数,使用(rand() % (b-a+1))+ a;
要取得(a,b]的随机整数,使用(rand() % (b-a))+ a + 1;
*/
return (rand()%90000)+10000;
}
//暴力递归
int Process(string input, int index){
if(index==input.length()) return 1;
if(input[index]=='0') return 0;
int res=Process(input, index+1);
if(index==input.length()-1) return res;
if(((input[index]-'0')*10+input[index+1]-'0')<27)
res+=Process(input, index+2);
return res;
}
//动态规划
int dp(string input){
vector<int>con(input.length()+1);
//把空串的情况存放在空串会发何时能的对应位置上
//空串的时候,只有一种结果,所以此时的值为1
con[input.length()]=1;
//最后一位如果是0,则此处无解,否则此处是一种字母,结果为1
con[input.length() - 1] = input[input.length() - 1] == '0' ? 0 : 1;
for(int i=input.length()-2; i>=0; i--){
//此时无法代表任何字符,因此次违章的结果为0
if (input[i] == '0') con[i] = 0;
else
//当前字符不是"0"。如果此位置和下一个位置组合的值小于27,说明还能组合出一个结果
con[i] = con[i + 1] + (((input[i] - '0') * 10 + (input[i + 1] - '0')) < 27 ?
con[i + 2] : 0);
}
return con[0];
}
int main(){
//把数字转成字符串
string input=to_string (CreatRandomNum());
//暴力递归
//cout<<Process(input, 0)<<endl;
//动态规划
//cout<<dp(input)<<endl;
cout<<input<<endl;
Process(input, 0)==dp(input)?cout<<"good"<<endl:cout<<"fucking !!! fuck!!!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
题目四
一个合法的括号匹配序列有以下定义:
- ①空串""是一个合法的括号匹配序列
- ②如果"X"和"Y"都是合法的括号匹配序列,"XY"也是一个合法的括号匹配序列
- ③如果"X"是一个合法的括号匹配序列,那么"(X)"也是一个合法的括号匹配序列
- ④每个合法的括号序列都可以由以上规则生成。
例如: "","()","()()","((()))"都是合法的括号序列对于一个合法的括号序列我们又有以下定义它的深度:
- ①空串""的深度是0
- ②如果字符串"X"的深度是x,字符串"Y"的深度是y,那么字符串"XY"的深度为max(x,y)
- 3、如果"X"的深度是x,那么字符串"(X)"的深度是x+1
例如: "()()()"的深度是1,"((()))"的深度是3。求一个只有"("和“”)“”两种符号的字符串最长的合法子串有多长。
思路:
看到子串,看到子数组的大套路——想每个位置开头会怎么怎么样,每个位置结尾会怎么怎么样。
找的合法串,必须以0位置结尾,必须以1位置结尾,必须以2位置结尾。正确结果必在其中。比如下方字符串,以0位置结尾的长度为0,因为“)”无法构成合法串;以1位置的长度是0,因为“)(”无法构成合法串。。。以此类推
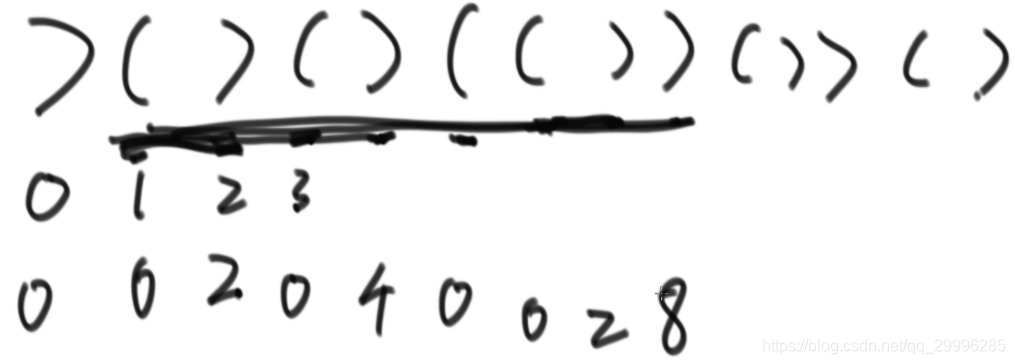
那么单独以一个位置,怎么求合法串长度?
从左到右求,当求到 i 位置的时候,说明 i-1 位置已经被求过了。
如果 i 位置是 “(”,则和发出按长度是0,因为任何合法串都不可能以"("结尾。
如果 i 位置是 “)”,则查看 i-1 位置的结果。如果 i-1 位置的合法串长度是4,则向前四个位置,查看 i-5 的位置是不是“(”,即:
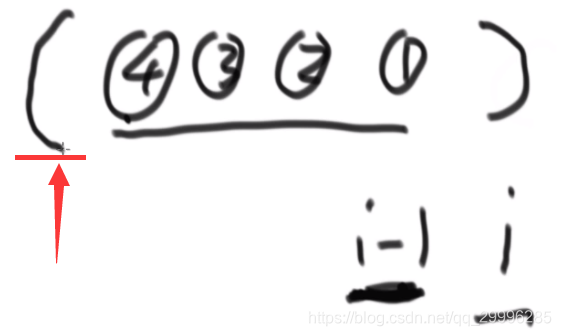
因此,此时 i 位置的长度最小是 6.为什么说最小呢?因为 i-6 的位置(假设 i-6=k)可能还会有一段合法串,即:
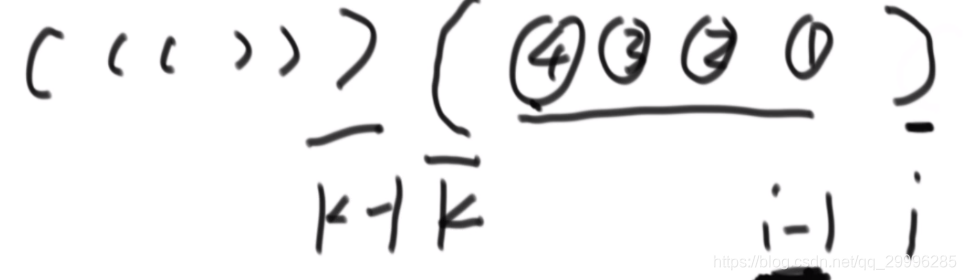
既然如此,那么前面会不会还继续有合法串等着我们加进去?即:
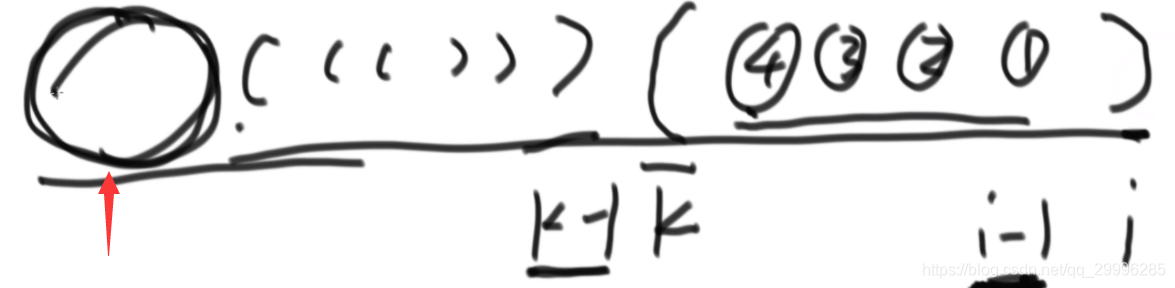
答案是不会的。因为如果前面那一块是合法的,那么这一块一定在计算位置 k 的时候,就被算过了。
实现代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//写一个用于生成随机括号串的发生器
string Creatinput(){
int len=(rand()%51)+50;
int input=0;
string res;
while(len--){
//创造一个只产生 0 和 1 的随机数的函数
input=rand()%2;
if(input==0) res.push_back('(');
else res.push_back(')');
}
return res;
}
//动态规划计算最长子串的长度
int LongestChild(string input){
if(input.length()==0) return 0;
vector<int>dp(input.length());
int pre=0, res=0;
//对于位置 i
for(int i=1; i<input.length(); i++){
//如果 i 的位置是 ),才会可能有合法串
if(input[i]==')'){
//查看 i-1 位置的合法串长度
pre=i-dp[i-1]-1;
//如果不越界,并且是(,说明位置 i 的合法长度起码是 dp[i - 1] + 2
//如果pre>0,说明pre前面的有没有合法串也需要看看
if (pre >= 0 && input[pre] == '(')
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 2 + (pre > 0 ? dp[pre - 1] : 0);
}
//不断更新最大值
res=max(res, dp[i]);
}
return res;
}
int main(){
string input=Creatinput();
cout<<input<<endl;
cout<<LongestChild(input)<<endl;
return 0;
}
题目五
请编写一个程序,对一个栈里的整型数据,按升序进行排序(即排序前,栈里的数据是无序的,排序后最大元素位于栈顶),要求最多只能使用一个额外的栈存放临时数据,但不得将元素复制到别的数据结构中。
思路
用一个辅助栈。我们将辅助栈中的元素按照从小到大排序,最后将辅助栈中的元素倒回原始栈,那么原始栈中的元素就是从大到小排序了。

入栈出现实现过程:
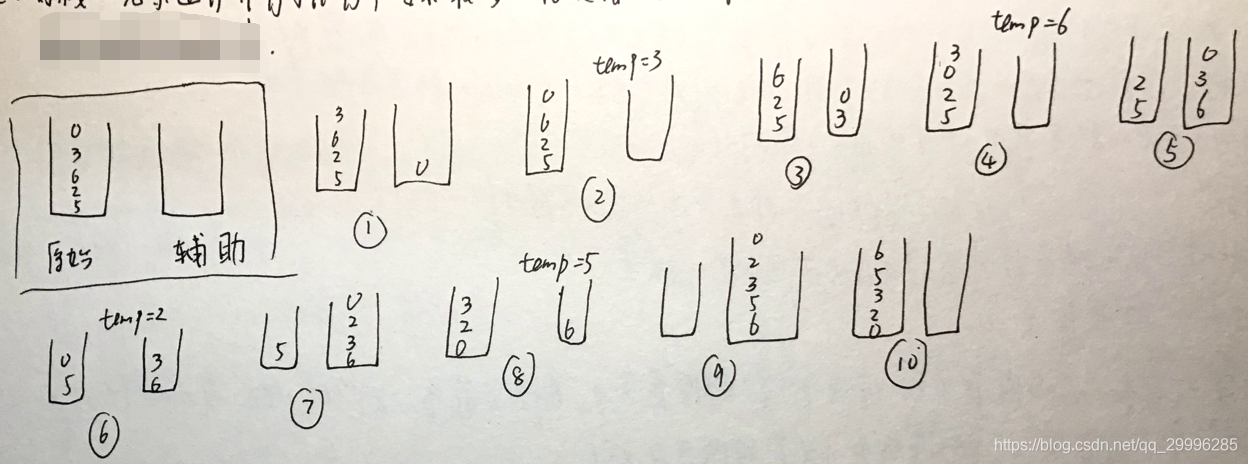
原始栈每弹出一个元素,则将该元素与辅助栈的栈顶进行比较
- 小于栈顶——入栈
- 大于栈顶——将辅助栈中的元素依次弹出,压入原始栈中,直到栈顶大于该元素或者辅助栈空了为止
实现代码
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
int CreatRandom(){
return rand();
}
//栈内元素逆序
void StackSortStack(stack<int>&input){
if(input.size()==0) return;
stack<int>helper;
int temp;
while (input.size()) {
temp = input.top();
input.pop();
//辅助栈为空,则将元素压入
if (!helper.size()) helper.push(temp);
else {
//辅助栈不空,且元素值大于辅助栈栈顶
while (helper.size() && temp > helper.top()) {
//将辅助栈中的元素压回原始栈
input.push(helper.top());
helper.pop();
}
//此时辅助栈为空,或者辅助栈的栈顶大于该元素
helper.push(temp);
}
}
//将元素从辅助栈倒回原始栈
while(helper.size()){
input.push(helper.top());
helper.pop();
}
}
int main(){
int len=10;
stack<int>first;
//创建无序栈
while(len--)
first.push(CreatRandom());
StackSortStack(first);
while(first.size()){
cout<<first.top()<<endl;
first.pop();
}
return 0;
}
题目六
牛牛和羊羊都很喜欢青草。今天他们决定玩青草游戏。最初有一个装有n份青草的箱子,牛牛和羊羊依次进行,牛牛先开始。在每个回合中,每个玩家必须吃一些箱子中的青草,所吃的青草份数必须是4的x次幂,比如1,4,16,64等等。不能在箱子中吃到有效份数青草的玩家落败。假定牛牛和羊羊都是按照最佳方法进行游戏,请输出胜利者的名字。
思路
打表找规律,找数学原理就别指望了。面试场那么紧张,就别指着退什么数学原理了。
先找暴力解(下图中——左面是草的份数,右面是谁赢):

暴力解法——打表找规律,观察结果:
string winner1(int n){
if(n<5)
return (n==0 || n==2)?"后手":"先手";
int base=1;
while(base<=n){
////因为吃了base份青草之后,对方变成了先手,我变成了后手。
//因此,此时的后手赢,就是我赢
if(winner1(n-base)=="后手"){
return "先手";
}
//防止溢出
if(base>n/4){
break;
}
base *=4;
}
return "后手";
}
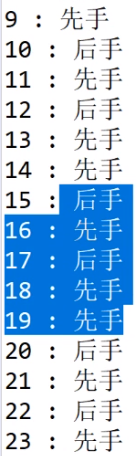 这个数,模5之后得到5或者2,就是后手赢。
这个数,模5之后得到5或者2,就是后手赢。
就是打表找规律,写帖子的人说发现什么数学原理,就是为了让你佩服他而已,没用。
实现代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string winner1(int n){
if(n<5)
return (n==0 || n==2)?"后手":"先手";
int base=1;
while(base<=n){
////因为吃了base份青草之后,对方变成了先手,我变成了后手。
//因此,此时的后手赢,就是我赢
if(winner1(n-base)=="后手"){
return "先手";
}
//防止溢出
if(base>n/4){
break;
}
base *=4;
}
return "后手";
}
string winner2(int n){
if(n%5==0 || n%5==2){
return "后手";
}else{
return "先手";
}
}
int main(){
int input;
while(cin>>input){
cout<<winner1(input)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
题目七
二叉树每个结点都有一个int型权值,给定一棵二叉树,要求计算出从根结点到叶结点的所有路径中,权值和最大的值为多少。
思路:
后面会讲树形dp,树形动态规划。
递归方式——看代码就能看懂了,不解释了。
int maxValue(TreeNode* root, int pre){
if(!root) return 0;
//如果存在两个子树,则累加根节点到该节点的值
if((!root->left)&&(!root->right))
return pre+root->val;
//左子树累加和==累加根节点到该节点的值+左子树的累加和
int left=maxValue(root->left, pre+root->val);
int right=maxValue(root->right, pre+root->val);
//选择最大的作为结果
return max(left, right);
}
非递归方式——模仿非递归先序遍历
如果当前节点是叶节点,则与记录最大值的变量Max进行比较,不断更新Max。遍历过程如下:
非递归先序遍历的写法
- 准备一个栈。先把头结点a入栈
- 从栈中拿出头结点,拿出就打印
- 检查a有没有右孩子,有就将右孩子入栈
- 检查a有没有左孩子,有则入栈
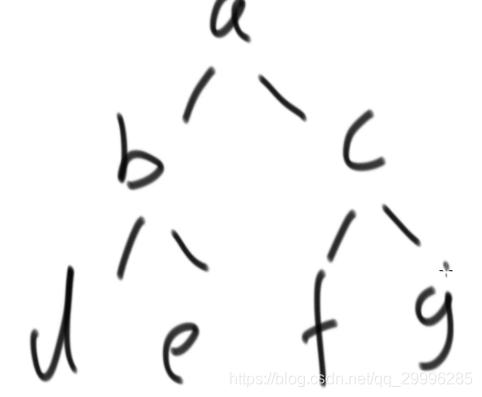
int preorder(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
stack<TreeNode*>helper;
helper.push(root);
TreeNode* tool;
while (helper.size()) {
//2
tool = helper.top();
helper.pop();
//3
cout << tool->value << endl;
if (tool->right) {
helper.push(tool->right);
}
//4
if (tool->left) {
helper.push(tool->left);
}
}
}
实现代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int i=0):
val(i), left(nullptr), right(nullptr){};
};
int CreatNum(){
return (rand()%10)+1;
}
TreeNode* CreatTree(vector<int>con){
if(!con.size()) return nullptr;
int index=0;
TreeNode*root=new TreeNode(con[index++]);
queue<TreeNode*>q;
TreeNode* temp;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()&&index<con.size()){
temp=q.front();
q.pop();
if(con[index]&&index<con.size()){
TreeNode*left=new TreeNode(con[index++]);
temp->left=left;
q.push(left);
}
if(con[index]&&index<con.size()){
TreeNode*right=new TreeNode(con[index++]);
temp->right=right;
q.push(right);
}
}
return root;
}
//递归
int maxValue(TreeNode* root, int pre){
if(!root) return 0;
if((!root->left)&&(!root->right))
return pre+root->val;
int left=maxValue(root->left, pre+root->val);
int right=maxValue(root->right, pre+root->val);
return max(left, right);
}
//非递归
int maxValue1(TreeNode* root){
int Max=0;
stack<TreeNode*>st;
if(root!=nullptr) st.push(root);
map<TreeNode*,int>record;
TreeNode*helper=nullptr;
while(!st.empty()){
helper=st.top();
st.pop();
//叶节点,则记录当前路径是否为最大值
if(helper->left==nullptr && helper->right==nullptr)
Max=max(Max, record[helper]);
if(helper->right){
record[helper->right]=record[helper]+
helper->right->val;
st.push(helper->right);
}
if(helper->left){
record[helper->right]=record[helper]+
helper->left->val;
st.push(helper->left);
}
}
return Max;
}
int main(){
vector<int>con;
int len=20;
while(len--)
con.push_back(CreatNum());
cout<<maxValue1(CreatTree(con))<<endl;
return 0;
}
题目八
递归函数逆序一个栈。
思路
逆序一个栈,即每次获取栈底元素并返回。当栈为空时进行入栈操作。因此整个过程分为两部分:
- 1、递归的获取栈底元素并返回
- 2、栈为空时进行入栈操作
1、递归的获取栈底元素并返回
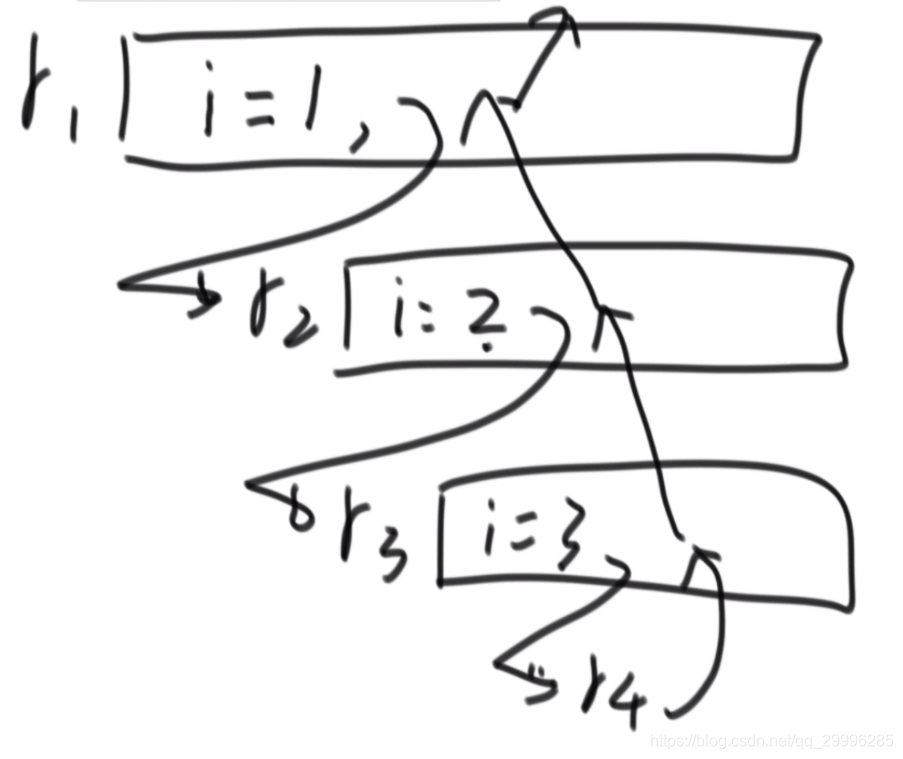
假设栈底到栈顶为1,2,3。可以设计一个递归函数getLatsElement,每次进入函数就从栈中弹出一个元素并存入变量r中,另返回值last的值等于进一步递归获得的返回值。
- 若弹出元素后栈不为空,则继续向下递归;
- 若栈为空,则返回返回值。
过程如下:
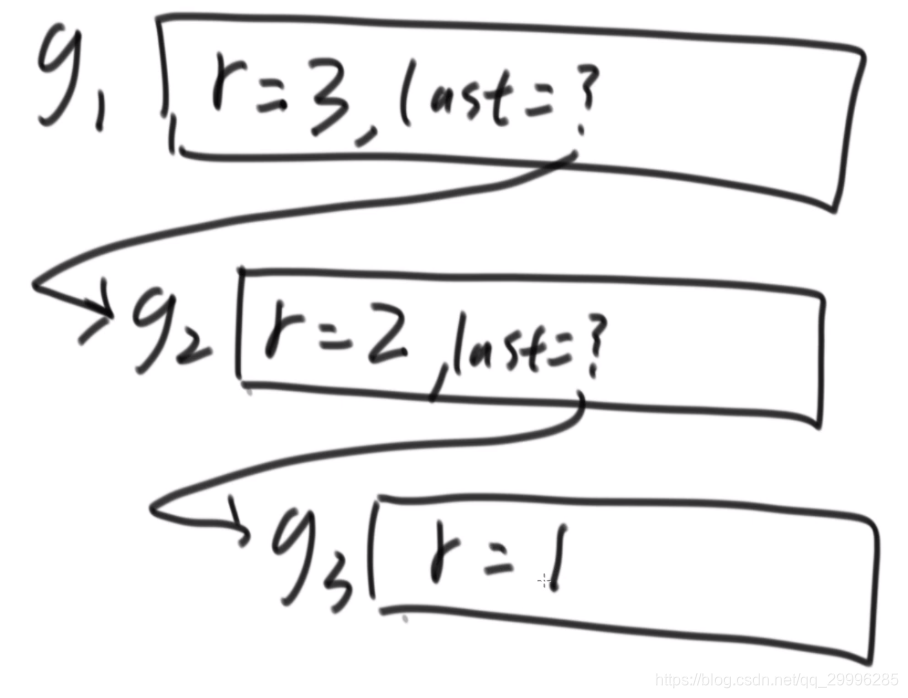
//获取栈底元素并返回
int getLatsElement(stack<int>&st){
int res=st.top();
st.pop();
if(st.empty()) return res;
int last=getLatsElement(st);
st.push(res);
return last;
}
2、栈为空时进行入栈操作
不断调用函数g,以获取栈底元素。当栈为空时,将获取到的值入栈即可。
void Reverse(stack<int>&st){
if(st.empty()) return;
//存储获取到的栈底元素
int i=getLatsElement(st);
//递归调用,不断深挖
Reverse(st);
//栈为空时会返回,此时执行push入栈操作
st.push(i);
}
实现代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//获取栈底元素并返回
int getLatsElement(stack<int>&st){
int res=st.top();
st.pop();
if(st.empty()) return res;
int last=getLatsElement(st);
st.push(res);
return last;
}
void Reverse(stack<int>&st){
if(st.empty()) return;
//存储获取到的栈底元素
int i=getLatsElement(st);
//递归调用,不断深挖
Reverse(st);
//栈为空时会返回,此时执行push入栈操作
st.push(i);
}
int main(){
stack<int>st;
vector<int>vec={1,2,3};
for(auto i:vec){
st.push(i);
}
Reverse(st);
while(st.size()){
cout<<st.top()<<endl;
st.pop();
}
return 0;
}
 算法挑战:经典编程题解析
算法挑战:经典编程题解析





















 510
510

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








