前言
最近在看Servlet中用注解代替web.xml初始化Servlet Context,servlet规范提到:
In a web application, classes using annotations will have their annotations processed
only if they are located in the WEB-INF/classes directory, or if they are packaged
in a jar file located in WEB-INF/lib within the application.
根据这段描述,如果用注解添加自定义Servlet:MyServlet(已经删除web.xml),代码如下:
@WebServlet(name = "MyServlet", urlPatterns = "*.do")
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
super.service(req, res);
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("<html>Hello World</html>");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
要求MyServlet要在WEB-INF/classes里或者WEB-INF/lib中jar包里。
问题:classpath和这两个路径是什么关系?spring配置里用的classpath*和classpath有什么区别?怎么在servlet要读取classpath里的文件?webapp的classpath是哪个目录?WEB-INF文件夹是classpath吗?webapp里除了WEB-INF文件夹下的文件,其他文件能用servlet读取吗?webapp的文件结构?JSP文件要不要放在WEB-INF/下?
理解classpath
根据官网的描述:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/essential/environment/paths.html
classpath是java执行时,用到的class的路径。查看java --help可以找到相关的参数:
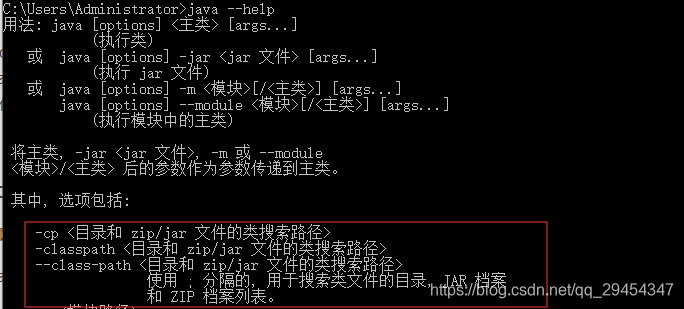
classpath可以包含多个目录,用;号分隔。目录中可以包含.class文件也可以是jar文件或zip文件。
其中 “.” 代表了当前目录
理解classloader
然后是classloader,java 8 api里描述了2种classloader(注意,不同jdk版本classloader的种类有区别)
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/ClassLoader.html#
- bootstrap,java自带的
- user-defined,用户定义的
bootstrap class loader较好理解,CLASS_PATH里定义的目录下的class,都由boostrap class loader负责。
至于,user-defined的class loader,可以参考tomcat 8.5.X的文档:https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-8.5-doc/class-loader-howto.html
可以看到tomcat自定义了好几种class loader。
简而言之,这些class loader将class文件都加载进了jvm。
问题:除了class文件,classpath里的其他文件呢?classpath里的jar文件的里面的其他文件呢(比如jar里面的META-INF目录下的文件)?
通过classloader获取resource
classpath里的非.class文件,包括jar里面的,都可以通过Class.getResource/Class.getResourceAsStream读取,源码如下:
public java.net.URL getResource(String name) {
name = resolveName(name);
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0();
if (cl==null) {
// A system class.
return ClassLoader.getSystemResource(name);
}
return cl.getResource(name);
}特别注意的是路径的问题。假设classpath里的内容如下
classpath (包括一个org目录和一个YY.jar)
org/yxm/XX.class
org/yxm/xx.xml
YY.jar (包括META-INF目录和org目录)
META-INF/yy.xml
META-INF/YYY.properties
org/yy/yy.class
org/yy/yy-config.xml
- 读取xx.xml, 路径是 “org/yxm/xx.xml” --> class.getResource("/org/yxm/xx.xml");
- 读取yy.xml,路径是"/yy.xml"
- 读取YYY.properties, 路径是 "/YYY.properties"
- 读取yy-confg.xml, 路径是"/org/yy/yy-confg.xml"
jar包中的META-INF目录下的文件,被视为classpath root路径下的文件.
注意,路径带"/"开头,则表示根目录下;如果路径不是带"/"开头的,则表示当前Class路径的相对路径。
api doc说明:
- If the
namebegins with a'/'('\u002f'), then the absolute name of the resource is the portion of thenamefollowing the'/'.- Otherwise, the absolute name is of the following form:
modified_package_name/nameWhere the
modified_package_nameis the package name of this object with'/'substituted for'.'('\u002e').
java webapp的文件架构
了解这个主要是为了弄清楚,在java webapp中,classpath是怎么定义的。
根据Servlet 3.1文档的描述,推荐的webapp文件架构是:

根据tomcat 的描述:https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-8.5-doc/class-loader-howto.html
WEB-INF/classes和WEB-INF/lib 是classpath的一部分(特别注意,WEB-INF/下的其他文件和文件夹不属于classpath。另外,idea会自动将root resource文件夹下的文件在打成war包的时候,放在WEB-INF/classes下)。使用Class.getResource可以读取WEB-INF/classes和WEB-INF/lib目录下的文件,那如果想读取其他的文件呢?
ServletContext接口也提供了getResource方法,所有在webapp root目录下的文件,都可以通过此方法读取。特别的是jar中的/META-INF/resource文件夹(jar包中META-INF/resource目录下的文件被当成webapp root目录下的文件),servlet 3.1 是说明如下:
The getResource and getResourceAsStream methods take a String with a leading
“/” as an argument that gives the path of the resource relative to the root of the
context or relative to the META-INF/resources directory of a JAR file inside the
web application’s WEB-INF/lib directory. These methods will first search the root
of the web application context for the requested resource before looking at any of the
JAR files in the WEB-INF/lib directory. The order in which the JAR files in the
WEB-INF/lib directory are scanned is undefined. This hierarchy of documents may
exist in the server’s file system, in a Web application archive file, on a remote server,
or at some other location.
根据上面这段的描述,请求"/xxx.html",如果在某个jar的META-INF/resources/目录下,那么这个请求会指向这个html; 否则,404 not found。
所以不要把Class.getResource和ServletContext.getResource搞混了。
spring配置中的classpath: xxx.xml 和 classpath*: xxx.xml
这2个的区别参考官方的说明:
在很多博客上有人说 classpath*是专门用来查找jar包内文件的,这是胡说八道。
classpath和classpath*都是在classpath中查找,之前已经说清楚了,WEB-INF/classes和WEB-INF/lib/xxx.jar都在classpath中,不存在“classpath* 专门用来查找jar包内文件”的说法。
两者的区别主要在于:classpath找到一个满足的就会停止查找。而classpath*会找到所有的。所以classpath*需要更长的查找时间,因为它会遍历所有的jar包。注意2者的区别就知道什么情况下用哪个了。
举例,有几个jar包中META-INF/下有spring的配置文件,格式是xxxxx-spring-config.xml,则使用:
classpath*: /xxxxx-spring-config.xml,可以把他们全部找到。
forward和web.xml中的路径
servlet.forward("")和web.xml中都需要配置一些文件的路径或者jsp的路径,他们的路径与ServletContext的路径规则一致,都是从webapp的根路径开始查找。用"/"开头的就是从根路径开始查找,没有"/"开头的就是相对路径.







 本文探讨了在web应用中,如何理解和使用classpath,包括webapp的文件架构,classloader的工作原理,以及如何通过classloader获取resource。特别强调了Spring中classpath:和classpath*:的区别,并解释了在Servlet中读取不同路径资源的方法。
本文探讨了在web应用中,如何理解和使用classpath,包括webapp的文件架构,classloader的工作原理,以及如何通过classloader获取resource。特别强调了Spring中classpath:和classpath*:的区别,并解释了在Servlet中读取不同路径资源的方法。
















 157
157

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








