一、Spring Boot整合JPA
1、创建Spring Boot项目JPADemo

2、创建ORM实体类
ORM: Object Relation Mapping 对象关系映射
(1)创建评论实体类Comment

package net.yc.lesson07.bean;
import javax.persistence.*;
/**
* 评论实体类
* */
@Entity(name = "t_comment")
public class Comment {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "content")
private String content;
@Column(name = "author")
private String author;
@Column(name = "a_id")
private Integer aId;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public Integer getaId() {
return aId;
}
public void setaId(Integer aId) {
this.aId = aId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Comment{" +
"id=" + id +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", aId=" + aId +
'}';
}
}
@Entity中的name对应数据库中表名
GenerationType.IDENTITY为MySQL中的自增使用的策略,不同类型的数据库使用策略不同
(2)创建文章实体类Article
package net.yc.lesson07.bean;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.List;
@Entity(name = "t_article")
public class Article {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "title")
private String title;
@Column(name = "content")
private String content;
//查询时把子表一并查出来
@OneToMany(fetch = FetchType.EAGER) // FetchType.LAZY 懒加载
@JoinTable(name = "t_comment", joinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "a_id")},
inverseJoinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "id")})
private List<Comment> commentList;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public List<Comment> getCommentList() {
return commentList;
}
public void setCommentList(List<Comment> commentList) {
this.commentList = commentList;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Article{" +
"id=" + id +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", commentList=" + commentList +
'}';
}
}
3、创建自定义接口 - ArticleRepository

4、添加数据源依赖,配置数据源属性
(1)在pom.xml文件添加阿里巴巴数据源依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.6</version>
</dependency>
(2)在全局配置文件里配置数据源

spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/blog?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.datasource.druid.max-active=100
spring.datasource.druid.min-idle=10
spring.datasource.druid.initial-size=20
(3)在测试类里编写测试方法

- 运行测试

二、利用JPA实现个性化操作
1、创建接口CommentRepository

package net.yc.lesson07.repository;
import net.yc.lesson07.bean.Comment;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
/**
*
* 评论仓库接口
*/
public interface CommentRepository extends JpaRepository<Comment, Integer> {
/**根据文章ID进行分页查询评论
* nativeQuery = true 表示使用原生SQL语句,否则使用的是实体对象
* @param aId 查询条件字段
* @param pageable 可分页对象,分页查询需要该参数
* @return 返回一个分页对象,包含page的相关信息及查询结果集
*/
@Query(value = "select * from t_comment where a_id =?1",nativeQuery = true)
Page<Comment> findCommentPagedByArticleId01(Integer aId, Pageable pageable);
/**根据文章ID进行分页查询评论
* 没有设置nativeQuery 默认就是false,表示使用HQL语句,使用的是实体对象
* @param aId 查询条件字段
* @param pageable 可分页对象,分页查询需要该参数
* @return 返回一个分页对象,包含page的相关信息及查询结果集
*/
@Query(value = "select c from t_comment c where c.aId = ?1")
Page<Comment> findCommentPagedByArticleId02(Integer aId, Pageable pageable);
}
2、创建测试类CommentTests

3、在测试类里创建测试方法
(1)创建测试方法testFindCommentPagedByArticleId01()

- 运行测试

- 修改页面索引,显示第二页

设置排序方式 :
Sort.Direction.DESC - 降序;Sort.Direction.ASC - 升序

- 运行测试

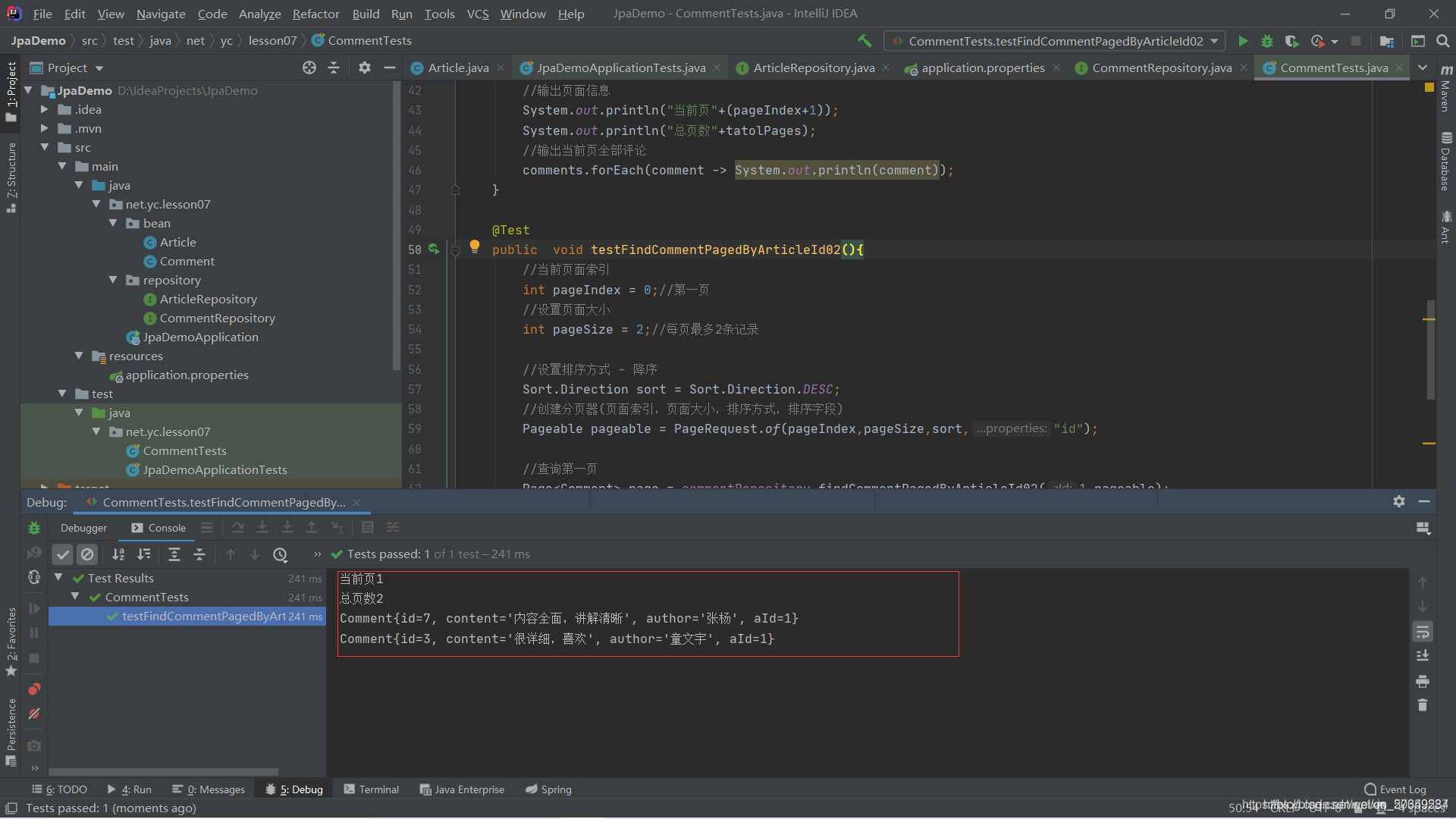
(2)创建测试方法testFindCommentPagedByArticleId02()

-
运行测试
-
不论是原生sql查询还是基于对象的查询,最终分页查询的效果是相同的
























 1041
1041

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








