A simple mathematical formula for e is
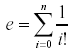
where n is allowed to go to infinity. This can actually yield very accurate approximations of e using relatively small values of n.
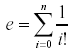
where n is allowed to go to infinity. This can actually yield very accurate approximations of e using relatively small values of n.
Output
Output the approximations of e generated by the above formula for the values of n from 0 to 9. The beginning of your output should appear similar to that shown below.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<iomanip>
//#define P 3.141592653
using namespace std;
int function(int k)
{
if (k == 0 || k == 1)
return 1;
else
return k*function(k - 1);
}
void main()
{
double arr[10],sum=0;
cout << 'n' << ' ' << 'e' << endl;
cout << '-' << ' ' << "-----------" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
arr[i] = 1.0 / function(i);
sum += arr[i];
if (i == 0 || i == 1)
cout << i << ' ' << fixed << setprecision(0) << sum << endl;
else if (i == 2)
cout << i << ' ' << fixed << setprecision(1) << sum << endl;
else
cout << i << ' ' <<fixed<<setprecision(9)<< sum<< endl;
}
system("pause");
}





















 404
404

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








