给定一个二叉树(具有根结点 root), 一个目标结点 target ,和一个整数值 K 。
返回到目标结点 target 距离为 K 的所有结点的值的列表。 答案可以以任何顺序返回。
示例 1:
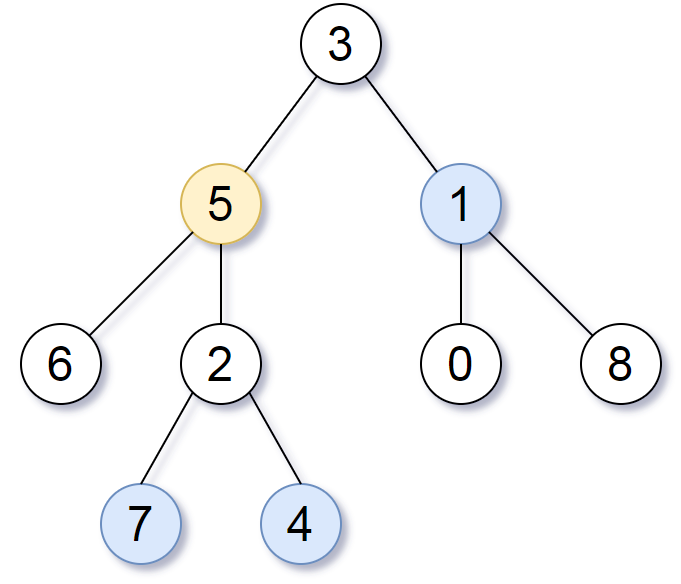
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, K = 2 输出:[7,4,1] 解释: 所求结点为与目标结点(值为 5)距离为 2 的结点,值分别为 7,4,以及 1注意,输入的 "root" 和 "target" 实际上是树上的结点。上面的输入仅仅是对这些对象进行了序列化描述。
提示:
- 给定的树是非空的,且最多有
K个结点。 - 树上的每个结点都具有唯一的值
0 <= node.val <= 500。 - 目标结点
target是树上的结点。 0 <= K <= 1000.
思路:这道题博猪一开始的思路居然是展开成双向链表。。。(愚蠢至极),后来看到了discuss的通过记录已找到的子节点来one pass的方法就可以找到距离为k的节点,实在是巧妙。
思路的核心思想是如果当前节点root距离目标节点的距离为len,那么当前节点的子节点root->left或者root->right距离目标节点的距离就是len+1,除了当前子节点就是目标节点的子树里面的情况(如上图所示,目标节点是5,那么以root节点(3)为起点,它的子节点都比root节点离5更远,除了5,6,2,7,4这5个已经在目标节点的子树或者更靠近目标节点的情况,其他节点都满足这个性质),那么我们要怎么修正对于5,6,2,7,4这5个节点的距离呢?我们就需要一个函数,首先找到以目标节点为叶节点向上追溯到根节点的距离目标节点的值,简单来说就是先通过一个函数把目标节点至根节点的距离值找出来,存入hashmap中,如下所示:
节点5:距离0 (目标节点的距离设为0)
节点2,7,4,6:距离-1 (距离-1表示这些节点是目标节点下面的点或者不在目标节点子树上)
节点3:距离1 (目标节点的父节点的距离逐个加1)
我们把计算出的值存入hashmap中,在dfs过程中如果发现当前节点在hashmap中,就修正对应节点的length,然后看是否和目标K的距离相等即可。
参考代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int find(unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> &map, TreeNode* root, TreeNode* target) {
if (root == nullptr) return -1;
if (root == target) {
map[root] = 0;
return 0;
}
int left = find(map, root->left, target);
if (left >= 0) {
map[root] = (left + 1);
return left + 1;
}
int right = find(map, root->right, target);
if (right >= 0) {
map[root] = (right + 1);
return right + 1;
}
return -1;
}
void distanceKCore(vector<int> &res, unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> &map, TreeNode* root, int K,int length) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
if (map.find(root) != map.end()) length = map[root];
if (length == K) res.push_back(root->val);
distanceKCore(res, map, root->left, K, length + 1);
distanceKCore(res, map, root->right, K, length + 1);
}
vector<int> distanceK(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* target, int K) {
vector<int> res;
unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> map;
find(map, root, target);
distanceKCore(res, map, root, K,map[root]);
return res;
}
};





 本文探讨了在二叉树中寻找与特定目标节点距离为K的所有节点值的有效算法。通过一次深度优先搜索(DFS),结合哈希映射记录各节点至目标节点的距离,巧妙修正了目标节点子树内节点的距离计算,最终返回距离为K的节点值列表。
本文探讨了在二叉树中寻找与特定目标节点距离为K的所有节点值的有效算法。通过一次深度优先搜索(DFS),结合哈希映射记录各节点至目标节点的距离,巧妙修正了目标节点子树内节点的距离计算,最终返回距离为K的节点值列表。
















 1090
1090

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








