一、Linux下SPI驱动介绍
内核版本:2.6.35
Linux下SPI驱动和I2C驱动很类似,他们都是一种总线,且都不支持热拔插,因为一般情况下spi或者i2c设备都是直接焊接在板子上的,不像USB设备那样随时插拔,所以根据总线——设备——驱动模型,spi和i2c设备都可以通过xxx_board_info结构体进行注册,Linux下spi驱动的架构如下:
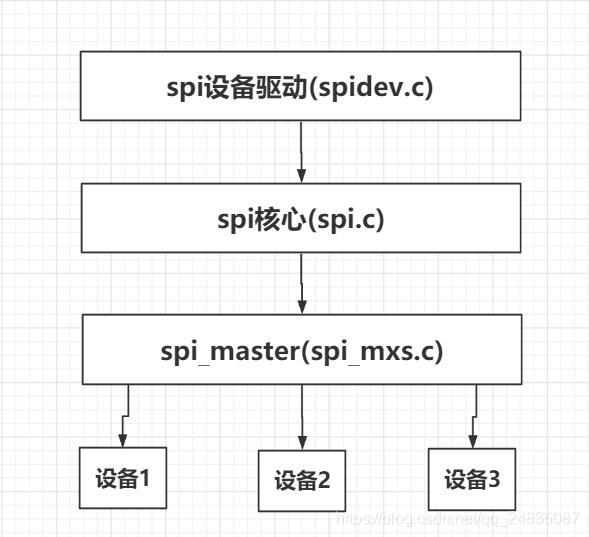
spi核心层提供spi master、spi设备和驱动的注册、卸载函数,以及spi通信函数。
spi master是Linux虚拟处理的一个概念,实际上就是spi主机,一般是在芯片内部,芯片有多少个spi接口,就代表有几个master,每个master下面可以挂多个spi设备,但是每个设备都需要一个单独的片选信号。spi master就相当于i2c的adapter,spi master的驱动芯片厂商已经写好,不需要我们去编写,它会操作芯片内部寄存器实现和挂在该master下面的设备进行spi通信。
应用层和挂在某个master下的spi设备通信流程如下:
用户层操作spi设备驱动(open、write、read)——spi设备驱动调用spi核心层提供的通信函数sync或async——调用对应spi master的transfer函数,最终实现和spi设备的通信。
下面就开始编写一个Linux下spi驱动——RC522驱动
二、RC522设备
根据总线——设备——驱动模型,首先需要注册一个spi设备——rc522设备:
首先介绍下几个比较重要的结构体:
1. spi_board_info
struct spi_board_info {
char modalias[SPI_NAME_SIZE];//spi设备名 驱动的名字需和设备名保持一致
const void *platform_data;
void *controller_data;
int irq;
u32 max_speed_hz;//spi最大时钟频率
u16 bus_num;//spi主机序号,表明该设备是挂在哪一个spi master下
u16 chip_select;//片选脚
u8 mode;//spi模式 SPI_CPHA SPI_CPOL共有四种组合方式
};
spi_board_info用来描述一个spi板级设备信息,其中包括设备名、要使用哪一个spi主机、spi模式以及使用哪个片选脚,这里的片选是由spi 主机自动控制的,一个设备只能对应一个片选,但是也可以不使用这个片选,可以申请一个普通IO口当作片选,最后再调用spi_new_device注册设备即可。
SPI_CPHA选择对数据线采样的时机,0选择每个时钟周期的第一个沿跳变时采样数据,1选择第二个时钟沿采样数据;SPI_CPOL选择每个时钟周期开始的极性,0表示时钟以低电平开始,1选择高电平开始。这两个比特位有四种组合,对应SPI_MODE_0~SPI_MODE_3。
2. spi_device
spi_device结构体用来描述一个spi设备,可以根据前面板级设备信息注册一个spi设备。
struct spi_device {
struct device dev;
struct spi_master *master;
u32 max_speed_hz;//spi最大时钟频率
u8 chip_select;//片选脚
u8 mode;//spi 模式
#define SPI_CPHA 0x01 /* clock phase */
#define SPI_CPOL 0x02 /* clock polarity */
#define SPI_MODE_0 (0|0) /* (original MicroWire) */
#define SPI_MODE_1 (0|SPI_CPHA)
#define SPI_MODE_2 (SPI_CPOL|0)
#define SPI_MODE_3 (SPI_CPOL|SPI_CPHA)
#define SPI_CS_HIGH 0x04 /* chipselect active high? */
#define SPI_LSB_FIRST 0x08 /* per-word bits-on-wire */
#define SPI_3WIRE 0x10 /* SI/SO signals shared */
#define SPI_LOOP 0x20 /* loopback mode */
#define SPI_NO_CS 0x40 /* 1 dev/bus, no chipselect */
#define SPI_READY 0x80 /* slave pulls low to pause */
u8 bits_per_word;
int irq;
void *controller_state;
void *controller_data;
char modalias[SPI_NAME_SIZE];//spi设备名
};
rc522_dev.c:
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/spi/spi.h>
static struct spi_board_info rc522_board_info =
{
.modalias = "rc522",
.max_speed_hz = 8000000,
.bus_num = 1,
.chip_select = 0,
.mode = SPI_MODE_0,
};
static struct spi_device* rc522_dev = NULL;
static int rc522_dev_init(void)
{
struct spi_master *rc522_master = NULL;
rc522_master = spi_busnum_to_master(rc522_board_info.bus_num);//根据spi总线编号获取一个spi master
if(rc522_master != NULL)
{
rc522_dev = spi_new_device(rc522_master,&rc522_board_info);//注册spi设备
if(rc522_dev != NULL)
{
printk("module init ok \n");
return 0;
}
else
{
printk("create rc522_dev error \n");
return -1;
}
}
else
{
printk("rc522_master not found \n");
return -1;
}
}
static void rc522_dev_exit(void)
{
spi_unregister_device(rc522_dev);
printk("module exit ok \n");
}
module_init(rc522_dev_init);
module_exit(rc522_dev_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("xzx2020");
三、RC522驱动
rc522驱动有个重要的结构体spi_driver:
struct spi_driver {
const struct spi_device_id *id_table;
int (*probe)(struct spi_device *spi);
int (*remove)(struct spi_device *spi);
void (*shutdown)(struct spi_device *spi);
int (*suspend)(struct spi_device *spi, pm_message_t mesg);
int (*resume)(struct spi_device *spi);
struct device_driver driver;
};
struct device_driver {
const char *name;//驱动名字,需和设备名保持一致
struct bus_type *bus;
struct module *owner;
const char *mod_name; /* used for built-in modules */
bool suppress_bind_attrs; /* disables bind/unbind via sysfs */
#if defined(CONFIG_OF)
const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
#endif
int (*probe) (struct device *dev);
int (*remove) (struct device *dev);
void (*shutdown) (struct device *dev);
int (*suspend) (struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume) (struct device *dev);
const struct attribute_group **groups;
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
struct driver_private *p;
};
我们需要实现的是spi_driver的probe和remove函数,然后在probe函数里实现字符设备注册,在remove函数里实现字符设备卸载。
spi_write:spi写入若干字节
spi_write_then_read:spi写入若干字节并读取若干字节
rc522_drv.c:
这里的片选脚由spi_master自动控制。
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/spi/spi.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>//gpio_request gpio_free函数
#include <../arch/arm/mach-mx28/mx28_pins.h>
#define DEVICE_NAME "rc522_drv" //驱动名称
#define RST_PIN MXS_PIN_TO_GPIO(PINID_SSP0_DATA7) //p2.7
#define CS_PIN MXS_PIN_TO_GPIO(PINID_SSP0_DATA6) //p2.6
#define RC522_RST_Enable() gpio_direction_output(RST_PIN,0)
#define RC522_RST_Disable() gpio_direction_output(RST_PIN,1)
#define RC522_CS_Enable() gpio_direction_output(CS_PIN,0)
#define RC522_CS_Disable() gpio_direction_output(CS_PIN,1)
static struct spi_device* rc522_dev = NULL;
static struct cdev *rc522_cdev = NULL;
static struct class *rc522_class = NULL;
static struct device *rc522_device = NULL;
static dev_t device_id;
static int rc522_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
int ret = -1,ret2 = -1;
gpio_free(RST_PIN);
gpio_free(CS_PIN);
ret = gpio_request(RST_PIN, "RC522_RST");
ret2 = gpio_request(CS_PIN, "RC522_CS");
printk("RST_PIN=%d CS_PIN=%d\n",ret,ret2);
RC522_RST_Disable();
udelay(1);
RC522_RST_Enable();
udelay(1);
RC522_RST_Disable();
return 0;
}
static int rc522_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
RC522_RST_Enable();
gpio_free(RST_PIN);
//gpio_free(CS_PIN);
return 0




 本文详细介绍了在Linux环境下SPI驱动的架构及其实现过程,特别聚焦于RC522 RFID模块的驱动开发。从SPI核心层、设备注册到RC522设备的初始化、通信函数的使用,涵盖了spi_board_info和spi_device结构体解析,以及字符设备的注册与卸载等关键步骤。
本文详细介绍了在Linux环境下SPI驱动的架构及其实现过程,特别聚焦于RC522 RFID模块的驱动开发。从SPI核心层、设备注册到RC522设备的初始化、通信函数的使用,涵盖了spi_board_info和spi_device结构体解析,以及字符设备的注册与卸载等关键步骤。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 2428
2428












