练习六:支持向量机
目录
1.包含的文件。
2.支持向量机。
3.垃圾邮件分类。
1.包含的文件。
| 文件名 | 含义 |
| ex6.py | 支持向量机主程序(第一个实验) |
| ex6data1.mat | 实验1的数据集1 |
| ex6data2.mat | 实验1的数据集2 |
| ex6data3.mat | 实验1的数据集3 |
| plotData.py | 数据集可视化 |
| visualizeBoundary.py | 决策边界可视化 |
| gaussianKernel.py | 高斯核函数 |
| ex6_spam.py | 垃圾邮件分类主程序(第二个实验) |
| spamTrain.mat | 邮件训练集 |
| spamTest.mat | 邮件测试集 |
| spamSample1.txt | 垃圾邮件事例1 |
| spamSample2.txt | 垃圾邮件事例2 |
| vocab.txt | 词汇表 |
| emailSample1.txt | 邮件事例1 |
| emailSample2.txt | 邮件事例2 |
| processEmail.py | 邮件预处理 |
| emailFeatures.py | 从邮件中提取特征 |
红色部分需要自己填写。
2.支持向量机
- 加载需要的包和初始化:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as scio
from sklearn import svm
import plotData as pd
import visualizeBoundary as vb
import gaussianKernel as gk
plt.ion()
np.set_printoptions(formatter={'float': '{: 0.6f}'.format})2.1绘制数据
- 编写plotData.py,可视化数据:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def plot_data(X, y):
plt.figure()
# ===================== Your Code Here =====================
# Instructions : Plot the positive and negative examples on a
# 2D plot, using the marker="+" for the positive
# examples and marker="o" for the negative examples
#
count = 0
for i in y:
if i == 1:
plt.scatter(X[count,0],X[count,1],marker='+',color = 'b')
else:
plt.scatter(X[count,0],X[count,1],marker='o',color = 'r')
count = count+1
- 测试代码:
# ===================== Part 1: Loading and Visualizing Data =====================
# We start the exercise by first loading and visualizing the dataset.
# The following code will load the dataset into your environment and
# plot the data
print('Loading and Visualizing data ... ')
# Load from ex6data1:
data = scio.loadmat('ex6data1.mat')
X = data['X']
y = data['y'].flatten()
m = y.size
# Plot training data
pd.plot_data(X, y)
input('Program paused. Press ENTER to continue')- 测试结果:
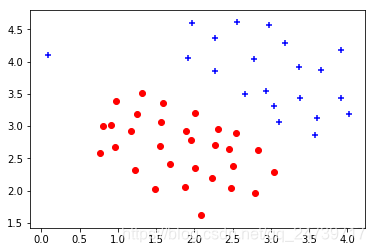
2.2训练SVM
- 可视化决策边界visualizeBoundary.py:
def visualize_boundary(clf, X, x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max): #x,y轴的取值范围
h = .02
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))#在x,y轴上以0.02为间隔,生成网格点
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])#预测每个网格点的类别0/1
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) #转型为网格的形状
plt.contour(xx, yy,Z, level=[0],colors='r') #等高线图 将0/1分界线(决策边界)画出来
- 训练线性SVM:





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 866
866

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








