接下来分析Spring源码的最后一个部分SpringMVC的实现。先来两篇文章回顾下SpringMVC和Servlet
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_23536449/article/details/98957647
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_23536449/article/details/98955020
1.XmlWebApplicationContext的UML图
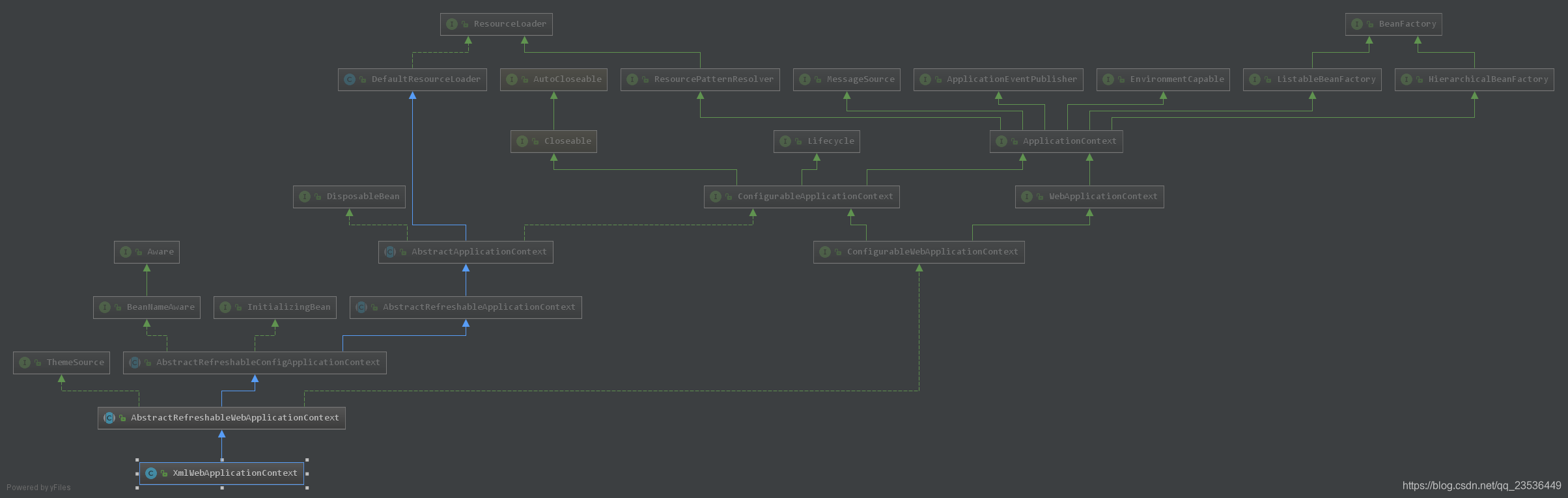
本篇章中的新加的类如下:
WebApplicationContext:用于为Web应用程序提供配置的界面。 这在应用程序运行时是只读的,但如果实现支持,则可以重新加载;此接口将{@code getServletContext()}方法添加到通用ApplicationContext接口,并添加一些大家都知道的 * 根上下文必须在引导过程中必须绑定值到的属性名称
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext:由可配置的Web应用程序上下文实现的接口。由{@link ContextLoader}和{@link org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet}提供支持.注意:在调用继承自{@link org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext} 的{@link #refresh}方法之前,需要调用此接口的setter。它们不会导致自己初始化上下文。该方法的set方法有setServletContext(ServletContext)、setServletConfig(ServletConfig servletConfig)、setNamespace(String namespace)、 setConfigLocation(String configLocation)。
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext:用于为Web环境实现{@link org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext}接口。 * 提供“configLocations”属性,通过Web应用程序启动时的ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口填充;此类与AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext一样易于子类化:您需要实现的只是{@link #loadBeanDefinitions}方法;实现应该从{@link #getConfigLocations}方法返回的位置指定的文件中加载bean定义。该类中最引人入胜的方法
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext, this.servletConfig);
}
/**
* Register web-specific scopes ("request", "session", "globalSession", "application")
* with the given BeanFactory, as used by the WebApplicationContext.
* @param beanFactory the BeanFactory to configure
* @param sc the ServletContext that we're running within
*/
public static void registerWebApplicationScopes(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ServletContext sc) {
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_REQUEST, new RequestScope());
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_SESSION, new SessionScope(false));
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_GLOBAL_SESSION, new SessionScope(true));
if (sc != null) {
ServletContextScope appScope = new ServletContextScope(sc);
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_APPLICATION, appScope);
// Register as ServletContext attribute, for ContextCleanupListener to detect it.
sc.setAttribute(ServletContextScope.class.getName(), appScope);
}
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletRequest.class, new RequestObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletResponse.class, new ResponseObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(HttpSession.class, new SessionObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(WebRequest.class, new WebRequestObjectFactory());
if (jsfPresent) {
FacesDependencyRegistrar.registerFacesDependencies(beanFactory);
}
}
/**
* Register web-specific environment beans ("contextParameters", "contextAttributes")
* with the given BeanFactory, as used by the WebApplicationContext.
* @param bf the BeanFactory to configure
* @param servletContext the ServletContext that we're running within
* @param servletConfig the ServletConfig of the containing Portlet
*/
public static void registerEnvironmentBeans(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory bf, ServletContext servletContext, ServletConfig servletConfig) {
if (servletContext != null && !bf.containsBean(WebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME)) {
bf.registerSingleton(WebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME, servletContext);
}
if (servletConfig != null && !bf.containsBean(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME)) {
bf.registerSingleton(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME, servletConfig);
}
if (!bf.containsBean(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME)) {
Map<String, String> parameterMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
if (servletContext != null) {
Enumeration<?> paramNameEnum = servletContext.getInitParameterNames();
while (paramNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
String paramName = (String) paramNameEnum.nextElement();
parameterMap.put(paramName, servletContext.getInitParameter(paramName));
}
}
if (servletConfig != null) {
Enumeration<?> paramNameEnum = servletConfig.getInitParameterNames();
while (paramNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
String paramName = (String) paramNameEnum.nextElement();
parameterMap.put(paramName, servletConfig.getInitParameter(paramName));
}
}
bf.registerSingleton(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME,
Collections.unmodifiableMap(parameterMap));
}
if (!bf.containsBean(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME)) {
Map<String, Object> attributeMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
if (servletContext != null) {
Enumeration<?> attrNameEnum = servletContext.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNameEnum.nextElement();
attributeMap.put(attrName, servletContext.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
bf.registerSingleton(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME,
Collections.unmodifiableMap(attributeMap));
}
}
该方法是AbstractApplicationContext提供的模板方法如下图的实现
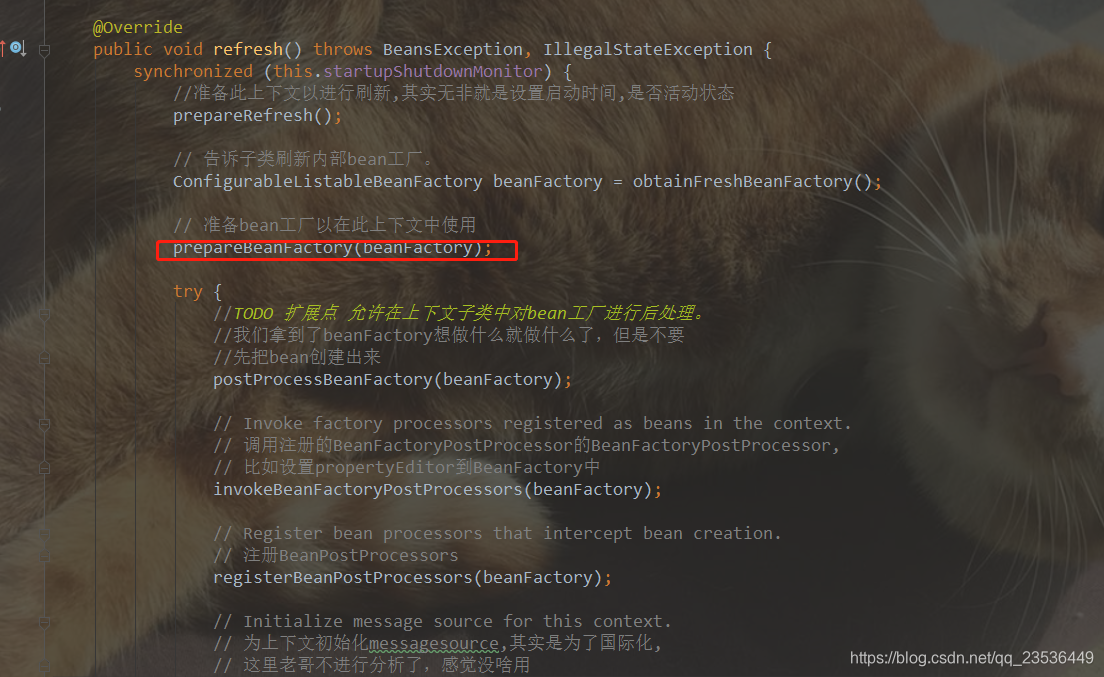
/**
*在标准初始化之后修改应用程序上下文的内部bean工厂。 将加载所有bean定义,但尚未实例化任何bean。
* 这允许在某些ApplicationContext实现中注册特殊的BeanPostProcessors等
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
*/
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
}2.我们知道了ServletContextListener的使用方法后,下面就来分析ContextLoaderListener.contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event)
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}该方法的实现在其父类ContextLoader类中
/**
* 使用构造时提供的应用程序上下文初始化Spring的给定servlet上下文的Web应用程序上下文,
* 或者根据“{@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM contextClass}”和
* “{@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM contextConfigLocation}”
* context-params创建一个新的Web应用程序上下文
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the new WebApplicationContext
* @see #ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
//web.xml存在多个applicationContext配置,抛出异常
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
//将servletContext存储在本地实例变量中,以保证它在ServletContext关闭时可用。
if (this.context == null) {
//初始化webApplicationContext
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
// 上下文是否为ConfigurableWebApplicationContext的子类
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
//如果还未激活;如果通过构造函数传递的WebApplicationContext可能isActive为true了
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// 上下文尚未刷新 - >提供诸如此类的服务
//设置父上下文,设置应用程序上下文ID等
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
//注入上下文实例时没有显式父 - >
//确定根Web应用程序上下文的父级(如果有)。
//这里我们不会用到的,所以不分析了
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
//设置webApplicationContext属性
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
//当前线程的类加载器是否为ccl
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
//放到map里了
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
//返回WebApplicationContext对象
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}a.判断servletContext.getAttribute()是否已经有了一个WebApplicationContext对象,有的话抛出异常
b.createWebApplicationContext(servletContext)方法创建一个WebApplicationContext对象;
/**
* 实例化此加载器的根WebApplicationContext,或者
* 默认上下文类或自定义上下文类(如果已指定)。
* <p>此实现期望自定义上下文实现
* {@link ConfigurableWebApplicationContext}界面。 可以在子类中重写。
* <p>In addition, {@link #customizeContext} gets called prior to refreshing the
* context, allowing subclasses to perform custom modifications to the context.
* @param sc current servlet context
* @return the root WebApplicationContext
* @see ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
*/
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
//如果class不是继承ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 类抛出个异常
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
//反射创建ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
/**
* 返回要使用的WebApplicationContext实现类,如果未指定,则使用默认的XmlWebApplicationContext或自定义上下文类。
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the WebApplicationContext implementation class to use
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
*/
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 获取contextClass配置WebApplicationContext
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
//如果不为null;加载className对应的Class
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
//从ContextLoader.properties配置文件中加载
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}创建真的很简单的呐,首先会从类似如下方式中去获取配置的WebApplicationContext对应的className
<context-param>
<param-name>contextClass</param-name>
<param-value>ConfigurableWebApplicationContext的实现类名称</param-value>
</context-param>如果他没有配置那么咱们会从一个叫ContextLoader.properties的配置中去拿,Spring给咱们配置了个XmlWebApplicationContext
# Default WebApplicationContext implementation class for ContextLoader.
# Used as fallback when no explicit context implementation has been specified as context-param.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
然后反射创建该className对应的实例对象就好了。
c.创建好了当然就是要配置啦,所以方法来到了configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);对于为啥要判断isActive()我在上面已经说了,可以通过构造函数的方式传进来一个WebApplicationContext,如果咱们不调用他的refresh()方法,他就不是isActive()。这时候需要Spring给咱们refresh()
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
//设置ConfigurableWebApplicationContext的id
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
//设置ServletContext到wac中哎嘿嘿
wac.setServletContext(sc);
//获取contextConfigLocation参数
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
//在刷新上下文时,无论如何都会调用wac环境的#initPropertySources;
//为了用于#refresh之前发生的任何后处理或初始化在此急切地确保servlet属性源到位
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
wac.refresh();
}看到了咱们通过如下代码
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}将这种配置方式配置的xml设置到了WebApplicationContext中了
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:**/applicationContext*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>然后是customizeContext(sc,wac)方法,该方法提供了一个操作ApplicationContext的扩展点
/**
* 配置化该ContextLoader创建的{@link ConfigurableWebApplicationContext},在配置位置已经提供给
* 上下文之后,但在上下文调用<em>refreshed<em/>之前
*
* <p>The default implementation {@linkplain #determineContextInitializerClasses(ServletContext)
* determines} what (if any) context initializer classes have been specified through
* {@linkplain #CONTEXT_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM context init parameters} and
* {@linkplain ApplicationContextInitializer#initialize invokes each} with the
* given web application context.
*
* 默认的{@linkplain #determineContextInitializerClasses(ServletContext)determines}实现;如果通过
* {@linkplain #CONTEXT_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM context init parameters}配置了ApplicationContextInitializer
* 那么将会调用每个{@linkplain ApplicationContextInitializer#initialize}使用给定的webApplicationContext
*
*
* <p>Any {@code ApplicationContextInitializers} implementing
* {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered Ordered} or marked with @{@link
* org.springframework.core.annotation.Order Order} will be sorted appropriately.
* @param sc the current servlet context
* @param wac the newly created application context
* @see #CONTEXT_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM
* @see ApplicationContextInitializer#initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext)
*/
protected void customizeContext(ServletContext sc, ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
//获取配置的ContextInitializerClasses类
List<Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>> initializerClasses =
determineContextInitializerClasses(sc);
//TODO 扩展点
//这些class类必须是符合ApplicationContextInitializer.class的#initialize标准的才给应用
for (Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>> initializerClass : initializerClasses) {
Class<?> initializerContextClass =
GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializerClass, ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
if (initializerContextClass != null && !initializerContextClass.isInstance(wac)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(String.format(
"Could not apply context initializer [%s] since its generic parameter [%s] " +
"is not assignable from the type of application context used by this " +
"context loader: [%s]", initializerClass.getName(), initializerContextClass.getName(),
wac.getClass().getName()));
}
this.contextInitializers.add(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(initializerClass));
}
//排序下
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.contextInitializers);
//按照顺序挨个应用initializer到WebApplicationContext
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> initializer : this.contextInitializers) {
initializer.initialize(wac);
}
}最后refresh();该方法是AbstractApplicationContext实现的,具体的就不解析了,前面咱们已经解析过了。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//准备此上下文以进行刷新,其实无非就是设置启动时间,是否活动状态
prepareRefresh();
// 告诉子类刷新内部bean工厂。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 准备bean工厂以在此上下文中使用
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//TODO 扩展点 允许在上下文子类中对bean工厂进行后处理。
//我们拿到了beanFactory想做什么就做什么了,但是不要
//先把bean创建出来
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 调用注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,
// 比如设置propertyEditor到BeanFactory中
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 注册BeanPostProcessors
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 为上下文初始化messagesource,其实是为了国际化,
// 这里老哥不进行分析了,感觉没啥用
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化应用消息广播
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// TODO 留给子类初始化其他特殊bean
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 检查并注册listener beans
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 初始化剩下的(非懒惰的)singletons,有些bean 比如那些实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// 和BeanPostProcessor需要提前初始化,所以叫初始化剩余的
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 完成刷新,发布相应的事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
// 销毁已创建的单例bean避免占用资源
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
// 取消刷新,重置active 标志
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
//从我们开始,重置Spring核心中的常见内省缓存
//可能再也不需要单例bean的元数据......
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}d.将咱们刚才创建的WebApplicationContext对象塞到ServletConext的attributes中哎嘿嘿
e.然后就是将我们的WebApplicationContext对象暴露出去了,为了让咱们能够在web项目中用如下方式获取到ApplicationContext,Spring操作还是骚啊。
ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
public static WebApplicationContext getCurrentWebApplicationContext() {
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl != null) {
WebApplicationContext ccpt = currentContextPerThread.get(ccl);
if (ccpt != null) {
return ccpt;
}
}
return currentContext;
}3.WebApplicationContext.refresh之前对于咱们的ConfigurableApplicationContext的骚操作示例
定义MyApplicationContextInitializer实现ApplicationContextInitializer接口
/**
* @author 周宁
* @Date 2019-08-13 16:46
*/
public class MyApplicationContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<XmlWebApplicationContext> {
@Override
public void initialize(XmlWebApplicationContext applicationContext) {
System.out.println("MyApplicationContextInitializer initialize");
}
}web.xml中配置下
<context-param>
<param-name>contextInitializerClasses</param-name>
<param-value>org.springframework.studymvc.acini.MyApplicationContextInitializer</param-value>
</context-param>然后在启动web应用,看到控制台的输出
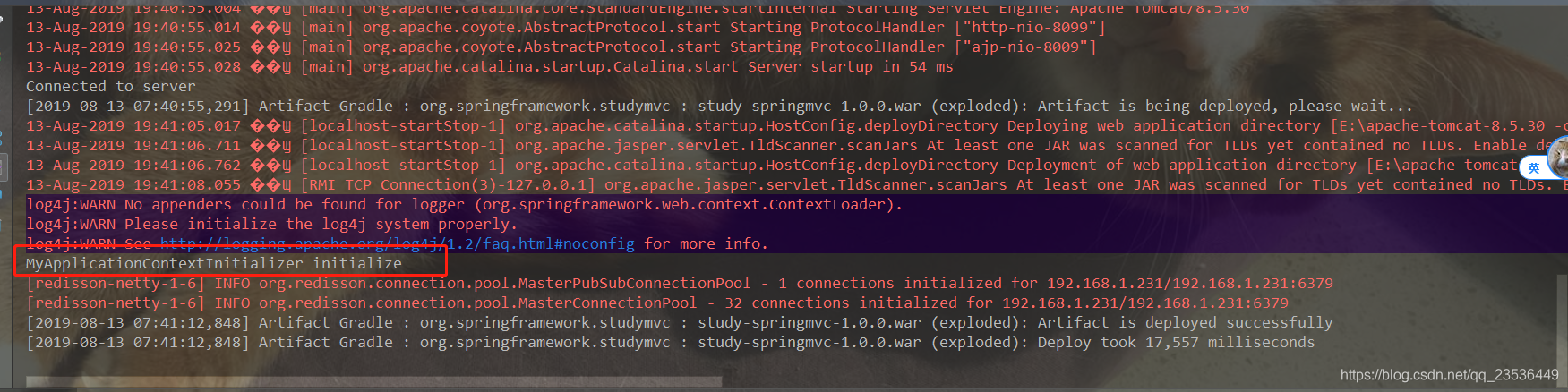





















 11万+
11万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








