SpringMVC处理请求DispatcherServlet分析
1.DispatcherServlet
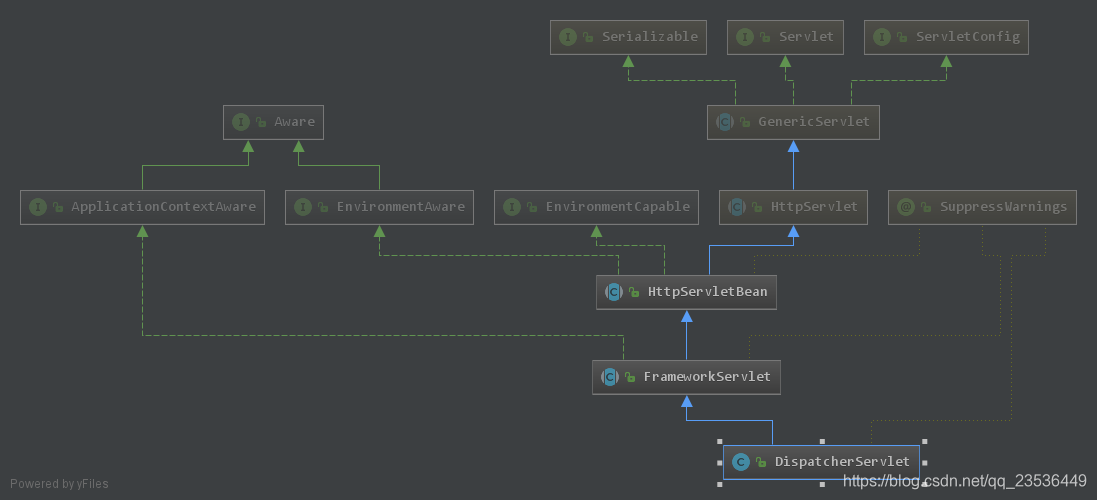
HttpServletBean:处理{@link javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet}的简单扩展 扩展配置参数当做bean的属性 例如:{@code web.xml}中的{@code servlet})({@code init-param})条目.适用于任何类型servlet的便捷超类。配置参数的类型转换是自动的,相应的setter方法将使用转换后的值进行调用。 子类也可以指定必需的属性。 不会匹配bean属性setter的参数将被忽略.这个通用的servlet基类不依赖于Spring {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext}概念 简单的servlet通常不加载它们自己servlet上下文,而是从Spring根应用程序上下文访问服务bean,可以通过过滤器的{@link #getServletContext()ServletContext}访问。用于给DispatcherServlet类通过Spring的Setter方式注入属性的一个类。
FrameworkServlet:Spring的Web框架的基本servlet。 提供集成 基于JavaBean的整体解决方案中的Spring应用程序上下文。该类提供的功能:为每个DispatcherServlet实例管理WebApplicationContext,确定servlet的配置在servlet命名空间中的bean;根据请求处理发布事件,无论请求是否成功处理。子类必须实现{@link #doService}来处理请求。 因为这会直接扩展{@link HttpServletBean}而不是HttpServlet,所以bean属性会自动映射到它上面。子类可以覆盖{@link #initFrameworkServlet()} 用于自定义初始化。检测servlet init-param级别的“contextClass”参数,如果找不到,则返回默认上下文类 {@link org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext}. 请注意,使用默认的{@code FrameworkServlet},自定义上下文类需要实现 * {@link org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext ConfigurableWebApplicationContext}。接受一个可选的“contextInitializerClasses”servlet init-param,它指定一个或多个 {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer ApplicationContextInitializer}类。托管的Web应用程序上下文将委派给这些初始化程序,允许进行其他程序配置, * 例如 在{@link org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#getEnvironment() * context的环境中添加属性源或激活配置文件}。另请参阅{@link org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader}, * 它支持“contextInitializerClasses”context-param,其中“root”Web应用程序上下文具有相同的语义。将“contextConfigLocation”servlet init-param传递给上下文实例, * 将其解析为可能由多个逗号和空格分隔的多个文件路径,例如“test-servlet.xml,myServlet.xml”。 * 如果没有明确指定,则上下文实现应该从servlet的命名空间构建一个默认位置。注意:使用Spring的默认ApplicationContext实现时,如果有多个配置位置,以后的bean定义会 * 覆盖在早期加载的文件中定义的。 这可以用来通过额外的XML文件故意覆盖某些bean定义。帮我们管理了WebApplicationContext、将doGet、doPost、doDelete请求委托给子类实现,支持通过servlet的init-param设置contextClass属性设置WebApplicationContext类型,通过init-param的contextInitializerClasses可以配置ApplicationContextInitializer,通过contextConfigLocation配置将servlet配置传递给上下文WebApplicationContext。
DispatcherServlet:HTTP请求处理程序/控制器的中央调度程序,例如 用于Web UI控制器或基于HTTP的远程服务调用。分发请求到到已注册的处理程序以处理Web请求,提供方便的映射和异常处理工具。该servlet非常灵活:通过适当的adapter class,它可被用于几乎任何workflow,它提供了以下区别于请求驱动的 * web mvc框架的有用功能:
* <ul>
* <li>它基于JavaBeans配置机制。
* <li>它可以通过使用任何{@link HandlerMapping}实现 - 预构建或作为应用程序的一部分提供 - 控制对处理程序对象的请求路由。
* 默认为{@link org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping}和
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping} .
* HandlerMapping对象可以在servlet的应用程序上下文中定义为bean,实现 HandlerMapping接口,覆盖默认的HandlerMapping(如果存在)。 HandlerMappings可以被赋予任何bean名称(它们按类型进行测试)。
*
* <li>它可以使用任何{@link HandlerAdapter}; 这允许使用任何处理程序接口。
* 默认适配器是{@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter},
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter},
* 适用于Spring的{@link org.springframework.web.HttpRequestHandler}和
* { @link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller}接口。
* 默认的{@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter}也将被注册。
* HandlerAdapter对象可以作为bean添加到应用程序上下文中,覆盖默认的HandlerAdapter。
* 与HandlerMappings一样,HandlerAdapters可以被赋予任何bean名称(它们按类型进行测试)。
*
* <li>可以通过{@link HandlerExceptionResolver}指定调度程序的异常解析策略,例如将某些异常映射到错误页面。
* 默认为{@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver},
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver}和
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver}。
* 可以通过应用程序上下文覆盖这些HandlerExceptionResolvers.HandlerExceptionResolver可以被赋予任何bean名称(它们按类型进行测试)。
*
* <li>可以通过{@link ViewResolver}实现指定其视图解析策略,将符号视图名称解析为View对象。
* 默认为{@link org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver}。
* ViewResolver对象可以作为bean添加到应用程序上下文中,覆盖默认的ViewResolver。
* ViewResolvers可以被赋予任何bean名称(它们按类型进行测试)。
*
* <li>如果用户未提供{@link View}或视图名称,则配置的{@link RequestToViewNameTranslator}会将当前请求转换为视图名称。
* 相应的bean名称是“viewNameTranslator”; 默认是
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator}。
*
* <li>解决多部分请求的策略由{@link org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartResolver}实现确定。
* 包括Apache Commons FileUpload和Servlet 3的实现; 典型的选择是
* {@link org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver}。
* MultipartResolver bean名称是“multipartResolver”; 默认为none。
*
* <li>它的语言环境解析策略由{@link LocaleResolver}确定。开箱即用的实现通过HTTP接受标头,cookie或会话工作。
* LocaleResolver bean名称是“localeResolver”; 默认值为{@link org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver}。
*
* <li>其主题解析策略由{@link ThemeResolver}决定。包括固定主题和cookie和会话存储的实现。
* ThemeResolver bean名称是“themeResolver”; 默认为{@link org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver}。
* </ul>注意:只有在调度程序中存在相应的{@code HandlerMapping}(用于类型级注释)和/或{@code HandlerAdapter} (用于方法级注释)时,才会处理{@code @RequestMapping}注释。 </ b>默认情况下就是这种情况。但是,如果要定义自定义{@code HandlerMappings}或{@code HandlerAdapters},则需要确保定义相应的自定义{@code DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping} * 和/或{@code AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter}
Web应用程序可以定义任意数量的DispatcherServlet.</b> 每个servlet将在其自己的命名空间中运行,使用映射,处理程序等加载其自己的应用程序上下文。 * 只有{@link org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener}加载的根应用程序上下文(如果有)将被共享。对请求进行处理的类;支持多个DispatcherServlet配置(通过不同命名空间区分)。
2.https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_23536449/article/details/98957647文章提到过Servlet的生命周期,DispatcherServlet是个特殊的Servlet,我们来看下init方法---->HttpServletBean.init()
/**
* 将配置参数映射到此servlet包装成的bean的属性,以及
* 调用子类初始化。
* 我的理解就是将当前servlet(DispatcherServlet)封装成一个spring管理的bean
* @throws ServletException if bean properties are invalid (or required
* properties are missing), or if subclass initialization fails.
*/
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
// 从init-param这种格式的配置中获取参数并封装为PropertyValues类型
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
//包装为一个BeanWrapper
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
//注册resourceLoader
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
//注册一个属性编辑器用于解析bean的Resource类型属性注入
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
//TODO 空的实现让我们自己遐想的操作
initBeanWrapper(bw);
//给DispatcherServlet 对应的bean的属性赋值
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
/**
* 从ServletConfig init参数创建的PropertyValues实现。
*/
private static class ServletConfigPropertyValues extends MutablePropertyValues {
/**
* 将ServletConfig配置的参数封装为ServletConfigPropertyValues类型
* 并做了验证;后面直接使用Spring提供的BeanWrapperImpl直接给bean赋值
* 很方便啊
*
* @param config ServletConfig we'll use to take PropertyValues from
* @param requiredProperties set of property names we need, where
* we can't accept default values
* @throws ServletException if any required properties are missing
*/
public ServletConfigPropertyValues(ServletConfig config, Set<String> requiredProperties)
throws ServletException {
//不能缺少的属性
Set<String> missingProps = (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(requiredProperties) ?
new HashSet<String>(requiredProperties) : null);
//
Enumeration<String> paramNames = config.getInitParameterNames();
while (paramNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String property = paramNames.nextElement();
Object value = config.getInitParameter(property);
addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(property, value));
if (missingProps != null) {
missingProps.remove(property);
}
}
// Fail if we are still missing properties.
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(missingProps)) {
throw new ServletException(
"Initialization from ServletConfig for servlet '" + config.getServletName() +
"' failed; the following required properties were missing: " +
StringUtils.collectionToDelimitedString(missingProps, ", "));
}
}
}
上面的方法解析我们配置在servlet的init-param,并将参数封装到PropertyValues中,通过将我们当前的servlet对象(DispatcherServlet)封装为Spring的BeanWrapperImpl做到了给servlet对象的属性注入。initServletBean()
2.initServletBean()由子类FrameworkServlet实现
/**
* 重写{@link HttpServletBean}的方法,在设置任何bean属性后调用。 创建此servlet的WebApplicationContext。
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//创建当前DispatcherServlet的WebApplicationContext
//当前DispatcherServlet的WebApplicationContext和咱们的ContextLoaderListener创建的可能并不不是同一个
//可能DispatcherServlet的WebApplicationContext的实例的parent是ContextLoaderListener创建的
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
//TODO 留给子类扩展的操作
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}3.在debug initWebApplicationContext()方法之前我们先了解下DispatcherServlet与WebApplicationContext的关系。
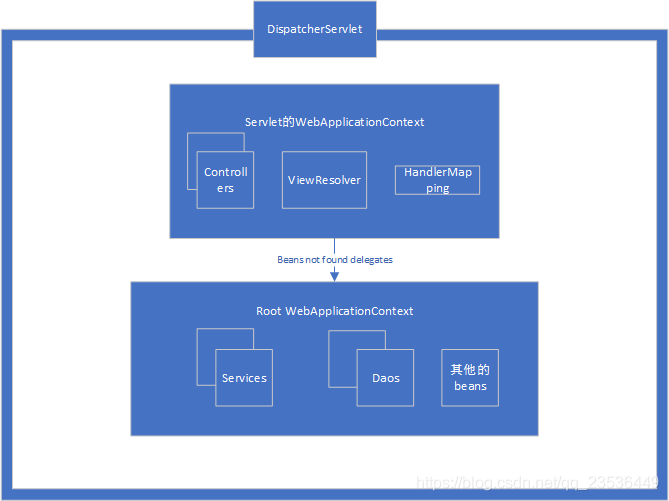
SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet会创建自己的WebApplicationContext,并且该上下文的parent属性是RootWebApplicationContext,而RootWebApplicationContext是由ContextLoadListener创建是所有的DispatcherServlet公共的。SpringMVC查找beans一般是先从Servlet的WebApplicationContext中找找不到再从它对应的父WebApplicationContext找。所以说我们可以通过在Servlet的WebApplicationContext的bean配置覆盖Root WebApplicationContext。
由上面我们也可以联想到如果只存在一个DispatcherServlet时我们也可以没必要定义ContextLoadListener,把所有的Bean都定义在Servlet的WebApplicationContext里面即可
4.initWebApplicationContext()方法分析
/**
* 初始化并发布此servlet的WebApplicationContext。
* <p>委托{@link #createWebApplicationContext}实际创建上下文。 可以在子类中重写。
* @return the WebApplicationContext instance
* @see #FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #setContextClass
* @see #setContextConfigLocation
*/
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//获取rootContext,该Context就是通过ContextLoaderListener创建的XmlWebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
//当前DispatcherServlet对应的webApplicationContext不是null,我们通过构造函数注入的emmm
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
// 赋值给wac
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
//通过构造函数给DispatcherServlet设置的WebApplicationContext尚未refresh()操作
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
//上下文尚未刷新 - >提供诸如此类的服务
//设置父上下文,设置应用程序上下文ID等
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
// 如果咱们通过构造函数设置的WebApplicationContext还没有设置parent
// 设置ContextLoaderListener创建的WebApplicationContext
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
//没有通过构造函数注入WebApplicationContext
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
// 如果没有通过构造函数注入一个WebApplicationContext实例,尝试从servletContext指定的属性中
// 获取一个WebApplicationContext
// init-param的contextAttribute属性指定的
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
// 没有定义的啊,那咱们就给DispatcherServlet创建一个吧!!!
// 并将咱们的ContextLoaderListener创建的WebApplicationContext设置为该DispatcherServlet
// 的WebApplicationContext的parent
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
//如果refreshEventReceived为false,在当前DispatchServlet的WebApplicationContext的refresh()后
//也会触发onRefresh(wac)
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
// 将WebApplicationContext发布为servlet context的一个attribute
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}a.从ServletContext中查找通过ContextLoaderListener创建的WebApplicationContext
/**
* 为此Web应用程序查找自定义{@code WebApplicationContext}。
* @param sc ServletContext to find the web application context for
* @param attrName the name of the ServletContext attribute to look for
* @return the desired WebApplicationContext for this web app, or {@code null} if none
*/
public static WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc, String attrName) {
Assert.notNull(sc, "ServletContext must not be null");
Object attr = sc.getAttribute(attrName);
if (attr == null) {
return null;
}
if (attr instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) attr;
}
if (attr instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) attr;
}
if (attr instanceof Exception) {
throw new IllegalStateException((Exception) attr);
}
if (!(attr instanceof WebApplicationContext)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Context attribute is not of type WebApplicationContext: " + attr);
}
return (WebApplicationContext) attr;
}b.构造函数的方式传递给当前DispatcherServlet的WebApplicationContext的处理逻辑
c.通过contextAttribute进行初始化;我们可以通过配置servlet的contextAttribute属性指定ServletContext的attribute中的WebApplicationContext
protected WebApplicationContext findWebApplicationContext() {
String attrName = getContextAttribute();
if (attrName == null) {
return null;
}
WebApplicationContext wac =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext(), attrName);
if (wac == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No WebApplicationContext found: initializer not registered?");
}
return wac;
}d.创建并配置调用WebApplicationContext的refresh()方法
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" +
contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]");
}
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation());
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
//配置当前DispatcherServlet的servlet的一些东西
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
//设置nameSpace
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
//添加一个Listener
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
//在刷新上下文时,无论如何都会调用wac环境的#initPropertySources;
//为了用于#refresh之前发生的任何后处理或初始化在此急切地确保servlet属性源到位
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
//TODO 扩展点emmm
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
wac.refresh();
}
在方法中看到wac注册了一个监听器

根据前面分析ApplicationContext的源码我们知道在执行refresh()方法的某个步骤会出发监听器。即如下的onRefresh()方法
/**
* Callback that receives refresh events from this servlet's WebApplicationContext.
* <p>The default implementation calls {@link #onRefresh},
* triggering a refresh of this servlet's context-dependent state.
* @param event the incoming ApplicationContext event
*/
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
this.refreshEventReceived = true;
onRefresh(event.getApplicationContext());
}e.将该Servlet的WebApplicationContext保存到ServletContext中。
5.DispatcherServlet.onRefresh()
/**
* 此实现调用{@link #initStrategies}
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* 初始化此servlet使用的策略对象。
* <p>可以在子类中重写以初始化其他策略对象。
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}放到后面分析。






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








