人工智能学习78-Bbox工具类—快手视频
人工智能学习79-Bbox工具类—快手视频
人工智能学习80-Bbox工具类—快手视频
工具类utils_bbox.py
主要提供三个方法,一是方法DecodeBox用于根据网络输出计算预测框坐标、尺寸、以及预测物体分类。其中坐标和尺寸都是归一化数据,需要转化为绝对数据。二是方法yolo_correct_boxes用于将预测框归一化数据转化为绝对数据。三是方法get_anchors_and_decode用在方法DecodeBox中计算预测框归一化数据。
import tensorflow as tf
from keras import backend as K
import random
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 对box进行调整,将相对坐标和宽高转化为真实图片的绝对坐标值
# input_shape 图片大小[416, 416]
# image_shape 实际输入图片大小
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image):
# -----------------------------------------------------------------#
# 把y轴放前面是因为方便预测框和图像的宽高进行相乘
# cast(x, dtype) 将张量转换为不同的dtype并返回
# -----------------------------------------------------------------#
box_yx = box_xy[..., ::-1] # -1代表转化向量顺序,box_yx应该是比率
box_hw = box_wh[..., ::-1] # -1代表转化向量顺序,box_hw应该是比率
input_shape = K.cast(input_shape, K.dtype(box_yx)) # box子图片大小
image_shape = K.cast(image_shape, K.dtype(box_yx)) # 原图片大小[416, 416]
if letterbox_image:
# -----------------------------------------------------------------#
# 这里求出来的offset是图像有效区域相对于图像左上角的偏移情况
# round(x):获取小于x的最大整数
# min(x, axis=None, keepdims=False):计算张量中最小元素的值
# K.min(input_shape/image_shape)原图[416,416]与输入图片宽高比率最小值
# new_shape指的是缩放后图像宽高
# (input_shape - new_shape)/2./input_shape [416,416]减new_shape宽高的一半与[416,416]的比率
# -----------------------------------------------------------------#
new_shape = K.round(image_shape * K.min(input_shape/image_shape)) # 将输入图片input_shape转化为image_shape同比例尺寸
offset = (input_shape - new_shape)/2./input_shape # offset应该是比例,除2是因为上下/左右两部分偏移,offset是二维比率
scale = input_shape/new_shape # 输入图片与转化尺寸后图片比例
box_yx = (box_yx - offset) * scale # 预测框左上角减offset乘缩放比率转化为原图[416,416]上的比率
box_hw *= scale # 预测框宽高转化为原图[416,416]上的比率
box_mins = box_yx - (box_hw / 2.) # 图片左上角坐标
box_maxes = box_yx + (box_hw / 2.) # 图片右下角坐标
boxes = K.concatenate([box_mins[..., 0:1], box_mins[..., 1:2], box_maxes[..., 0:1], box_maxes[..., 1:2]])
boxes *= K.concatenate([image_shape, image_shape]) # boxes(比例) * image_shape返回具体像素数
return boxes
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 训练时:返回归一化grid, feats, box_xy, box_wh
# 预测时:返回归一化box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs
# feats 卷积后输出特征图 shape分别为(m,13,13,3,85),(m,26,26,3,85),(m,52,52,3,85)
# anchors 为先验框中心坐标,形如[10,13, 16,30, 33,23] anchors.shape:(3, 2)
# num_classes 物体分类数量
# input_shape 处理图片大小[416, 416]
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def get_anchors_and_decode(feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, calc_loss=False):
# utils_bbox.py feats= Tensor("conv2d_59/BiasAdd:0", shape=(?, ?, ?, 255), dtype=float32)
# 其中255代表3*(5+80),3是每个方格扩展3个box,5代表x,y,w,h,是否存在物体,80代表80类物体分类
num_anchors = len(anchors)
# ------------------------------------------#
# grid_shape指的是特征层的宽和高
# k.shape 返回张量或变量的符号形状
# ------------------------------------------#
grid_shape = K.shape(feats)[1:3]
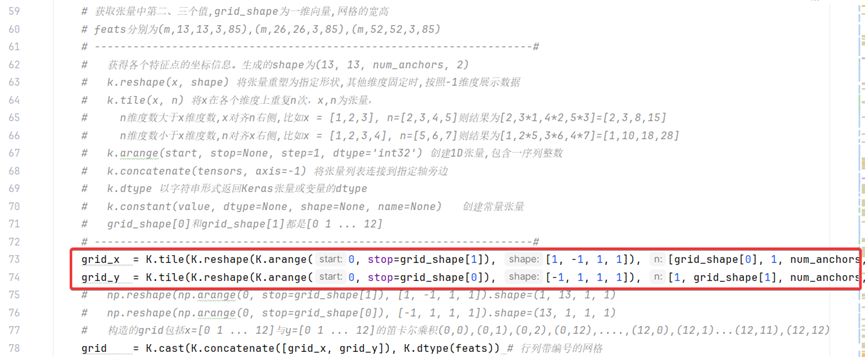
# 获取张量中第二、三个值,grid_shape为一维向量,网格的宽高
# feats分别为(m,13,13,3,85),(m,26,26,3,85),(m,52,52,3,85)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 获得各个特征点的坐标信息。生成的shape为(13, 13, num_anchors, 2)
# k.reshape(x, shape) 将张量重塑为指定形状,其他维度固定时,按照-1维度展示数据
# k.tile(x, n) 将x在各个维度上重复n次,x,n为张量,
# n维度数与x必须相同,比如x = [1,2,3], n=[2,3,4]则结果为[1*2,2*3,3*4]=[2,6,12]
# k.arange(start, stop=None, step=1, dtype='int32') 创建1D张量,包含一序列整数
# k.concatenate(tensors, axis=-1) 将张量列表连接到指定轴旁边
# k.dtype 以字符串形式返回Keras张量或变量的dtype
# k.constant(value, dtype=None, shape=None, name=None) 创建常量张量
# grid_shape[0]和grid_shape[1]都是[0 1 ... 12]
# --------------------------------------------------------------------#
grid_x = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[1]), [1, -1, 1, 1]), [grid_shape[0], 1, num_anchors, 1])
grid_y = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[0]), [-1, 1, 1, 1]), [1, grid_shape[1], num_anchors, 1])
# np.reshape(np.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[1]), [1, -1, 1, 1]).shape=(1, 13, 1, 1)
# np.reshape(np.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[0]), [-1, 1, 1, 1]).shape=(13, 1, 1, 1)
# 构造的grid包括x=[0 1 ... 12]与y=[0 1 ... 12]的笛卡尔乘积(0,0),(0,1),(0,2),(0,12),....,(12,0),(12,1)...(12,11),(12,12)
grid = K.cast(K.concatenate([grid_x, grid_y]), K.dtype(feats)) # 行列带编号的网格
# ---------------------------------------------------------------#
# 将先验框进行拓展,生成的shape为(13, 13, num_anchors, 2) 最后一个维度包含2个元素,是先验框的中心坐标
# reshape(x, shape):将张量重塑为指定的形状
# tile(x, n): 通过按`n平铺`x`创建张量`
# ---------------------------------------------------------------#
anchors_tensor = K.reshape(K.constant(anchors), [1, 1, num_anchors, 2])
# anchors_tensor shape=(1, 1, 3, 2)
# randName = random.random().__str__()
# print("utils_bbox.py ValueError: Duplicate node name in graph: 'packed' random={}".format(randName))
# with tf.name_scope(randName): #因为错误ValueError: Duplicate node name in graph: 'packed',添加随机命名
anchors_tensor = K.tile(anchors_tensor, [grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], 1, 1])
#print('utils_bbox.py get_anchors_and_decode() anchors_tensor=',anchors_tensor)
#utils_bbox.py get_anchors_and_decode() anchors_tensor= Tensor("yolo_loss/Tile_2:0", shape=(?, ?, 3, 2), dtype=float32)
# anchors_tensor shape=(?, ?, 3, 2) 可理解为将先验框anchors转化为 13*13*3*2 13*13是网格点,3代表特征层数量,2代表先验框的宽和高
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测结果调整成(batch_size,13,13,3,85)
# 13*13代表特征图为13行13列
# 3代表每个方格扩充三个box
# 85可拆分成4 + 1 + 80
# 4代表的是中心宽高的调整参数:x,y,w,h
# 1代表的是框的置信度
# 80代表的是种类
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 1.feats.shape=(?, ?, ?, 255)
feats = K.reshape(feats, [-1, grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], num_anchors, num_classes + 5])
# 2.feats.shape=(?, ?, ?, 3, 85)
# ------------------------------------------#
# 对先验框进行解码,并进行归一化
# 对预测框坐标feats[..., :2]归一化并+grid在除grid_shape宽高,进行归一化
# 对预测框宽高feats[..., 2:4]归一化
# feats[..., :2]指的是最后一维度前两个元素为x,y
# feats[..., 2:4]指的是最后一维度第三、四个元素为w,h
# ------------------------------------------#
box_xy = (K.sigmoid(feats[..., :2]) + grid) / K.cast(grid_shape[..., ::-1], K.dtype(feats)) # 将预测框x,y根据grid归一化
box_wh = K.exp(feats[..., 2:4]) * anchors_tensor / K.cast(input_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats)) # 将预测框w,h根据anchors归一化
# ------------------------------------------#
# 获得预测框的置信度
# feats[..., 4:5]指的是最后一维度第五个元素为置信度
# feats[..., 5:]指的是最后一维度第6到24个元素存放one-hot码,标识物体种类编号
# ------------------------------------------#
box_confidence = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 4:5]) # 预测框的置信度根据sigmoid归一化
box_class_probs = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 5:]) # 预测框中物体种类根据sigmoid归一化
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 在计算loss的时候返回grid, feats, box_xy, box_wh
# 在预测的时候返回box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
if calc_loss == True:
return grid, feats, box_xy, box_wh
return box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 图片预测
# 返回预测框boxes_out xywh shape=(?, 4), dtype=float32,
# 是否包含物体scores_out shape=(?,), dtype=float32),
# 80类物体分类序号0-79之间 classes_out shape=(?,), dtype=int32
# 返回boxes_out, scores_out, classes_out
# boxes_out = Tensor("concat_9:0", shape=(?, 4), dtype=float32) 预测框x,y,w,h
# scores_out = Tensor("concat_10:0", shape=(?,), dtype=float32) 是否包含物体
# classes_out = Tensor("concat_11:0", shape=(?,), dtype=int32) 为80类物体分类序号0-79之间
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def DecodeBox(outputs, # 模型定义的输出,是nets\yolo.py中yolo_body函数中的张量[P5, P4, P3]
anchors, # 先验框 [116,90],[156,198],[373,326] [30,61],[62,45],[59,119] [10,13],[16,30],[33,23]
num_classes, # 目标分类数
image_shape, # 实际输入图片大小
input_shape, # 处理图片大小[416, 416]
anchor_mask=[[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]], # 先验框的序号
max_boxes=100, # 同一图片中最大识别物体数量
confidence=0.5,
nms_iou=0.3,
letterbox_image=True):
box_xy = [] #预测框XY坐标
box_wh = [] # 预测框宽高
box_confidence = [] # 预测框物体置信度
box_class_probs = [] # 预测框物体种类
# 循环遍历每个特征图计算预测框归一化x,y,w,h,置信度,物体分类
for i in range(len(outputs)): # outputs为三个特征层,遍历每个特征层中矩形框
# 预测时:返回归一化box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs
sub_box_xy, sub_box_wh, sub_box_confidence, sub_box_class_probs = \
get_anchors_and_decode(outputs[i], anchors[anchor_mask[i]], num_classes, input_shape)
box_xy.append(K.reshape(sub_box_xy, [-1, 2])) # 转化为2列多行数据,行数可扩展
box_wh.append(K.reshape(sub_box_wh, [-1, 2]))
box_confidence.append(K.reshape(sub_box_confidence, [-1, 1])) # 转化为1列多行数据,行数可扩展
box_class_probs.append(K.reshape(sub_box_class_probs, [-1, num_classes])) # 转化为num_classes列,行数可扩展
# concatenate(tensors, axis=-1) 将张量列表连接到指定轴旁边
box_xy = K.concatenate(box_xy, axis = 0) # 预测框xy坐标
box_wh = K.concatenate(box_wh, axis = 0) # 预测框宽高
box_confidence = K.concatenate(box_confidence, axis = 0) # 预测框置信度
box_class_probs = K.concatenate(box_class_probs, axis = 0) # 预测框物体种类
#print('utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() box_confidence=', box_confidence)
#print('utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() box_class_probs=', box_class_probs)
#utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() box_confidence = Tensor("concat_5:0", shape=(?, 1), dtype=float32)
#utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() box_class_probs = Tensor("concat_6:0", shape=(?, 80), dtype=float32)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 在图像传入网络预测前会进行letterbox_image给图像周围添加灰条,因此生成的box_xy, box_wh是相对于有灰条的图像的
# 我们需要对其进行修改,去除灰条的部分。 将box_xy、和box_wh调节成y_min,y_max,xmin,xmax
# 如果没有使用letterbox_image也需要将归一化后的box_xy, box_wh调整成相对于原图大小的
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
boxes = yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image) # 返回的boxes是实际像素数
box_scores = box_confidence * box_class_probs #预测框物体不同种类得分概率
#print('utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() boxes=', boxes)
#print('utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() box_scores=', box_scores)
#utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() boxes = Tensor("mul_81:0", shape=(?, 4), dtype=float32)
#utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() box_scores = Tensor("mul_82:0", shape=(?, 80), dtype=float32)
# -----------------------------------------------------------#
# 判断得分是否大于score_threshold
# -----------------------------------------------------------#
mask = box_scores >= confidence
#print('utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() mask=', mask)
#utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() mask= Tensor("GreaterEqual:0", shape=(?, 80), dtype=bool)
max_boxes_tensor = K.constant(max_boxes, dtype='int32')
boxes_out = []
scores_out = []
classes_out = []
for c in range(num_classes): # 遍历每类物体
# -----------------------------------------------------------#
# 取出所有box_scores >= score_threshold的框,和成绩
# -----------------------------------------------------------#
class_boxes = tf.boolean_mask(boxes, mask[:, c])
class_box_scores = tf.boolean_mask(box_scores[:, c], mask[:, c])
# -----------------------------------------------------------#
# 非极大抑制
# 保留一定区域内得分最大的框
# -----------------------------------------------------------#
nms_index = tf.image.non_max_suppression(class_boxes, class_box_scores, max_boxes_tensor, iou_threshold=nms_iou)
# -----------------------------------------------------------#
# 获取非极大抑制后的结果
# 下列三个分别是:框的位置,得分与种类
# gather(reference, indices):检索张量引用中索引“indexes”的元素`
# ones_like(x, dtype=None, name=None):实例化与另一个张量形状相同的all-ones变量
# append(self, *args, **kwargs):将对象追加到列表的末尾。
# -----------------------------------------------------------#
class_boxes = K.gather(class_boxes, nms_index)
class_box_scores = K.gather(class_box_scores, nms_index)
classes = K.ones_like(class_box_scores, 'int32') * c
# classes 为80类物体分类序号0-79之间
boxes_out.append(class_boxes)
scores_out.append(class_box_scores)
classes_out.append(classes)
boxes_out = K.concatenate(boxes_out, axis=0) # 将列表boxes_out转化为张量
scores_out = K.concatenate(scores_out, axis=0)
classes_out = K.concatenate(classes_out, axis=0)
#print('utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() boxes_out=', boxes_out)
#print('utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() scores_out=', scores_out)
#print('utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() classes_out=', classes_out)
#utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() boxes_out = Tensor("concat_9:0", shape=(?, 4), dtype=float32)
#utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() scores_out = Tensor("concat_10:0", shape=(?,), dtype=float32)
#utils_bbox.py DecodeBox() classes_out = Tensor("concat_11:0", shape=(?,), dtype=int32)
return boxes_out, scores_out, classes_out
if __name__ == "__main__":
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(x):
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
return s
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测值的每个特征层调成真实值
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def get_anchors_and_decode(feats, anchors, num_classes):
# feats [batch_size, 13, 13, 3 * (5 + num_classes)]
# anchors [3, 2] 3代表每个方格扩展3个box,2代表扩展box的宽高
num_anchors = len(anchors)
# ------------------------------------------#
# grid_shape指的是特征层的高和宽,特征图feats第2,3维分别是宽和高
# grid_shape [13, 13]
# ------------------------------------------#
grid_shape = np.shape(feats)[1:3]
# --------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 获得各个特征点的坐标信息。生成的shape为(13, 13, num_anchors, 2)
# grid_x [13, 13, 3, 1]
# grid_y [13, 13, 3, 1]
# grid [13, 13, 3, 2]
# np.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[1])返回[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12]
# np.reshape(np.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[1]), [1, -1, 1, 1]).shape=(1, 13, 1, 1)
# np.reshape(np.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[0]), [-1, 1, 1, 1]).shape=(13, 1, 1, 1)
# 构造的grid包括x=[0 1 ... 12]与y=[0 1 ... 12]的笛卡尔乘积
# --------------------------------------------------------------------#
grid_x = np.tile(np.reshape(np.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[1]), [1, -1, 1, 1]),
[grid_shape[0], 1, num_anchors, 1])
grid_y = np.tile(np.reshape(np.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[0]), [-1, 1, 1, 1]),
[1, grid_shape[1], num_anchors, 1])
grid = np.concatenate([grid_x, grid_y], -1) #grid.shape=[13, 13, 3, 2]
# ---------------------------------------------------------------#
# 将先验框进行拓展,生成的shape为(13, 13, num_anchors, 2)
# [1, 1, 3, 2]
# [13, 13, 3, 2]
# ---------------------------------------------------------------#
anchors_tensor = np.reshape(anchors, [1, 1, num_anchors, 2]) # anchors_tensor.shape=[1, 1, 3, 2]
anchors_tensor = np.tile(anchors_tensor, [grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], 1, 1]) # anchors_tensor.shape=(13, 13, 3, 2)
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测结果调整成(batch_size,13,13,3,75)
# 75可拆分成3*(4 + 1 + 20)
# 4代表的是中心宽高的调整参数
# 1代表的是框的置信度
# 20代表的是种类
# feats原来shape=[4,13,13,75]
# feats.shape=(4, 13, 13, 3, 25)
# ---------------------------------------------------#
feats = np.reshape(feats, [-1, grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], num_anchors, num_classes + 5])
# ------------------------------------------#
# 对先验框进行解码,并进行归一化
# feats[..., :2]代表先验框x,y.通过sigmoid函数转化为0-1之间数值,在附加到grid网格上
# ------------------------------------------#
box_xy = sigmoid(feats[..., :2]) + grid # sigmoid归一化(0-1)数据后追加grid网格坐标
# box_xy.shape=(4, 13, 13, 3, 2) 最后一维包含25中前两个元素是x,y
# anchors_tensor= (13, 13, 3, 2)
# np.exp 是e指数函数
box_wh = np.exp(feats[..., 2:4]) * anchors_tensor
# box_wh.shape=(4, 13, 13, 3, 2) 最后一维25中前第3,4个元素是w,h,第5个元素是置信度,后面20个元素是不同物体类别
# ------------------------------------------#
# 获得预测框的置信度, feats最后一维数据中第5个是置信度
# ------------------------------------------#
box_confidence = sigmoid(feats[..., 4:5])
# box_confidence.shape=(4, 13, 13, 3, 1) 第5个元素是置信度,后面20个元素是不同物体类别
box_class_probs = sigmoid(feats[..., 5:]) # box_class_probs是20类物体分类向量
# box_class_probs.shape=(4, 13, 13, 3, 20) 后面20个元素是不同物体类别
box_wh = box_wh / 32 # 矩形框宽高缩小32倍
anchors_tensor = anchors_tensor / 32 # 先验框宽高缩小32倍
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(121)
plt.ylim(-2,15)
plt.xlim(-2,15)
plt.scatter(grid_x,grid_y)
plt.scatter(5,5,c='black')
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
anchor_left = grid_x - anchors_tensor/2 # 计算先验框左上角横坐标
anchor_top = grid_y - anchors_tensor/2 # 计算先验框左上角纵坐标
rect1 = plt.Rectangle([anchor_left[5,5,0,0],anchor_top[5,5,0,1]],anchors_tensor[0,0,0,0],anchors_tensor[0,0,0,1],
color="r",fill=False)
rect2 = plt.Rectangle([anchor_left[5,5,1,0],anchor_top[5,5,1,1]],anchors_tensor[0,0,1,0],anchors_tensor[0,0,1,1],
color="r",fill=False)
rect3 = plt.Rectangle([anchor_left[5,5,2,0],anchor_top[5,5,2,1]],anchors_tensor[0,0,2,0],anchors_tensor[0,0,2,1],
color="r",fill=False)
ax.add_patch(rect1)
ax.add_patch(rect2)
ax.add_patch(rect3)
ax = fig.add_subplot(122)
plt.ylim(-2,15)
plt.xlim(-2,15)
plt.scatter(grid_x,grid_y)
plt.scatter(5,5,c='black')
plt.scatter(box_xy[0,5,5,:,0],box_xy[0,5,5,:,1],c='r')
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
pre_left = box_xy[...,0] - box_wh[...,0]/2
pre_top = box_xy[...,1] - box_wh[...,1]/2
rect1 = plt.Rectangle([pre_left[0,5,5,0],pre_top[0,5,5,0]],box_wh[0,5,5,0,0],box_wh[0,5,5,0,1],color="r",fill=False)
rect2 = plt.Rectangle([pre_left[0,5,5,1],pre_top[0,5,5,1]],box_wh[0,5,5,1,0],box_wh[0,5,5,1,1],color="r",fill=False)
rect3 = plt.Rectangle([pre_left[0,5,5,2],pre_top[0,5,5,2]],box_wh[0,5,5,2,0],box_wh[0,5,5,2,1],color="r",fill=False)
ax.add_patch(rect1)
ax.add_patch(rect2)
ax.add_patch(rect3)
plt.show()
代码解释部分
方法yolo_correct_boxes第38行


在某一轴方向连接两个张量,返回连接后的张量。
例程:
nd1 = np.arange(6)
nd1 = nd1.reshape(2,3) #2*3
t1 = tf.convert_to_tensor(nd1)
nd2 = np.arange(9)
nd2 = nd2.reshape(3,3) #3*3
t2 = tf.convert_to_tensor(nd2)
t2 = K.concatenate([t1, t2], axis=0)
print('t2.shape===', t2.shape)
t2.shape=== (5, 3)
nd1 = np.arange(6)
nd1 = nd1.reshape(2,3) #2*3
t1 = tf.convert_to_tensor(nd1)
nd2 = np.arange(9)
nd2 = nd2.reshape(3,3) #3*3
t2 = tf.convert_to_tensor(nd2)
t2 = K.concatenate([t1, t2], axis=1)
print('t2.shape===', t2.shape)
ValueError: Dimension 0 in both shapes must be equal, but are 2 and 3. Shapes are [2] and [3]. for 'concat' (op: 'ConcatV2') with input shapes: [2,3], [3,3], [] and with computed input tensors: input[2] = <1>.
方法get_anchors_and_decode第73,74行
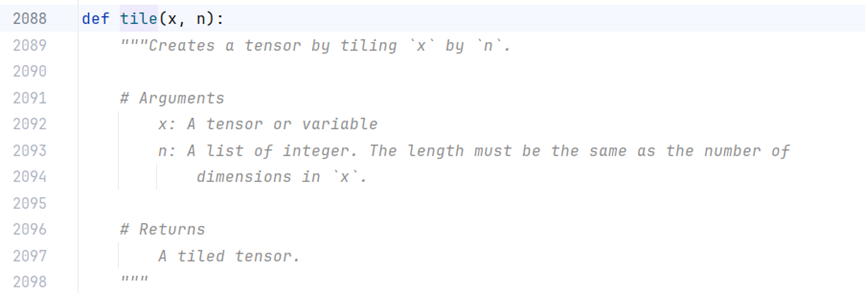
k.tile(x, n) 将x在各个维度上重复n次,x,n为张量,
n维度数大于x维度数,x对齐n右侧,比如x = [1,2,3], n=[2,3,4,5]则结果为[2,31,42,53]=[2,3,8,15]
n维度数小于x维度数,n对齐x右侧,比如x = [1,2,3,4], n=[5,6,7]则结果为[1,25,36,47]=[1,10,18,28]
例程:
x = np.arange(1*2*3)
x = np.reshape(x, (1, 2, 3))
print('x.shape===', x.shape)
n=[2, 3, 1]
y = K.tile(x, n)
print('y.shape===', y.shape)
x.shape=== (1, 2, 3)
y.shape=== (2, 6, 3)
方法get_anchors_and_decode第83行
anchors_tensor = K.reshape(K.constant(anchors), [1, 1, num_anchors, 2])
转化张量的尺寸
例程:
x = np.arange(1*2*3)
x = np.reshape(x, [1, 2, 3])
print('x.shape===', x.shape)
x.shape=== (1, 2, 3)
方法DecodeBox第188行
# -----------------------------------------------------------#
# 判断得分是否大于score_threshold
# -----------------------------------------------------------#
mask = box_scores >= confidence
例程:
x = np.arange(1*2*3)
x = np.reshape(x, [2, 3])
print('x === ', x)
y = x>3
print('y === ', y)
z = x[y]
print('z === ', z)
x === [[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]]
y === [[False False False]
[False True True]]
z === [4 5]
方法DecodeBox第206行
# -----------------------------------------------------------#
# 非极大抑制
# 保留一定区域内得分最大的框
# -----------------------------------------------------------#
nms_index = tf.image.non_max_suppression(class_boxes, class_box_scores, max_boxes_tensor, iou_threshold=nms_iou)
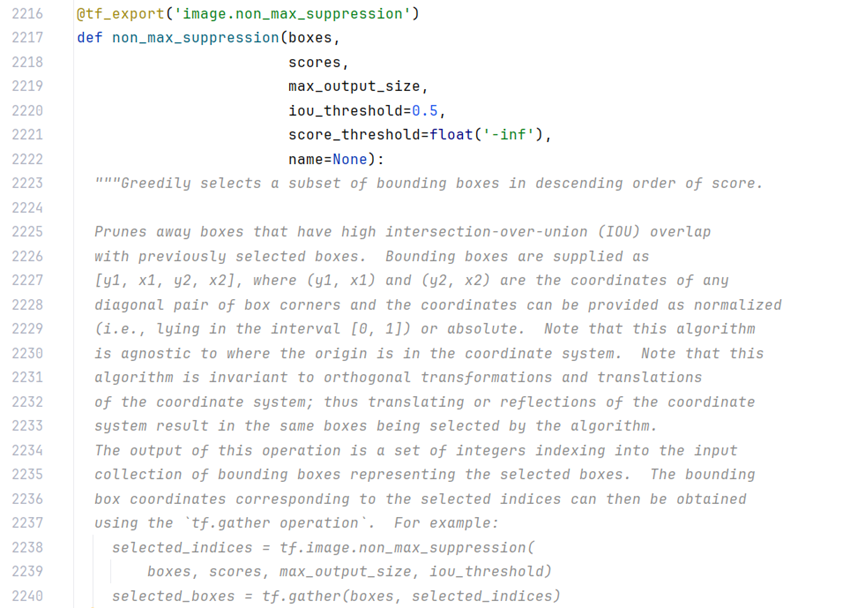
贪婪算法:就是boxes按scores由大到小排序,选定第一个,依次与之后boxes的做交并比iou ,删除交并比iou大于阈值的框,循环完成第一个boxes, 再选定第二个boxes,循环上述操作。直到比较完成所有boxes。选定的框iou不超过设定的iou阈值。依次删除iou最小的boxes,最后保留多少个boxes由参数max_output_size决定。
按照通俗语言理解:就是保留一个得分最大的boxes,删除其他得分低的boxes,最后保留多少boxes,由参数max_output_size决定。
例程:
boxes = np.array([[3, 5, 10, 20], [4, 8, 12, 15], [5, 7, 10, 14], [6, 9, 12, 19]], dtype = np.float32)
scores = np.array([0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8], dtype=np.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
index = sess.run(tf.image.non_max_suppression(boxes=boxes, scores=scores, iou_threshold=0.5, max_output_size=1))
print('index=', index)
max_boxes = sess.run(K.gather(boxes, index))
print('选择一个最大max_boxes=', max_boxes)
index2 = sess.run(tf.image.non_max_suppression(boxes=boxes, scores=scores, iou_threshold=0.5, max_output_size=2))
print('index=', index2)
max_boxes2 = sess.run(K.gather(boxes, index2))
print('选择两个最大max_boxes2=', max_boxes2)
index= [3]
选择一个最大max_boxes= [[ 6. 9. 12. 19.]]
index= [3 2]
选择两个最大max_boxes2= [[ 6. 9. 12. 19.]
[ 5. 7. 10. 14.]]
方法DecodeBox第215行
class_boxes = K.gather(class_boxes, nms_index)

根据索引获取张量中对应的数据。
例程:
boxes = np.array([[3, 5, 10, 20], [4, 8, 12, 15], [5, 7, 10, 14], [6, 9, 12, 19]], dtype = np.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
max_boxes = sess.run(K.gather(boxes, 0))
print('选择第一个元素 =', max_boxes)
max_boxes2 = sess.run(K.gather(boxes, 1))
print('选择第二个元素 =', max_boxes2)
选择第一个元素 = [ 3. 5. 10. 20.]
选择第二个元素 = [ 4. 8. 12. 15.]
方法DecodeBox第217行
classes = K.ones_like(class_box_scores, ‘int32’) * c
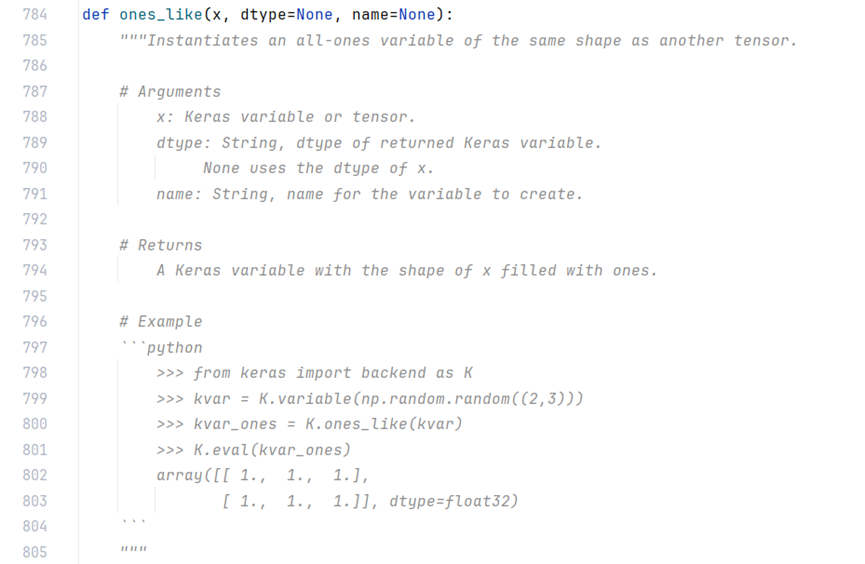
例程:
kvar = K.variable(np.random.random((2, 3)))
kvar_ones = K.ones_like(kvar)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(kvar_ones.eval())
[[1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1.]]





















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








