1. Normal Equation
Given a matrix equation
the normal equation is that which minimizes the sum of the square differences between the left and right sides:
It is called a normal equation because is normal to the range of
. Here,
is a normal matrix.
2. Normal Matrix
A square matrix is a normal matrix if
where is the commutator and
denotes the conjugate transpose.
正态矩阵,即具有性质的矩阵,即矩阵
的不同列正交。
3. 实对称矩阵的性质
- 实对称矩阵的特征值都是实数
- 实对称矩阵的特征向量都是实向量
- 实对称矩阵的属于不同特征值的特征向量正交(矩阵的属于不同特征值的特征向量线性无关,正交向量组必线性无关)
- 实对称矩阵的属于不同特征值的特征向量线性无关
阶实对称矩阵恰有
个线性无关的特征向量,进而有
个单位正交的特征向量
- 实对称矩阵必可对角化
- 若两实对称矩阵有相同的特征值,则二者相似
4. 矩阵的迹
- 是所有对角元的和
- 是所有特征值的和
5. Hermitian matrix
该矩阵为一方阵,
6. Rayleigh quotient
In mathematics, for a given complex Heimitian matrix 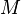 and nonzero vector
and nonzero vector 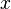 , the Rayleigh quotient
, the Rayleigh quotient  , is defined as:
, is defined as:

the conjugate transpose 
7. 向量范数
1-范数:
2-范数:
-范数:
p-范数:
8. 矩阵范数
Frobenius范数,或简称F-范数:

列和范数、谱范数和行和范数:
If the singular values are denoted by σi, then the Schatten p-norm is defined by

The most familiar cases are p = 1, 2, ∞. The case p = 2 yields the Frobenius norm, introduced before. The case p = ∞ yields the spectral norm, which is the matrix norm induced by the vector 2-norm (see above). Finally, p = 1 yields the nuclear norm (also known as the trace norm(迹范数), or the Ky Fan 'n'-norm), defined as


(Here  denotes a positive semidefinite matrix
denotes a positive semidefinite matrix 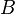 such that
such that  . More precisely, since
. More precisely, since  is a positive semidefinite matrix, its square root is well-defined.)
is a positive semidefinite matrix, its square root is well-defined.)
nuclear norm即矩阵的奇异值的和。
L-1 norm:





















 1429
1429

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








