Spring
今天课程计划
-
spring介绍
-
Spring-IOC-XML配置
-
创建Spring项目
-
测试体验Spring的入门案例
-
Bean的获取方式
-
Bean的创建方式
-
单例&懒加载
-
Bean的生命周期
-
Setter注入
-
构造方法注入
-
自动装配
学习目标
-
掌握SpringIoc-xml配置
-
了解Bean,IOC,Di等概念,理论
-
了解Bean的生命周期
一.介绍
1.容器
-
IOC容器
-
核心机制:控制反转(IOC),依赖注入(DI)
-
管理对象的容器(Bean)
-
优势:解耦组件,降低类与类之间的依赖
2.轻量级设计
-
配置简单:基于XML或者配置类或者注解,配置方式,无侵入式开发
-
资源占用低:适合小型项目,也可以扩展到大型项目
3.Bean生命周期管理
-
bean对象的创建到使用到销毁,都是由Spring负责的
-
全流程控制:从 创建 → 依赖注入 → 初始化 → 使用 →销毁
-
可定制:整个过程通过调用方法,灵活干预
4.解耦
-
类 与 类 之间的依赖关系,叫耦合
-
依赖: 删除/修改 一个类的时候,其他类,会不会报错/报红线
-
降低依赖程度:耦合度降低
5.内聚
-
责任单一原则
-
尽可能的让一个类,一个方法,只做一件事
-
一个非常重要的编程思想
-
要始终贯穿你的编程生涯
-
-
让类或者方法的功能,更加的单一,纯粹
-
高内聚
一句话总结:
Spring通过IOC容器,实现了 轻量级,解耦化的Bean对象管理,简化了开发的流程,并增强了系统的灵活性
高内聚,低耦合
二.核心
IOC
-
控制反转
DI
-
依赖注入
AOP
-
面向切面
三.优势
1 设计原则支持
-
高内聚:方法责任单一,符合责任单一原则
-
低耦合:类之间的依赖最小化,符合最少知道原则,避免跨级调用
2.简化开发与事务管理
-
普通事务
@Override
public void updateLoginTime(Long uid) {
SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisHealper.getSqlSession();
try {
//关闭自动提交
sqlSession.commit(false);
//获取Dao Mapper
AdminUserDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(AdminUserDao.class);
//这个sql语句执行时 根据程序执行逻辑 不可能出错 所以不需要返回值 也不需要对异常情况做处理
mapper.updateUserLoginTime(uid);
//风险
long i = 100/uid;
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
//产生了异常,回滚事务
sqlSession.rollback();
}finally {
//归还SqlSession
MyBatisHealper.backAndCommitSqlSession(sqlSession);
}
}
-
声明式事务
-
通过注解,实现事务自动回滚
-
无需手动编程,只需要添加一个简单的注解就可以了
-
3.灵活集成与扩展
-
Spring有完整的生态圈
-
市面上流行的框架和技术,基本上都兼容Spring
-
可以顺利和任意的框架整合在一起,无缝衔接
4.模块化设计
-
按需引入功能
-
MVC
-
aop等功能
5.核心机制
-
控制反转
-
依赖注入
SpringIOC
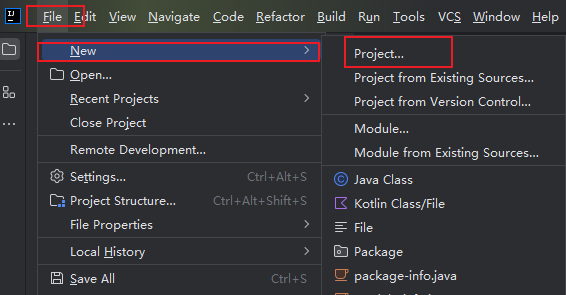
一.创建Spring项目
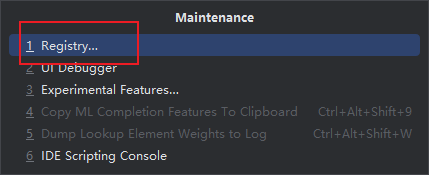
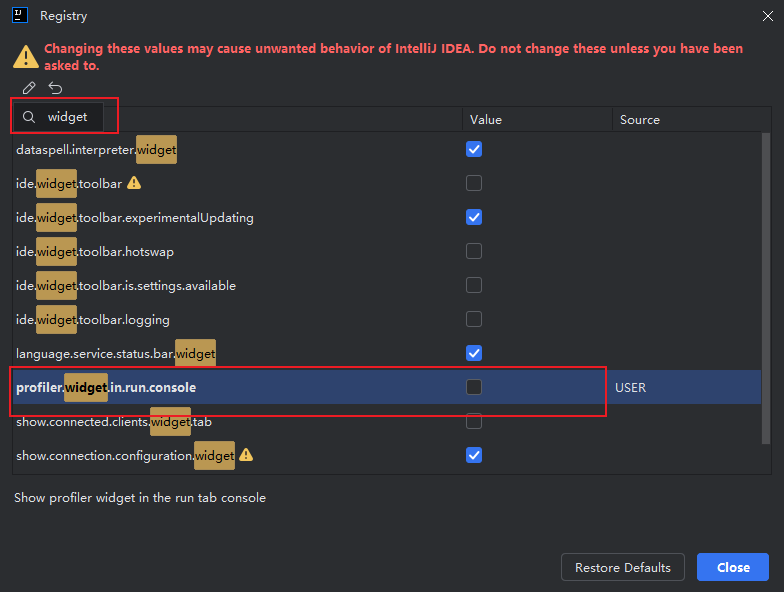
1.解决Idea 2024 版本下,main方法运行bug
Ctrl + Shift + Alt + /
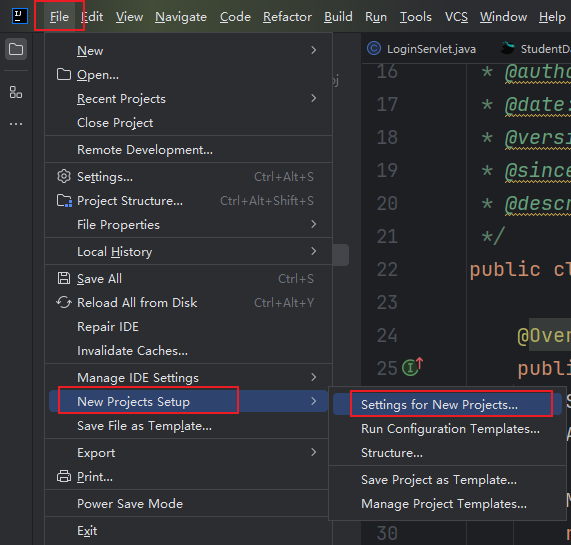
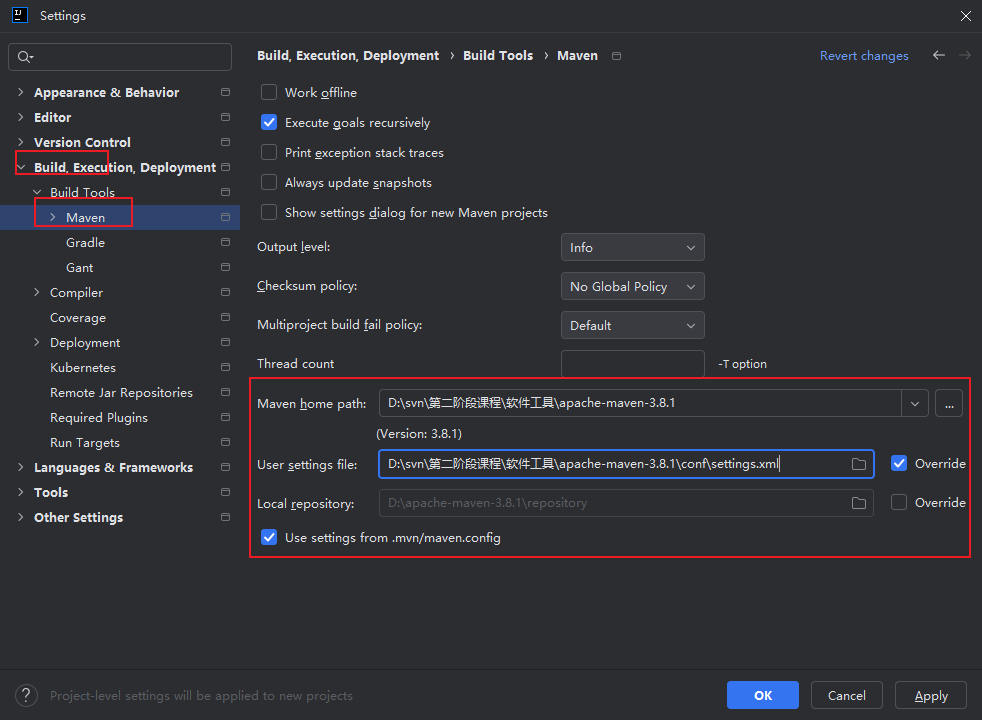
2.配置新项目的Maven
3.创建一个普通的Java项目
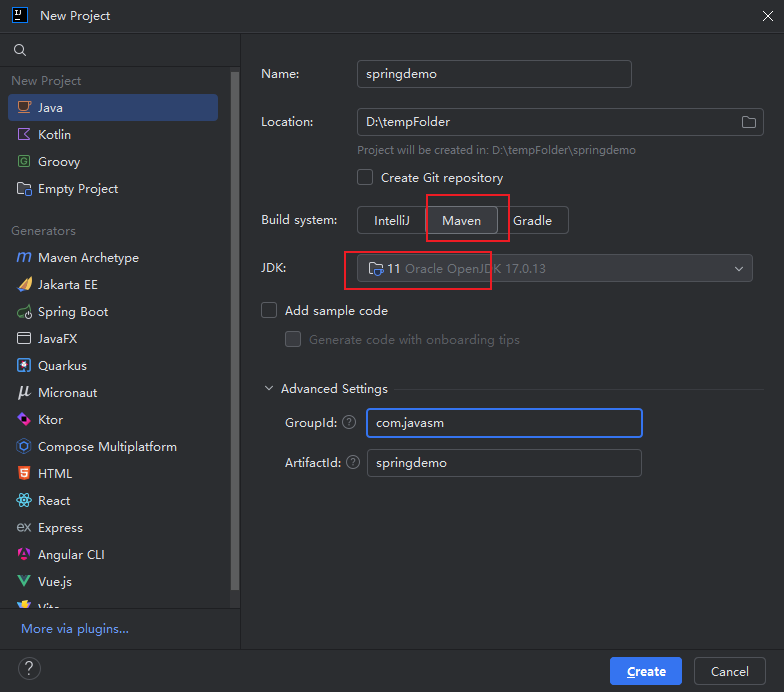
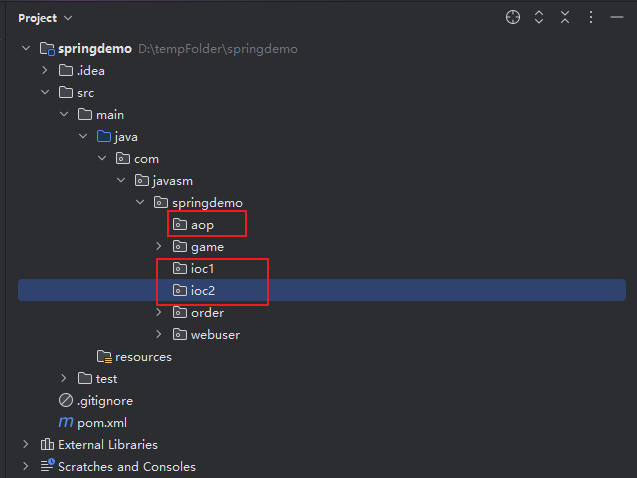
4.包设计
大家在平时编码过程中,一定要注意编码规范
类名:首字母,必须大写
包名:项目的性质.公司名.项目名.模块名
缩进:必须对齐
编码规范之后,能更容易找到bug,并且可以避免很多bug的产生
5.引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.18.30</version> </dependency>
6.创建Spring配置文件
Spring有两种启动模式:XML 和 注解
现在使用xml的配置文件,作为Spring项目的配置
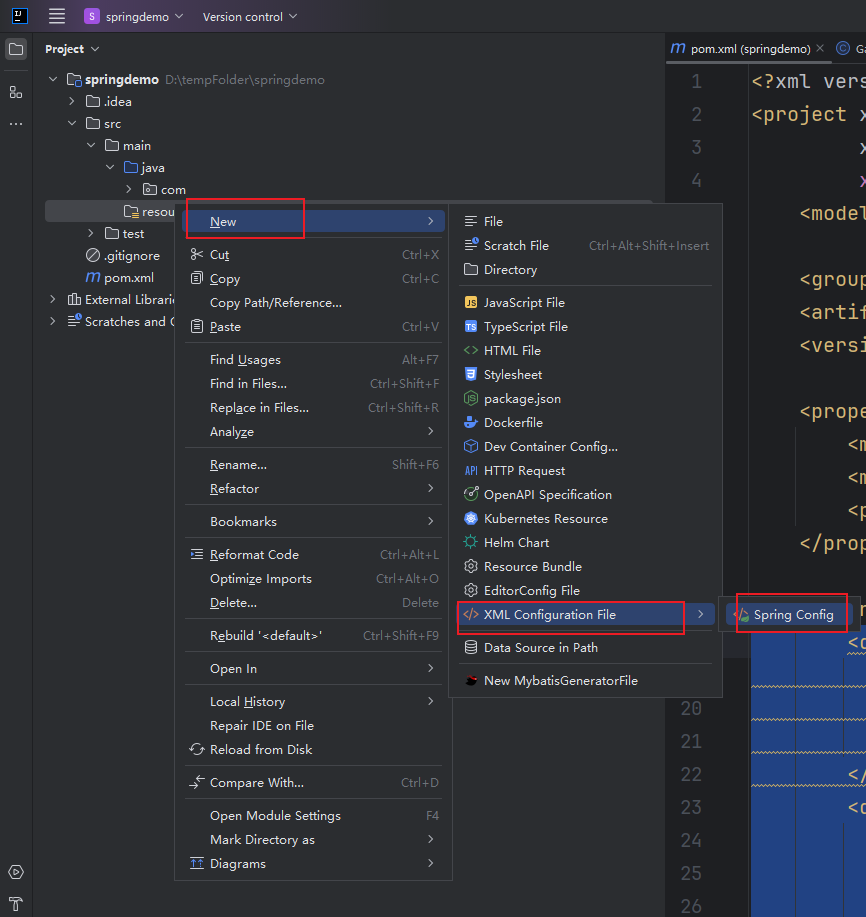
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> </beans>
7.第一个测试案例
体验一下Spring容器Bean的创建和获取
/**
* 每个类,天然都会有一个隐藏的无参构造方法
* 如果手写了一个有参构造方法之后,之前隐藏的无参构造就会消失
* 因为学习框架之后,很多框架在创建对象的时候,默认会调用无参构造
* 无参构造方法的消失会产生异常bug
* 所以,养成习惯,每次写有参构造的时候,都要记得随手随手添加一个无参构造方法,不管有没有用
*/
@ToString
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Student() {
}
public Student(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
-
修改配置文件 spring1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--相当于写了一个Student abc = new Student();--> <!--当前的Student类,创建对象的权力,交给了Spring容器--> <!--对象控制权的变化,被成为 控制反转 IOC--> <!--spring容器来管理对象,而不是程序员去管理--> <!--容器创建好了之后,把当前的对象装到容器里,起的名字是abc--> <!--不同的对象,在Spring容器中,不能重名--> <bean id="abc" class="com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.Student"/> </beans>
-
测试类
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
f1();
}
private static void f1() {
//从类的加载路径中,寻找配置文件 spring1.xml
//加载到程序中,解析xml
//读取到spring1.xml中的标签内容
//解析成功,创建一个Bean的集合,用来存储所有的Bean对象
//new bean对象,把new出来的对象,存入Bean的集合中,等待调用
//applicationContext 就是Spring容器对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring1.xml");
//通过bean的id来获取bean对象
Student abc = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("abc");
abc.id = 10;
System.out.println(abc);
}
}
8.启动原理
程序启动 → 读取XML文件 → 解析XML文件 → 读取bean标签里的内容(id和class属性) → 通过反射,调用类的无参构造方法 → 创建一个新的对象 → 创建出来的对象,存入Spring容器
-
异常
Caused by: java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.Student.<init>() 缺少无参构造方法
private static void f2() throws Exception{
//解析xml 读取<bean id="abc" class="com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.Student"/>
String id = "abc";
String className = "com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.Student";
//创建Bean对象
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(className);
//执行无参构造
Object o = aClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
//模拟创建Spring容器,存入对象
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(id,o);
//从容器中获取
Student object = (Student)map.get("abc");
object.id = 100;
System.out.println(object);
}
二.Bean的管理
1 获取Bean的方式
-
根据ID 获取Bean对象
Student abc = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("abc");
-
根据类型获取
Student student = applicationContext.getBean(Student.class);
-
根据id+类型
Student abc = applicationContext.getBean("abc", Student.class);
-
异常
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.Student' available: expected single matching bean but found 2: abc,stu 通过类型获取Bean对象,但是容器中,相同类型的Bean有多个
-
别名
通过别名和id名获取Bean对象
<bean id="abc" class="com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.Student"/>
<alias name="abc" alias="xyz"/>
Student abc = applicationContext.getBean("abc", Student.class);
Student xyz = applicationContext.getBean("xyz", Student.class);
2 创建Bean的方式
-
无参构造方法
<bean id="abc" class="com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.Student"/>
-
静态工厂
public class StudentStaticFactory {
public static Student f1(){
Student student = new Student(1001,"小明");
return student;
}
}
<bean id="xiaoming" class="com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.factory.StudentStaticFactory" factory-method="f1"/>
Student student = applicationContext.getBean("xiaoming", Student.class);
-
实例工厂
public class StudentFactory {
public Student f2(){
Student student = new Student(2001,"李雷");
return student;
}
}
<!--把工厂对象 单独添加到Spring容器中-->
<bean id="stufactory" class="com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.factory.StudentFactory"/>
<bean id="lilei" factory-bean="stufactory" factory-method="f2"/>
Student student = applicationContext.getBean("lilei", Student.class);
-
Spring工厂
public class StudentSpringFactory implements FactoryBean<Student> {
@Override
public Student getObject() throws Exception {
return new Student(3001,"韩梅梅");
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Student.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
//返回true 是单例
//返回 false 是多例
//这个方法可以选择不重写,在Spring容器中,Bean对象默认都是单例的
return true;
}
}
<bean id="han" class="com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.factory.StudentSpringFactory"/>
Student student = applicationContext.getBean("han", Student.class);
3 单例和懒加载
-
单例
Spring 的Bean在默认情况下,都是单例的.
-
多例
启动容器的时候,并没有创建Bean对象,只有调用的时候创建了
<bean id="abc" class="com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.Student" scope="prototype"/>
-
懒加载
不使用的Bean对象,不去创建对象
仅仅对单例生效
<bean id="abc" class="com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.Student" lazy-init="true"/>
全局懒加载
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
default-lazy-init="true"
>
4.生命周期管理
public class Student {
public Integer id;
public String name;
public Student() {
System.out.println("----------========Student() =====----------");
}
public Student(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public void t1(){
System.out.println("初始化方法");
}
public void t2(){
System.out.println("销毁方法");
}
}
<bean id="abc" class="com.javasm.springdemo.ioc1.Student" init-method="t1" destroy-method="t2" />
初始化方法:init-method
销毁方法:destroy-method
正常情况下,不会执行销毁方法,只有在容器关闭之前,执行销毁
1 无参构造 2 初始化方法 init 3 方法的调用 4 销毁的方法 5 关闭容器
三 依赖注入
| 方式 | 特点 |
|---|---|
| 构造器注入 | 强制依赖,不可以修改属性 |
| Setter注入 | 可选依赖,可变属性 |
1 Setter注入案例
-
新建Java类
-
实体类
-
给自己的属性,注入一些值
-
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class GameModel {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double price;
//英雄列表
private String[] heros;
//关卡
private List<String> levels;
//成就
private Set<String> achievements;
//配置
private Properties gameConfig;
//背包
private Map<String,String> items;
//公司
private Company company;
//玩家列表
private List<Player> playerList;
}
-
xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="game" class="com.javasm.springdemo.game.model.GameModel">
<property name="id" value="1001"/>
<property name="name" value="英雄联盟"/>
<property name="price" value="22.22"/>
<!--英雄列表-->
<property name="heros">
<array>
<value>提莫</value>
<value>亚索</value>
<value>剑圣</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--关卡-->
<property name="levels">
<list>
<value>黄风岭</value>
<value>努巴尼</value>
<value>狮驼岭</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--成就-->
<property name="achievements">
<set>
<value>顺手牵羊</value>
<value>借刀杀人</value>
<value>南蛮入侵</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--配置-->
<property name="gameConfig">
<props>
<prop key="model">全屏</prop>
<prop key="location">zh</prop>
</props>
</property>
<!--背包-->
<property name="items">
<map>
<entry key="1001" value="复活甲"/>
<entry key="1002" value="定风珠"/>
<entry key="1003" value="火麒麟"/>
</map>
</property>
<!--公司-->
<property name="company" ref="cp"/>
<property name="playerList">
<list>
<bean class="com.javasm.springdemo.game.model.Player">
<property name="id" value="2002"/>
<property name="nickname" value="追风的老人"/>
</bean>
<ref bean="p2"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="cp" class="com.javasm.springdemo.game.model.Company">
<property name="id" value="111"/>
<property name="name" value="拳头"/>
<property name="address" value="863软件园"/>
</bean>
<bean id="p2" class="com.javasm.springdemo.game.model.Player">
<property name="id" value="2003"/>
<property name="nickname" value="李火旺"/>
</bean>
</beans>
-
测试
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
f1();
}
private static void f1() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring2.xml");
GameModel game = applicationContext.getBean("game", GameModel.class);
System.out.println(game);
}
}
2 构造方法注入
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Music {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String time;
private Company company;
public Music(Integer id, String name, String time, Company company) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.time = time;
this.company = company;
}
}
-
XML
<bean id="music" class="com.javasm.springdemo.game.model.Music">
<constructor-arg name="id" value="1000" type="java.lang.Integer"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="云顶天宫"/>
<constructor-arg index="2" value="5分钟"/>
<constructor-arg index="3" ref="cp"/>
</bean>
-
测试
private static void f1() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring2.xml");
Music music = applicationContext.getBean("music", Music.class);
System.out.println(music);
}
3 自动装配
<bean id="game" class="com.javasm.springdemo.game.model.GameModel" autowire="byType"/>
autowire自动装配 byType:是去Spring容器中,寻找相同列席的bean对象,根据属性的类型进行寻找,类似于getBean(Company.class),找到了,自动赋值
<bean id="game" class="com.javasm.springdemo.game.model.GameModel" autowire="byName"/>
byName:去Spring容器中寻找,id=company,类型是Company的Bean对象,找到之后,自动赋值
四 总结
1 SpringIOC核心价值
-
解耦:降低耦合度
-
灵活:通过配置改变行为
2 重点必会的知识
-
理解Spring的启动原理
-
能描述什么是Spring
-
能描述什么是IOC和DI
-
依赖注入和控制反转都是什么意思
-
单例
-
知道Spring默认是单例模式
-
给你任意一个类,能把他修改成单例的
-
能用纸和笔写出来
-
-
构造方法和初始化方法的执行顺序
3 了解
-
懒加载
-
获取Bean的方式
-
创建Bean的方式
-
初始化和销毁
-
构造方法的调用
-
依赖注入的XML配置
在一些其他人的框架中,可能会看见类似的XML配置




















 167万+
167万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








