介绍
在上一篇文章中,我们介绍了Agentic RAG的概念,强调了它如何通过集成自主代理能力来扩展传统的检索增强生成(RAG)框架。在本期中,我们深入探讨LangGraph,一个用于协调逻辑工作流的创新框架。LangGraph使得创建具有复杂推理能力的多代理系统成为可能,是构建Agentic RAG架构的理想工具。


为什么选择 LangGraph 用于 Agentic RAG?
LangGraph 提供了一个强大的环境,用于创建有状态的工作流,在这里,代理可以在节点、工具和任务之间智能地互动。它与 LangChain 及其他先进的 AI 框架的兼容性,使得与检索和生成管道的无缝集成成为可能,这使其非常适合 Agentic RAG 的动态需求。
主要优势:
- \1. 工作流编排: 定义和管理具有条件逻辑和状态管理的多步骤工作流。
- \2. 工具集成: 轻松集成外部工具、API 和检索系统。
- \3. 可扩展性: 以最小的开销处理复杂的多代理工作流。
- \4. 灵活性: 设计能够动态适应上下文和输入的工作流。
LangGraph 架构用于 Agentic RAG
一个典型的 LangGraph 工作流用于 Agentic RAG 可能包括查询重写、文档检索、相关性评分和生成响应的组件。
流程图:Agentic RAG 中的 LangGraph 工作流程
[Start Query]
|
v
[Agent Node: Rewrite or Process Query]
|
+--> [Retrieve Documents: Knowledge Sources]
|
+--> [Grade Relevance]
|
+--> [Generate Response]
|
v
[End]
- • Start Query: 接收用户输入的查询。
- • Agent Node: 根据上下文和条件确定下一步。
- • Retrieve Documents: 从知识库中获取相关文档。
- • Grade Relevance: 对文档进行评分,以评估其与查询的上下文相关性。
- • Generate Response: 使用检索和处理的数据生成最终输出。
使用Agentic RAG对LangGraph进行基准测试
实验设置
- • 数据集: 研究论文、文章和常见问题的混合。
- • 评估指标: 相关性、准确性、响应时间和工作流程效率。
- • 基准: 传统 RAG 与使用 LangGraph 的 Agentic RAG。
结果:

代码解释:
该代码定义了一个 文档问答助手,允许用户上传 PDF 文件、提供 URL 或两者兼而有之,然后询问有关这些文档内容的问题。它利用了 LangChain 框架、LangGraph 和 Ollama API 进行嵌入和基于聊天的响应。助手是使用 Gradio 库 构建的,提供了一个易于使用的界面以与系统进行交互。
代码解析:
1. 导入
代码首先导入必要的模块:
- • LangChain 和 LangGraph:用于文档加载、向量存储创建、嵌入、消息处理和基于图的工作流程。
- • Gradio:用于构建用户友好的界面。
- • Pydantic:帮助定义和验证数据结构。
- • Validators:用于检查 URL 的有效性。
- • Tempfile:创建临时文件以处理 PDF 上传。
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader, PyPDFLoader
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain_ollama import OllamaEmbeddings, ChatOllama
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.tools.retriever import create_retriever_tool
from typing import Annotated, Sequence, Literal
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage, HumanMessage
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from langchain import hub
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langgraph.graph import END, StateGraph, START
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
import gradio as gr
import tempfile
import validators
from io import StringIO
2. 数据结构
- • AgentState: 一个
TypedDict,用于跟踪代理的状态,特别是一系列消息。这用于在交互过程中维护对话上下文。
class AgentState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[Sequence[BaseMessage], add_messages]
3. 处理来源
- •
process_sources(urls=None, pdf_files=None): - • 接受 URL 和/或 PDF 文件作为输入。
- • 对于 URL:
- • 验证格式。
- • 使用
WebBaseLoader从网络加载文档。 - • 对于 PDF:
- • 暂时保存上传的文件。
- • 使用
PyPDFLoader将 PDF 解析为文档。 - • 返回处理后的文档列表。
def process_sources(urls=None, pdf_files=None):
"""Process both URLs and PDF files"""
docs_list = []
# Handle URLs
if urls and urls.strip():
url_list = [url.strip() for url in urls.split(",")]
for url in url_list:
if validators.url(url):
try:
url_docs = WebBaseLoader(url).load()
docs_list.extend(url_docs)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error loading URL {url}: {e}")
# Handle PDFs
if pdf_files:
for pdf in pdf_files:
try:
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(delete=False, suffix='.pdf') as tmp:
tmp.write(pdf.read())
loader = PyPDFLoader(tmp.name)
docs_list.extend(loader.load())
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error loading PDF: {e}")
4. 评分文档相关性
- •
grade_documents(state): - • 确定文档是否与用户的查询相关。
- • 使用
ChatOllama和特定提示将文档评分为yes或no。 - • 提示要求模型评估文档内容是否与用户的问题一致。
def grade_documents(state) -> Literal["generate", "rewrite"]:
print("---CHECK RELEVANCE---")
classgrade(BaseModel):
binary_score: str = Field(description="Relevance score 'yes' or 'no'")
model = ChatOllama(temperature=0, model="llama3.2", streaming=True)
llm_with_tool = model.with_structured_output(grade)
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="""You are a grader assessing relevance of a retrieved document to a user question.
Document: {context}
Question: {question}
If the document contains keyword(s) or semantic meaning related to the user question, grade it as relevant.
Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no' score to indicate whether the document is relevant to the question.""",
input_variables=["context", "question"],
)
chain = prompt | llm_with_tool
messages = state["messages"]
question = messages[0].content
docs = messages[-1].content
scored_result = chain.invoke({"question": question, "context": docs})
return"generate"if scored_result.binary_score == "yes"else "rewrite"
5. 核心代理功能:
agent(state):
- • 通过调用代理的 LLM 能力与提供的工具处理一般查询。
def agent(state):
print("---CALL AGENT---")
messages = state["messages"]
model = ChatOllama(temperature=0, streaming=True, model="llama3.2")
model = model.bind_tools(tools)
response = model.invoke(messages)
return {"messages": [response]}
rewrite(state):
- • 使用语义推理重新表述用户的查询,以提高精确度。
def rewrite(state):
print("---TRANSFORM QUERY---")
messages = state["messages"]
question = messages[0].content
msg = [HumanMessage(content=f"""
Look at the input and try to reason about the underlying semantic intent / meaning.
Initial question: {question}
Formulate an improved question:""")]
model = ChatOllama(temperature=0, model="llama3.2", streaming=True)
response = model.invoke(msg)
return {"messages": [response]}
generate(state):
- • 利用相关文档内容,通过预构建的 RAG(检索与生成)提示回答用户的查询。
def generate(state):
print("---GENERATE---")
messages = state["messages"]
question = messages[0].content
docs = messages[-1].content
prompt = hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt")
llm = ChatOllama(temperature=0, streaming=True, model="llama3.2")
rag_chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
response = rag_chain.invoke({"context": docs, "question": question})
return {"messages": [HumanMessage(content=response)]}
6. 查询处理工作流程
process_query(urls, pdf_files, query):
- • 首先,将提供的URLs和PDF处理成文档列表。
- • 使用
RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter将这些文档拆分成更小的块。 - • 使用
OllamaEmbeddings对这些块进行嵌入,并将其存储在Chroma向量存储中。 - • 创建一个检索工具以在向量存储中进行搜索。
- • 定义一个基于LangGraph的工作流程,包含节点:
- •
agent: 管理对话流程。 - •
retrieve: 搜索相关文档。 - •
rewrite: 重新表述查询。 - •
generate: 生成最终答案。 - • 工作流程边缘根据条件定义这些节点之间的转换。
- • 执行图形以向用户提供其查询的响应。
def process_query(urls, pdf_files, query):
docs_list = process_sources(urls, pdf_files)
ifnot docs_list:
return"No valid documents provided. Please input URLs or upload PDFs."
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=50)
doc_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs_list)
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=doc_splits,
collection_name="rag-chroma",
embedding=OllamaEmbeddings(model="nomic-embed-text"),
)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
global tools
tools = [create_retriever_tool(
retriever,
"retrieve_documents",
"Search and return information from the provided documents."
)]
workflow = StateGraph(AgentState)
workflow.add_node("agent", agent)
workflow.add_node("retrieve", ToolNode(tools))
workflow.add_node("rewrite", rewrite)
workflow.add_node("generate", generate)
workflow.add_edge(START, "agent")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"agent",
tools_condition,
{"tools": "retrieve", END: END},
)
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"retrieve",
grade_documents,
{"generate": "generate", "rewrite": "rewrite"},
)
workflow.add_edge("generate", END)
workflow.add_edge("rewrite", "agent")
graph = workflow.compile()
inputs = {"messages": [HumanMessage(content=query)]}
response = ""
for output in graph.stream(inputs):
for key, value in output.items():
if value.get("messages"):
response = value["messages"][-1].content
return response
7. Gradio 界面
create_interface():
- • 构建一个包含两个选项卡的 Gradio 界面:
上传文档:
- • 用于输入 URL 的文本框。
- • 用于上传 PDF 的文件上传器。
- • 处理文档的按钮。
- • 显示处理结果的状态框。
聊天:
- • 用户查询的文本框。
- • 启动查询的按钮。
- • 显示响应的文本框。
def create_interface():
with gr.Blocks(title="Document Q&A Assistant") as interface:
gr.Markdown("# Document Q&A Assistant")
gr.Markdown("*You can provide URLs, PDF files, or both*")
with gr.Tab("Upload Documents"):
urls = gr.Textbox(label="Enter URLs (comma separated)", placeholder="https://example1.com, https://example2.com")
pdfs = gr.File(file_count="multiple", label="Upload PDF files", file_types=[".pdf"])
upload_btn = gr.Button("Process Documents")
upload_status = gr.Textbox(label="Upload Status")
defhandle_upload(urls, pdfs):
ifnot urls andnot pdfs:
return"Please provide either URLs, PDF files, or both"
docs = process_sources(urls, pdfs)
if docs:
return"Documents processed successfully!"
return"No valid documents provided. Please input valid URLs or PDF files"
upload_btn.click(
fn=handle_upload,
inputs=[urls, pdfs],
outputs=upload_status
)
with gr.Tab("Chat"):
query = gr.Textbox(label="Ask a question about the documents")
chat_btn = gr.Button("Ask")
response = gr.Textbox(label="Response")
chat_btn.click(
fn=process_query,
inputs=[urls, pdfs, query],
outputs=response
)
return interface
8. 应用程序启动
- • 当脚本被执行时,Gradio 界面被启动。
interface = create_interface()
if __name__ == "__main__":
interface.launch()
关键特性概述:
多模态文档支持:
- • 同时支持 URL 和 PDF。


相关性评分:
- • 确保响应基于最相关的文档。
工作流图:
- • 利用
StateGraph动态决定行动(例如,重写、检索、生成)。
嵌入和向量搜索:
- • 使用
OllamaEmbeddings和 Chroma 向量存储 进行高效的文档检索。
交互式用户界面:
- • 使用 Gradio 提供一个可访问的无代码界面。
结论
LangGraph 是推动 Agentic RAG 发展的关键工具,它能够实现动态的多代理工作流程,以适应复杂场景。它与 LangChain、Chroma 和 ChatOllama 等工具的无缝集成确保开发者能够高效构建可扩展和智能的检索增强系统。
如何学习大模型
下面这些都是我当初辛苦整理和花钱购买的资料,现在我已将重要的AI大模型资料包括市面上AI大模型各大白皮书、AGI大模型系统学习路线、AI大模型视频教程、实战学习,等录播视频免费分享出来,需要的小伙伴可以扫取。

现在社会上大模型越来越普及了,已经有很多人都想往这里面扎,但是却找不到适合的方法去学习。
作为一名资深码农,初入大模型时也吃了很多亏,踩了无数坑。现在我想把我的经验和知识分享给你们,帮助你们学习AI大模型,能够解决你们学习中的困难。
一、AGI大模型系统学习路线
很多人学习大模型的时候没有方向,东学一点西学一点,像只无头苍蝇乱撞,我下面分享的这个学习路线希望能够帮助到你们学习AI大模型。
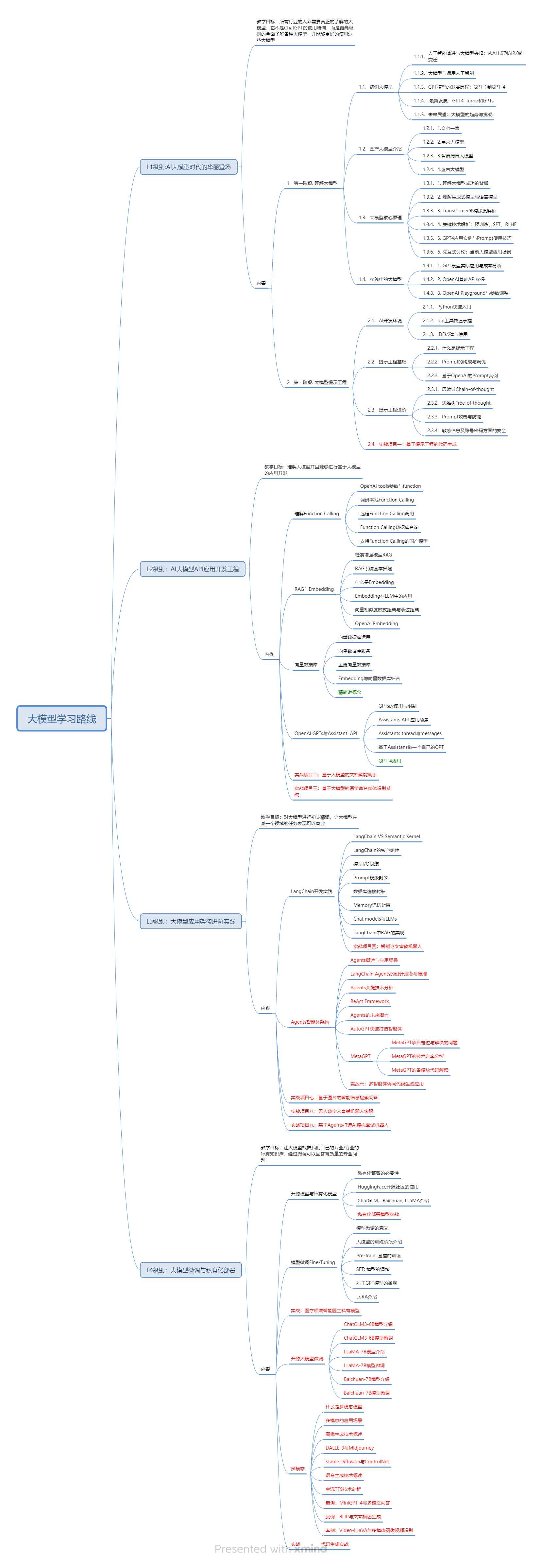
二、AI大模型视频教程
三、AI大模型各大学习书籍!

四、AI大模型各大场景实战案例

五、AI大模型面试题库

五、结束语
学习AI大模型是当前科技发展的趋势,它不仅能够为我们提供更多的机会和挑战,还能够让我们更好地理解和应用人工智能技术。通过学习AI大模型,我们可以深入了解深度学习、神经网络等核心概念,并将其应用于自然语言处理、计算机视觉、语音识别等领域。同时,掌握AI大模型还能够为我们的职业发展增添竞争力,成为未来技术领域的领导者。
再者,学习AI大模型也能为我们自己创造更多的价值,提供更多的岗位以及副业创收,让自己的生活更上一层楼。
因此,学习AI大模型是一项有前景且值得投入的时间和精力的重要选择。




















 123
123

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








