Java 泛型
泛型的出现是十分必要的,具体而言,它提供了以下几个方面的功能:
- 避免代码中的强制类型转换,在没有出现泛型前从集合中拿数据的类型是不确定的,使用时要进行类型转换
- 限定类型,List<String> 限定了集合中只能添加String元素,当添加Integer时,编译器会报错
- 实现一些特别的编程技巧,例如,提供一个方法拥有拷贝对象,在不提供额外的方法参数的情况下,使返回值类型和方法参数类型保持一致
1. 泛型分类
1.1 泛型接口
在定义接口时接口名后面加上<泛型参数名>,就定义了一个泛型接口,该泛型参数名的作用域存在于接口的定义和接口的主体内。
public interface GenericInterface<T> {
}
1.2 泛型类
与泛型接口类似,在类名后面加上<泛型参数名>,就定义了一个泛型类,该泛型参数名的作用域存在于类的定义和类的主体内。
public class GenericClass<K> {
private K k;
// 不是泛型方法,只是泛型类中的一个方法
public K notGenericMethod(K k) {
return k;
}
}
1.3 泛型方法
在方法返回值前加上<泛型参数名>,就定义了一个泛型方法,该泛型参数名的作用域包括方法的返回值,方法的参数,方法异常以及整个方法主题。
public class GenericClass<K> {
private K k;
// 不是泛型方法,只是泛型类中的一个方法
public K notGenericMethod(K k) {
return k;
}
// 才是一个泛型方法
public <Q, E extends Exception> Q genericMethod(Q q, K k) throws E{
return q;
}
}
2. 泛型的继承和实现
2.1 子类不是泛型类:
需要给父类传递类型常量
public class NotGenericSubClass extends GenericClass<String> implements GenericInterface<Integer> {
public String subTest() {
return super.notGenericMethod("hehehe");
}
}
当给父类传递的类型常量为String时,那么在父类中所有K都会被String替换!
2.2 子类是泛型类:
可以给父类传递类型常量,也可以传递类型变量
public class GenericSubClass<R> extends GenericClass<R> implements GenericInterface<R> {
}
3. 有界泛型
有界泛型三个重要的关键字:?、extends、super
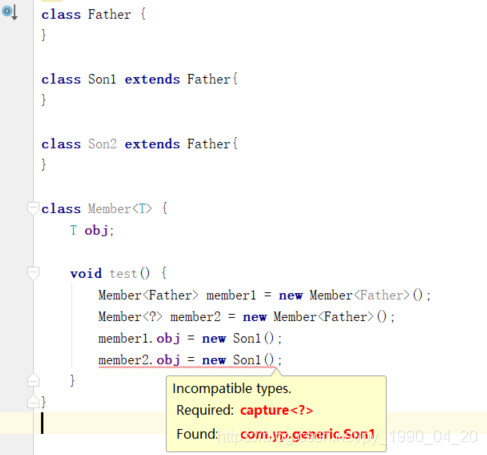
3.1 ? 通配符
表示通配符类型,用于表达任意的意思,需要注意的是,它指代的是“某一个任意类型”,但并不是Object
3.2 extends
<T extends UpperBound>: UpperBound为泛型T的上界,也就是说T必须是UpperBound或者它的子类,泛型上界可以用于定义以及声明代码处,不同的位置使用方法都有所不同
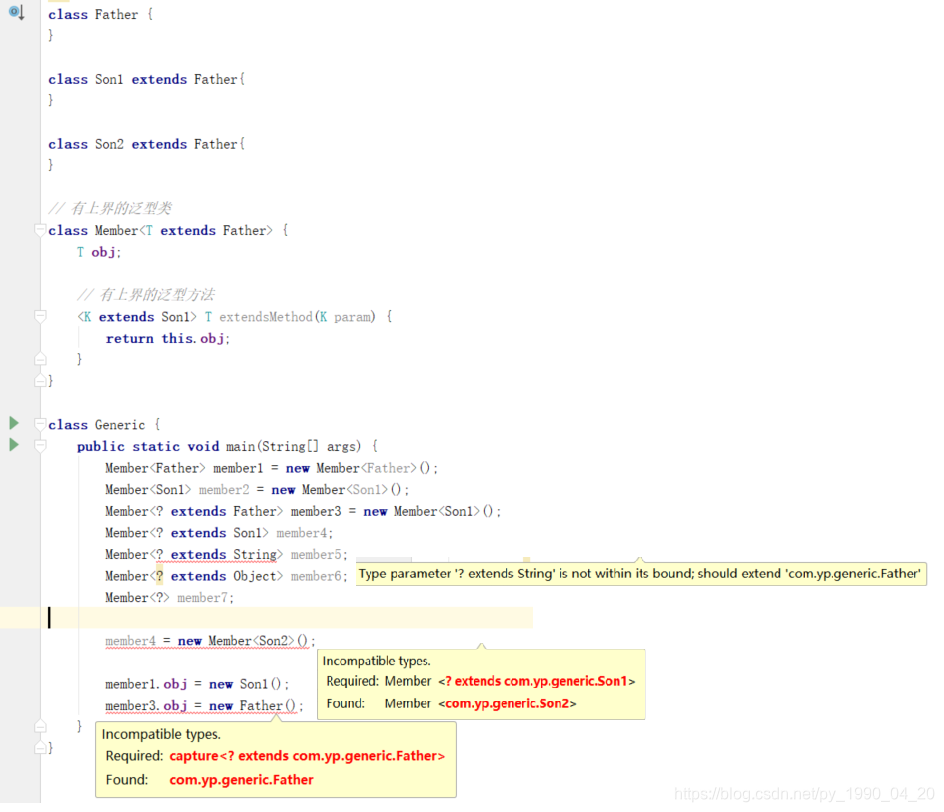
以上例子中使用了一个具备上界的泛型方法和一个具备上界的泛型类,它们体现了extends在泛型中的应用:
- 在方法、接口、或类的泛型定义时,需要使用泛型参数名(例如T或者K)
- 在声明位置使用泛型参数时,需要使用通配符,意义是“用来指定类的上界(该类或其子类)”
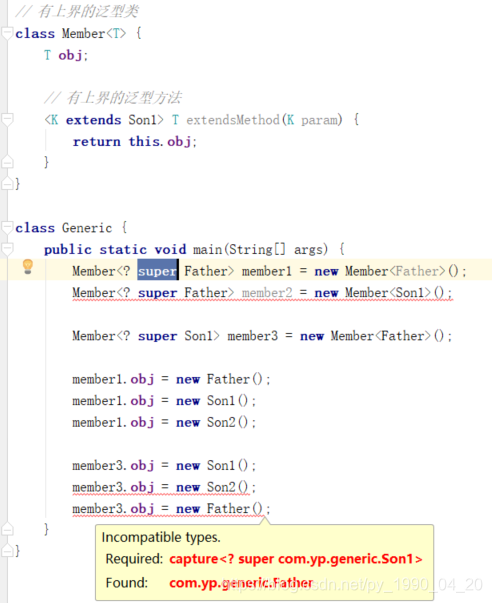
3.3 super
<? super LowerBound>: LowerBound为泛型T的下界,也就是说T必须是LowerBound或其父类
泛型下界只能应用于声明代码处
4. 复杂泛型
复杂的泛型也是由简单的泛型组合起来的,对于复杂泛型:
- 多个泛型参数定义有逗号分隔,例如<T, K>
- 同一个泛型参数如果有多个上界,那么各个上界之间用符号&连接
- 多个上界类型里最多只能有一个类,其他的必须为接口,如果上界里有类,那么必须放置在第一位
class Aclass {}
class Bclass {}
class ComplexGeneric<T extends Aclass, K extends Bclass & Serializable & Cloneable> {}
5. 泛型擦除
泛型擦除是指在编译器处理带泛型定义的类、接口或方法时,会在字节码指令集里抹去全部泛型类型的信息,泛型被擦除后在字节码里只保留泛型的原始类型。类型擦除的关键在于从泛型类型中清除类型参数的相关信息,然后在必要的时候添加类型检查和类型转换的方法。
原始类型是指抹去泛型信息后的类型,在Java语言中,它必须是一个引用类型(非基本数据类型),一般而言,它对应的是泛型的定义上界。
<T>对应得原始类型是Object,<T extends String>对应的原始类型就是String。
public class TypeErasureSample<T> {
public T v1;
public T v2;
public String v3;
}
public class TypeErasureSampleTest {
@Test
public void testTypeErasureSample() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
TypeErasureSample<String> typeErasureSample = new TypeErasureSample<>();
typeErasureSample.v1 = "String value";
Field v2 = TypeErasureSample.class.getDeclaredField("v2");
v2.set(typeErasureSample, 1);
for (Field field : TypeErasureSample.class.getDeclaredFields()) {
System.out.println(field.getName() + ":" + field.getType());
}
System.out.println(typeErasureSample.v1);
System.out.println(typeErasureSample.v2);
}
}
测试结果:
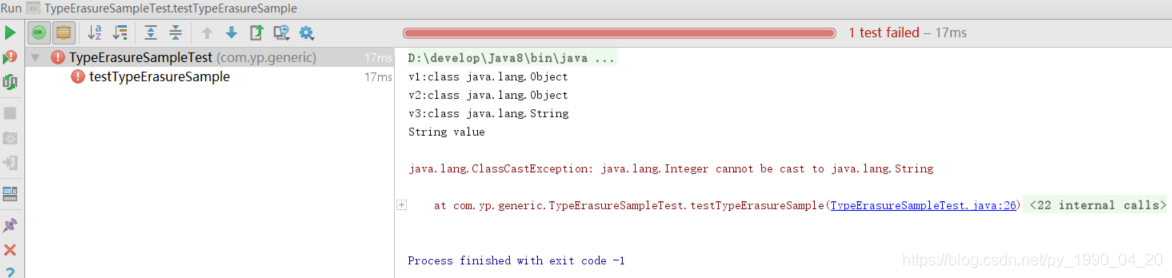
错误的原因就是System.out.println(typeErasureSample.v2)有一个强制转换操作,通过反编译,会发现是System.out.println((String)typeErasureSample.v2);
6. 擦除泛型带来的问题
6.1 类型变量不能是基本类型
泛型类型只能是应用类型,基本类型要使用包装类型,原因是泛型的原始类型是Object,二Object不能存储int等基本类型的值,只能存储基本类型的包装类型。
6.2 类型丢失
方法重载失败
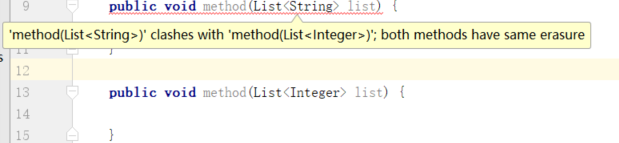
instanceof运算符失败
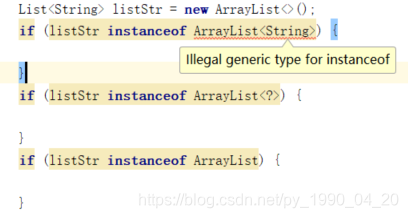
6.3 catch不能使用泛型异常类
try {
} catch(MyException<String> e1) {
} catch(MyException<Integer> e2) {
}
MyException<String>和 MyException<Integer>被擦除为MyException<Object>
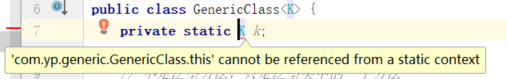
6.4 泛型类的静态方法和静态属性不能使用泛型
由于泛型类型中的泛型参数的实例化是在实例化对象的时候指定的,而静态变量和静态方法的使用是不需要实例化对象的,显然二者矛盾。
7. 反射泛型
那些泛型信息会被保留:
- 泛型接口、类、方法定义上的所有泛型
- 成员变量声明处的泛型
7.1 泛型接口和泛型类
public void getReflectType() {
Class<TypeErasureSample> typeErasureSampleClass = TypeErasureSample.class;
TypeVariable<Class<TypeErasureSample>>[] typeParameters = typeErasureSampleClass.getTypeParameters();
for (TypeVariable typeVariable : typeParameters) {
Type[] bounds = typeVariable.getBounds();
for (Type type : bounds){
System.out.println(type.getTypeName());
}
System.out.println(typeVariable.getName());
}
}
测试结果:
java.lang.Object
T
public void getSuperType() {
NotGenericSubClass notGenericSubClass = new NotGenericSubClass();
Class<? extends NotGenericSubClass> aClass = notGenericSubClass.getClass();
Type genericSuperclass = aClass.getGenericSuperclass();
if (genericSuperclass instanceof ParameterizedType) {
ParameterizedType parameterizedType = (ParameterizedType) genericSuperclass;
Type[] actualTypeArguments = parameterizedType.getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type type : actualTypeArguments) {
if (type instanceof Class) {
Class clazz = (Class) type;
System.out.println(clazz.getName());
}
}
}
}
测试结果:
java.lang.String
7.2 声明为泛型的字段
public Type getGenericType() {...}
7.3 泛型方法
public Type getGenericReturnType() {...}
public Type getGenericParameterType() {...}
public Type getGenericExceptionType() {...}





 本文深入解析Java泛型的各类应用场景,包括泛型接口、泛型类、泛型方法的定义及使用,探讨泛型的继承与实现机制,详解有界泛型、泛型擦除及其带来的问题,并介绍反射在泛型中的作用。
本文深入解析Java泛型的各类应用场景,包括泛型接口、泛型类、泛型方法的定义及使用,探讨泛型的继承与实现机制,详解有界泛型、泛型擦除及其带来的问题,并介绍反射在泛型中的作用。
















 8439
8439

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








