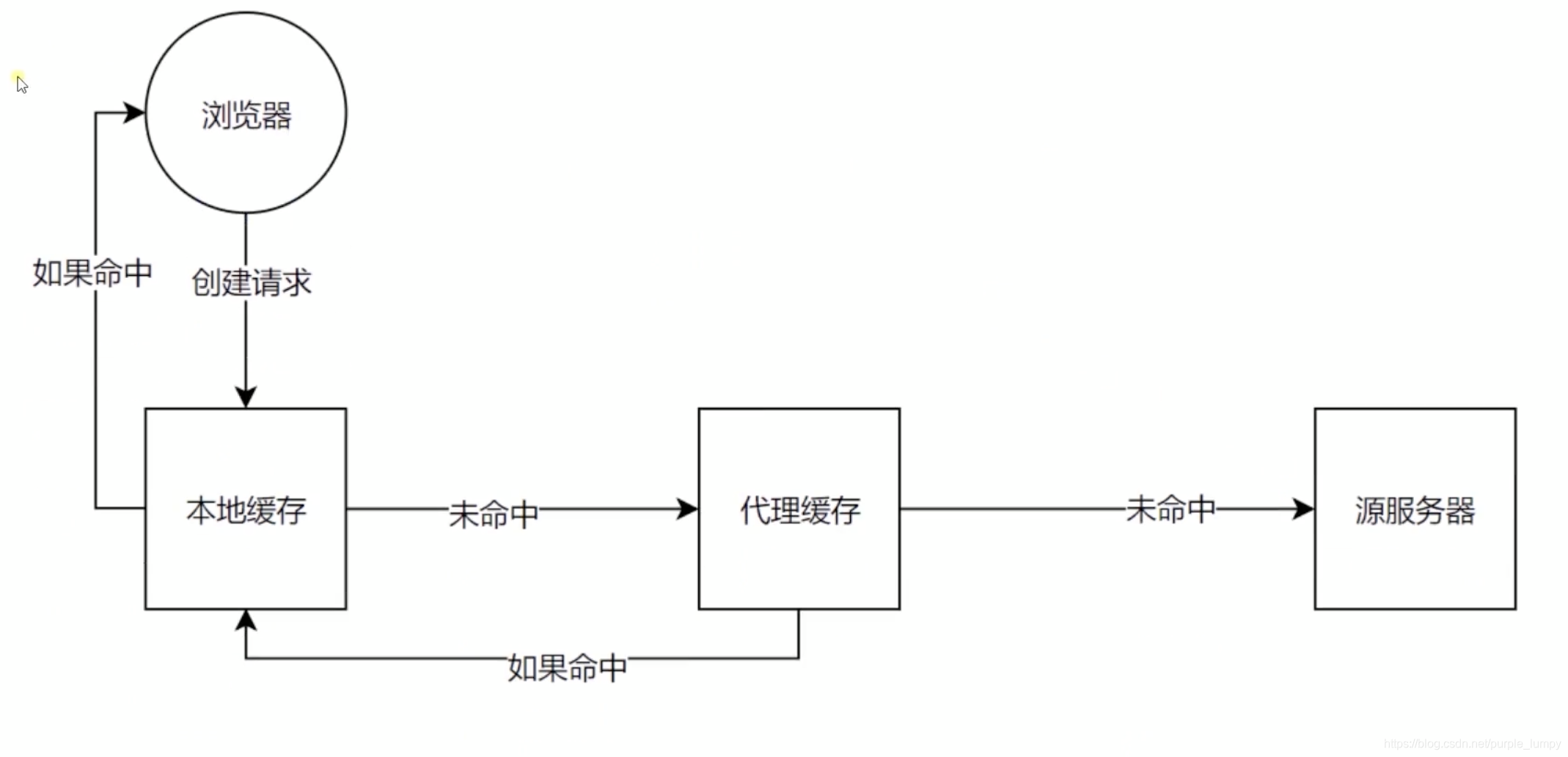
上篇文章我们知道,当我们给Catch-Control 设置了 no-catch 后,每次浏览器对这个资源的请求时,都会到服务器端进行资源验证,验证完之后,如果确定这个资源可以使用缓存,浏览器才会读取本地的缓存。
下面是浏览器请求数据过程中关于缓存的步骤。
进行数据验证,主要是有两个Header: Last-Modified 与 Etag .
Last-Modified 即上次修改时间。
它主要配合If-Modified-Since 或者 If-Unmodified-Since 这两个Header 使用。
(如果我们请求的一个资源,它返回的Header 中有Last-Modified 并指定了一个时间;那么下次浏览器再发送这个请求的时候就会带上这个时间,并把它放在 If-Modified-Since(通常) 或者 If-Unmodified-Since 这两个Header中;服务器就可以根据If-Modified-Since 或者 If-Unmodified-Since 这两个Header的值对比资源上次修改的时间,如果两个时间一致,那么就可以使用缓存)
Etag 它是一个更为严格的验证
它是用过数据签名的方式验证
它根据数据内容产生一个唯一的编码(数据不同,编码结果不同)。最典型的做法,是我们对数据内容做一个哈希计算。
它主要配合 If-Match 或者 If-None-Match 使用。
同上,通过对比资源的签名判断是否使用缓存。
下面我们来实验一下。
server.js 如下
const http = require('http')
const fs = require('fs')
http.createServer(function (request, response) {
console.log('request come', request.url)
if (request.url === '/') {
const html = fs.readFileSync('testMaxAge.html', 'utf8')
response.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Type': 'text/html'
})
response.end(html)
}
if (request.url === '/script.js') {
response.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Type': 'text/javascript',
'Cache-Control': 'max-age=20000000, no-cache',
'Last-Modified': '012345',
'Etag': '666'
})
response.end('console.log("script loaded")')
}
}).listen(8888)
console.log('serve listening on 8888')
testMaxAge.html 如下
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>MyHtml</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>hello world</div>
<div>don't speak</div>
<script src="/script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
好的,我们来启动服务。
打开localhost:8888 页面。
刷新两次页面后,我们可以看看 script.js 请求。确实是有 If-Modified-Since 和 If-None-Match 的。
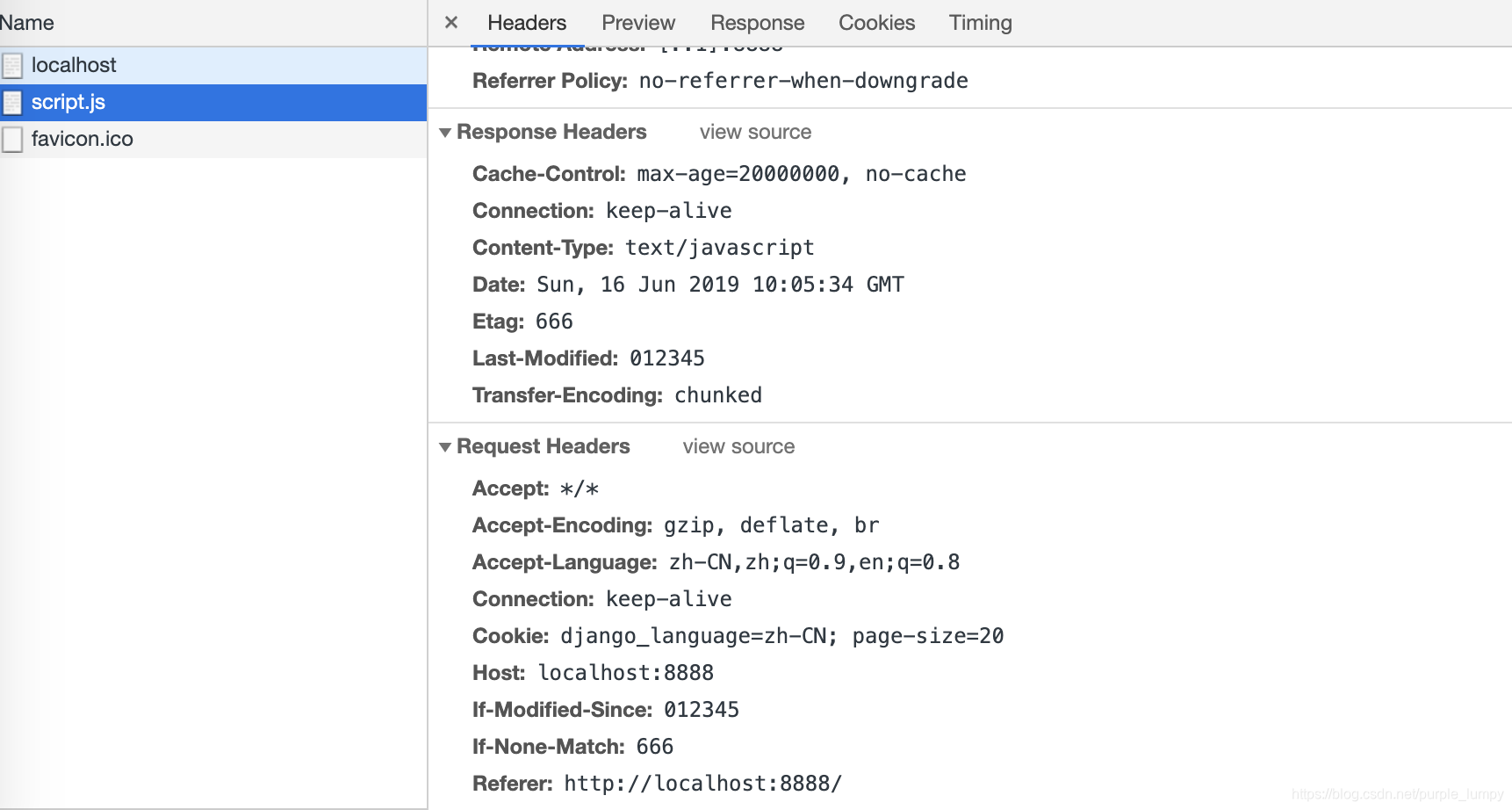
但是,这时候,这个请求还是会返回数据。
我们希望验证通过服务器端就不要返回数据了。
const http = require('http')
const fs = require('fs')
http.createServer(function (request, response) {
console.log('request come', request.url)
if (request.url === '/') {
const html = fs.readFileSync('testMaxAge.html', 'utf8')
response.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Type': 'text/html'
})
response.end(html)
}
if (request.url === '/script.js') {
const etag = request.headers['if-none-match'];
if (etag === '666') {
response.writeHead(304, {
'Content-Type': 'text/javascript',
'Cache-Control': 'max-age=20000000, no-cache',
'Last-Modified': '012345',
'Etag': '666'
})
response.end('')
} else {
response.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Type': 'text/javascript',
'Cache-Control': 'max-age=20000000, no-cache',
'Last-Modified': '012345',
'Etag': '666'
})
response.end('console.log("script loaded")')
}
}
}).listen(8888)
console.log('serve listening on 8888')
这时候,我们刷新两次浏览器,会发现在控制台仍然会有返回数据,这其实是浏览器将命中缓存中的数据显示出来的。浏览器实际上是根据HTTP code 304,来认定使用缓存数据的(当我们在304时,返回其他数据,会直接被忽略)。
Done.





 本文深入探讨了HTTP缓存控制机制,特别是Cache-Control头的no-cache指令如何促使浏览器每次请求资源时都向服务器验证资源状态。文章详细解析了Last-Modified与Etag两种资源验证方式,以及它们如何配合If-Modified-Since、If-Unmodified-Since、If-Match与If-None-Match头实现高效缓存管理。
本文深入探讨了HTTP缓存控制机制,特别是Cache-Control头的no-cache指令如何促使浏览器每次请求资源时都向服务器验证资源状态。文章详细解析了Last-Modified与Etag两种资源验证方式,以及它们如何配合If-Modified-Since、If-Unmodified-Since、If-Match与If-None-Match头实现高效缓存管理。
















 835
835

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








