Description
Cao Cao made up a big army and was going to invade the whole South China. Yu Zhou was worried about it. He thought the only way to beat Cao Cao is to have a spy in Cao Cao's army. But all generals and soldiers of Cao Cao were loyal, it's impossible to convince any of them to betray Cao Cao.
So there is only one way left for Yu Zhou, send someone to fake surrender Cao Cao. Gai Huang was selected for this important mission. However, Cao Cao was not easy to believe others, so Gai Huang must leak some important information to Cao Cao before surrendering.
Yu Zhou discussed with Gai Huang and worked out information to be leaked, in happening order. Each of the information was estimated to has
information to be leaked, in happening order. Each of the information was estimated to has
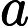
 value in Cao Cao's opinion.
value in Cao Cao's opinion.
Actually, if you leak information with strict increasing value could accelerate making Cao Cao believe you. So Gai Huang decided to leak exact information with strict increasing value in happening order. In other words, Gai Huang will not change the order of the
information with strict increasing value in happening order. In other words, Gai Huang will not change the order of the
 information and just select
information and just select
 of them. Find out how many ways Gai Huang could do this.
of them. Find out how many ways Gai Huang could do this.
So there is only one way left for Yu Zhou, send someone to fake surrender Cao Cao. Gai Huang was selected for this important mission. However, Cao Cao was not easy to believe others, so Gai Huang must leak some important information to Cao Cao before surrendering.
Yu Zhou discussed with Gai Huang and worked out
 information to be leaked, in happening order. Each of the information was estimated to has
information to be leaked, in happening order. Each of the information was estimated to has
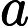
 value in Cao Cao's opinion.
value in Cao Cao's opinion.
Actually, if you leak information with strict increasing value could accelerate making Cao Cao believe you. So Gai Huang decided to leak exact
 information with strict increasing value in happening order. In other words, Gai Huang will not change the order of the
information with strict increasing value in happening order. In other words, Gai Huang will not change the order of the
 information and just select
information and just select
 of them. Find out how many ways Gai Huang could do this.
of them. Find out how many ways Gai Huang could do this.
Input
The first line of the input gives the number of test cases,
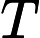






 .
.
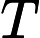 test cases follow.
test cases follow.
Each test case begins with two numbers








 and
and







 , indicating the number of information and number of information Gai Huang will select. Then
, indicating the number of information and number of information Gai Huang will select. Then
 numbers in a line, the
numbers in a line, the

 number
number
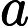




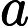




 indicates the value in Cao Cao's opinion of the
indicates the value in Cao Cao's opinion of the
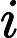

 information in happening order.
information in happening order.
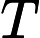






 .
.
 test cases follow.
test cases follow.
Each test case begins with two numbers









 and
and







 , indicating the number of information and number of information Gai Huang will select. Then
, indicating the number of information and number of information Gai Huang will select. Then
 numbers in a line, the
numbers in a line, the
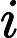

 number
number
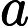




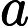




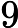
 indicates the value in Cao Cao's opinion of the
indicates the value in Cao Cao's opinion of the
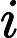

 information in happening order.
information in happening order.
Output
For each test case, output one line containing
Case #x: y, where
 is the test case number (starting from 1) and
is the test case number (starting from 1) and
 is the ways Gai Huang can select the information.
is the ways Gai Huang can select the information.
The result is too large, and you need to output the result mod by












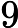
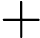

 .
.
 is the test case number (starting from 1) and
is the test case number (starting from 1) and
 is the ways Gai Huang can select the information.
is the ways Gai Huang can select the information.
The result is too large, and you need to output the result mod by













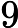


 .
.
Sample Input
2
3 2
1 2 3
3 2
3 2 1
Sample Output
Case #1: 3
Case #2: 0
Hint
In the first cases, Gai Huang need to leak 2 information out of 3. He could leak any 2 information as all the information value are in increasing order. In the second cases, Gai Huang has no choice as selecting any 2 information is not in increasing order.
题意:就是给你n个数,然后找里面有多少个长度为m的严格递增子序列。
思路:这道题我们用dp去做,dp[i][j]表示以第i个数结尾长度为j的严格递增子序列有多少个。显然可以得出递推式:dp[i][j]=∑dp[x][j-1](其中1<=x<i&&a[x]<a[i])。
那么剩下的就是如何求和的问题。如果直接暴力时间复杂度为n^3,显然是不行的。所以这里要用到树状数组优化就能ac了。还要注意一个问题就是,我们用到了树状数组,为了保证肯定能累加,也就是符合上面的a[x]<a[i],我们要按照a从小到大的顺序dp并且更新树状数组。下面给代码。
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<utility>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 1005
#define MOD 1000000007
int n, m, a[maxn], dp[maxn][maxn], c[maxn][maxn], r[maxn];//c为树状数组,r数组表示a数组的元素从小到大的下标,例如r[i]=j,j为a数组里面第i个小的数的下标
int lowbit(int x) {
return x&-x;
}
bool cmp(int x, int y) {
return a[x] < a[y] || (a[x] == a[y] && x>y);//两个值相等时,坐标后的优先,虽然没有这个判断也能过,但后来队友发现了,加了上去,题目并没说没有相同数据,所以我觉得还是需要加这个判断。
}
void update(int i, int j, int value) {
while (i <= n) {
c[i][j] += value;
c[i][j] %= MOD;
i += lowbit(i);
}
}
int sum(int i, int j) {
int sumnum = 0;
while (i >= 1) {
sumnum += c[i][j];
sumnum %= MOD;
i -= lowbit(i);
}
return sumnum;
}
int main() {
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
for (int tcase = 1; tcase <= t; tcase++) {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
r[i] = i;
sort(r + 1, r + 1 + n, cmp);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int id = r[i];
dp[id][1] = 1;
update(id, 1, 1);
for (int j = 2; j <= m; j++) {
dp[id][j] = sum(id - 1, j - 1);
update(id, j, dp[id][j]);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans = (ans + dp[i][m]) % MOD;
}
printf("Case #%d: %d\n", tcase, ans);
}
}







 本文探讨了在赤壁之战背景下的一种特殊算法问题,即寻找长度为m的严格递增子序列的数量。通过动态规划结合树状数组优化,解决了在大规模数据集下快速计算这一数量的挑战。
本文探讨了在赤壁之战背景下的一种特殊算法问题,即寻找长度为m的严格递增子序列的数量。通过动态规划结合树状数组优化,解决了在大规模数据集下快速计算这一数量的挑战。
















 236
236

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








